To preserve the integrity of gold and platinum, you must avoid direct contact with highly aggressive chemical mixtures like aqua regia. However, the more common threat comes from subtle surface contamination by organic materials, oils, and even atmospheric pollutants, which can degrade the unique performance of these metals without visibly destroying them.
Protecting gold and platinum goes beyond avoiding a few specific chemicals. The primary risk is not just outright corrosion from aggressive agents, but also surface contamination from seemingly harmless substances that can compromise their valued chemical and electrical properties.

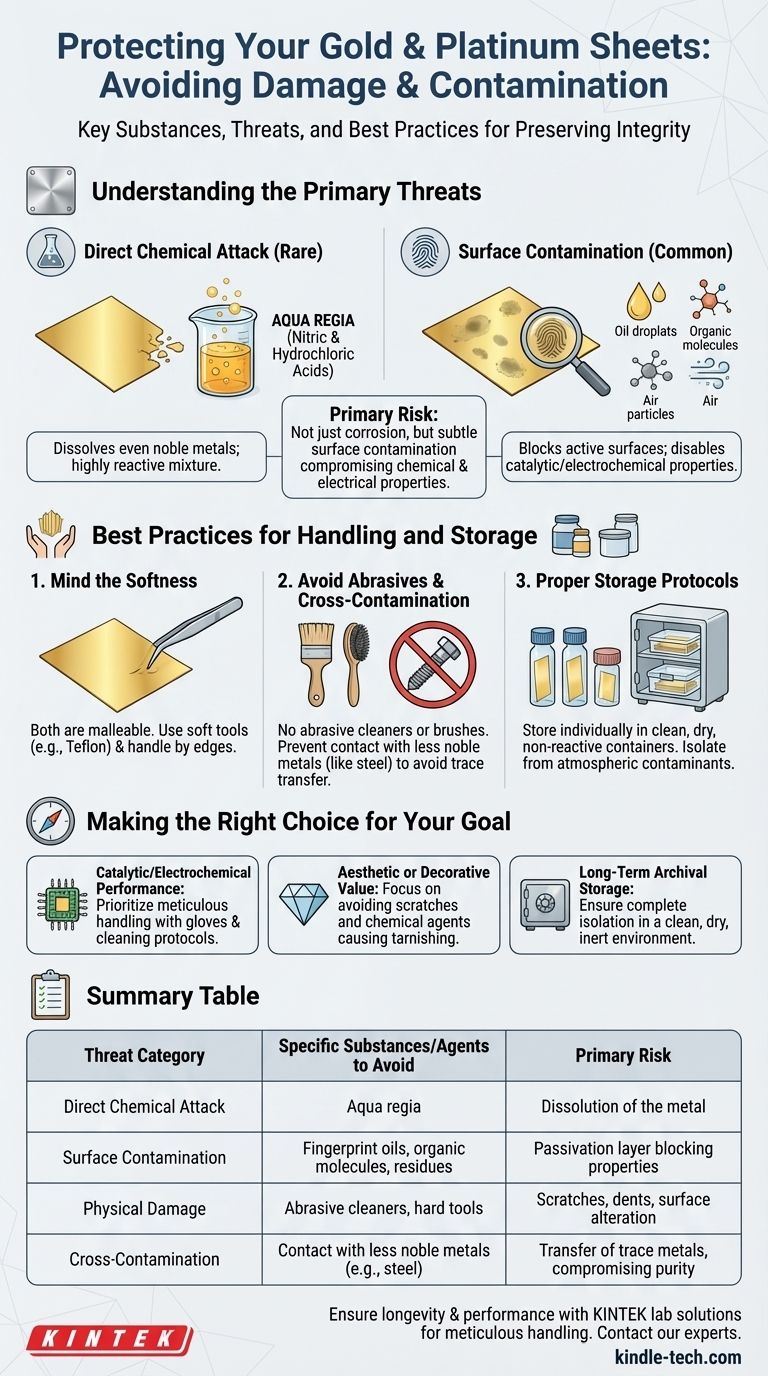
Understanding the Primary Threats
Damage to gold and platinum falls into two main categories: direct chemical attack, which is rare, and surface contamination, which is a far more frequent issue in technical applications.
