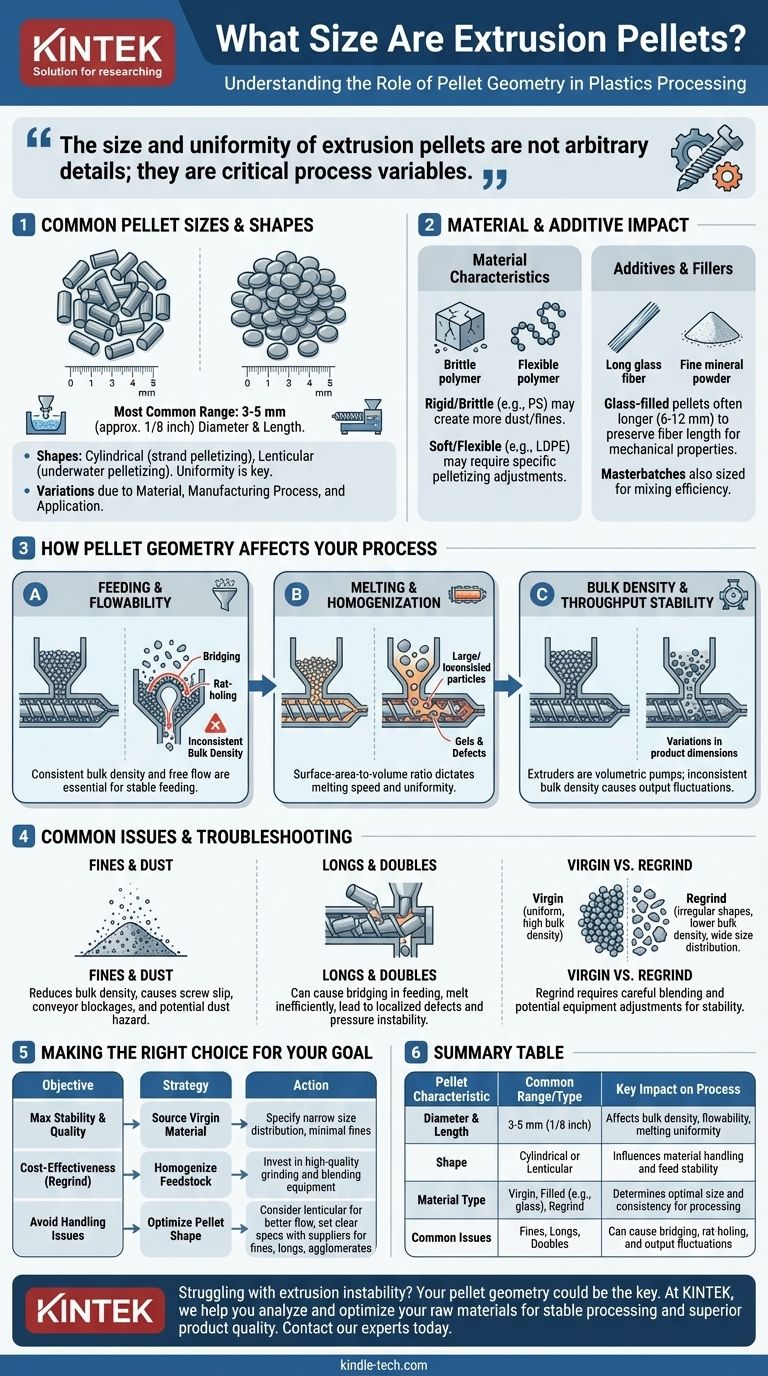
In the plastics industry, there is no single universal size for extrusion pellets, but a vast majority fall within a specific range. Most commonly, you will find thermoplastic pellets that are roughly 3-5 millimeters (about 1/8 inch) in diameter and length, often resembling small cylinders or lentils. The exact size and shape are deliberately controlled by the material manufacturer, as these properties have a direct impact on processing performance.
The size and uniformity of extrusion pellets are not arbitrary details; they are critical process variables. Understanding how pellet geometry affects material handling, melting, and extruder output is fundamental to achieving a stable process and high-quality final product.

Why There Is No Single "Standard" Size
The variation in pellet size is a function of the material's properties, the manufacturing process used to create it, and its intended application. This variability is a key factor to control.
The Common Range and Shape
Most virgin thermoplastic pellets are produced to be nominally 3 mm (1/8") in diameter and length.
They are typically cylindrical (from strand pelletizing) or lenticular (lens-shaped, from underwater pelletizing). This uniformity is by design.
Material-Specific Characteristics
Different polymers behave differently during pelletizing. For example, a rigid, brittle material like general-purpose polystyrene might create more dust or fines than a soft, flexible material like LDPE.
Compounders adjust their pelletizing equipment (die plate, knife speed) to create the most optimal pellet for a specific polymer grade.
The Impact of Additives and Fillers
Materials are rarely pure polymer. Compounds containing fillers like glass fiber, talc, or calcium carbonate can significantly alter the pellet.
Glass-filled pellets, for instance, are often longer (e.g., 6-12 mm) to preserve fiber length, which is critical for achieving desired mechanical properties in the final part. Masterbatches (concentrated color or additive pellets) may also be sized differently to ensure proper mixing.
How Pellet Geometry Impacts Your Process
The physical form of the raw material is the first input variable in any extrusion operation. Inconsistencies here will cascade through the entire process.
Feeding and Flowability
Uniform, free-flowing pellets are essential for a stable process. The goal is consistent bulk density in the feed hopper and throat.
Irregular shapes, excessive fines (dust), or "longs" (overly long pellets) can cause bridging (arching over the hopper outlet) or rat-holing (funneling down the center). Both conditions starve the extruder screw and cause output to fluctuate.
Melting and Homogenization
The melting process inside the extruder barrel is governed by the surface-area-to-volume ratio of the pellets.
Smaller pellets have a higher ratio, allowing them to absorb heat and melt more quickly and uniformly. Large or inconsistent pellets can travel further down the screw before melting completely, potentially leading to unmelted particles, gels, or other defects in the final product.
Bulk Density and Throughput Stability
An extruder is essentially a volumetric pump. For a given screw speed, it will deliver a consistent volume of material.
If the bulk density of the material in the feed throat changes due to inconsistent pellet size or shape, the mass of material being fed also changes. This directly translates to fluctuations in throughput and can cause variations in product dimensions and quality.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Common Issues
Perfectly uniform pellets are the ideal, but reality often involves managing imperfections. Knowing what to look for is critical for troubleshooting.
The Problem with Fines and Dust
Fines are fine powders or dust generated during pelletizing or transport. Excessive fines are highly problematic.
They can reduce bulk density, cause screw slip (where the screw turns but fails to convey material forward), and create blockages in conveying systems. In some cases, fine polymer dust can also pose a combustible dust hazard.
The Challenge of "Longs" and "Doubles"
Longs (pellets longer than the spec) or doubles (two pellets fused together) can get stuck in feeding equipment, especially in complex material handling systems.
These oversized particles also melt less efficiently, creating a risk of localized defects or extruder pressure instability as they are forced through the system.
Virgin vs. Regrind Material
While virgin material is typically uniform, regrind (reprocessed scrap material) is often highly irregular in shape and size. It usually has a lower bulk density and a wider distribution of particle sizes.
Using a high percentage of regrind requires careful blending with virgin material and may necessitate equipment adjustments (like grooved feed throats or specialized screws) to ensure stable processing.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Controlling your raw material is the first step toward controlling your process. Your approach should align with your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is maximum process stability and quality: Source virgin material from a reputable supplier and specify a narrow size distribution with minimal fines.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness using regrind: Invest in high-quality grinding and blending equipment to create a more homogenous feedstock before it enters the extruder.
- If your primary focus is avoiding material handling issues: Pay close attention to pellet shape (lenticular pellets often flow better than cylinders) and work with suppliers to set clear specifications for fines, longs, and agglomerates.
Ultimately, viewing pellets not as simple beads but as a critical engineering input empowers you to diagnose problems and optimize your entire extrusion operation.
Summary Table:
| Pellet Characteristic | Common Range / Type | Key Impact on Process |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter & Length | 3-5 mm (1/8 inch) | Affects bulk density, flowability, and melting uniformity |
| Shape | Cylindrical or Lenticular | Influences material handling and feed stability |
| Material Type | Virgin, Filled (e.g., glass), Regrind | Determines optimal size and consistency for processing |
| Common Issues | Fines, Longs, Doubles | Can cause bridging, rat-holing, and output fluctuations |
Struggling with extrusion instability or product defects? Your pellet geometry could be the key. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables that help you analyze and optimize your raw materials. Whether you're working with virgin thermoplastics, complex compounds, or regrind, understanding your pellets is the first step to a stable process and superior product quality.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's extrusion testing and material analysis needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High-Purity Titanium Foil and Sheet for Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Centrifuge Tubes
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
- Multi-zone Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is titanium used for in manufacturing? Leveraging High-Performance Properties for Critical Applications
- What is titanium disadvantages and advantages? Weighing Performance vs. Cost for Your Project
- What is the difference between metallic and non-metallic coating? A Guide to Sacrificial vs. Barrier Protection
- What are the advantages disadvantages and uses of sheet metal? The Ultimate Guide to Material Selection
- What are the disadvantages of using metal? Understanding Corrosion, Weight, and Cost Challenges



