The Mechanism of Direct Chemical Attack
Gold and platinum are known as noble metals because they resist corrosion and oxidation in most environments. Very few single acids can dissolve them.
The most cited exception is aqua regia, a mixture of concentrated nitric acid and hydrochloric acid. It works not because of its acidity, but because the mixture produces highly reactive chemical species (like free chlorine) that can oxidize gold and platinum, allowing them to dissolve.
The Pervasive Issue of Surface Contamination
For most applications, such as electrodes or catalysts, the biggest threat is not dissolution but the formation of an unwanted layer on the metal's surface.
This passivation layer can be formed by oils from fingerprints, organic molecules from the air, or residues from cleaning agents. While this layer doesn't damage the bulk metal, it blocks the active surface, effectively disabling its catalytic or electrochemical properties.
Reactions in Specific Environments
When used as electrodes, the combination of an electrolyte and applied voltage can create conditions harsh enough to corrode even gold or platinum. The selection of an appropriate electrolyte that is stable within the desired voltage window is critical to prevent unintended reactions with the metal sheet itself.
Best Practices for Handling and Storage
Because these metals are valuable and damage can be difficult to repair, prevention is the most effective strategy. This involves both careful handling and controlled storage.
The Softness of Noble Metals
Both gold and platinum are relatively soft and malleable. They can be easily scratched, dented, or deformed by improper handling.
Always handle sheets gently, ideally by the edges. Use tools made of softer materials, like Teflon-coated tweezers, to avoid marring the surface.
Avoiding Abrasives and Cross-Contamination
Never use abrasive cleaners, polishes, or brushes. These will remove metal and permanently alter the surface finish and dimensions.
Similarly, prevent contact with less noble metals. Storing a platinum sheet against a piece of steel can lead to cross-contamination, where trace amounts of iron transfer to the platinum surface, compromising its purity and performance.
Establishing Proper Storage Protocols
The ideal storage environment is clean, dry, and isolated. Store sheets individually in non-reactive containers, such as glass vials or dedicated plastic cases. This prevents them from scratching each other and protects them from atmospheric contaminants.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your protection strategy should align with your primary objective for using the material.
- If your primary focus is preserving catalytic or electrochemical performance: Your top priority is preventing surface contamination through meticulous handling with gloves and proper cleaning protocols.
- If your primary focus is maintaining aesthetic or decorative value: Your main goal is to avoid physical scratches and any chemical agents that could cause even minor tarnishing.
- If your primary focus is long-term archival storage: The key is complete isolation in a clean, dry, and inert environment to prevent any potential reaction or degradation over time.
Ultimately, protecting the value and function of gold and platinum relies on a mindful and disciplined approach to how they are handled, used, and stored.
Summary Table:
| Threat Category | Specific Substances/Agents to Avoid | Primary Risk |
|---|---|---|
| Direct Chemical Attack | Aqua regia (nitric & hydrochloric acid mix) | Dissolution of the metal |
| Surface Contamination | Fingerprint oils, organic molecules, cleaning agent residues | Passivation layer blocking catalytic/electrical properties |
| Physical Damage | Abrasive cleaners, polishes, hard tools | Scratches, dents, and permanent surface alteration |
| Cross-Contamination | Contact with less noble metals (e.g., steel) | Transfer of trace metals, compromising purity |
Ensure the longevity and performance of your precious metal components. KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables tailored for meticulous material handling and storage. Our products help you maintain the integrity of sensitive materials like gold and platinum. Contact our experts today to find the perfect solutions for your laboratory's specific needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High-Purity Titanium Foil and Sheet for Industrial Applications
- Platinum Sheet Electrode for Laboratory and Industrial Applications
- High Purity Zinc Foil for Battery Lab Applications
- Aluminum Foil Current Collector for Lithium Battery
- Battery Lab Equipment 304 Stainless Steel Strip Foil 20um Thick for Battery Test
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between metallic and non-metallic coating? A Guide to Sacrificial vs. Barrier Protection
- What are two disadvantages of metal? Understanding Corrosion and Weight Limitations
- What are the advantages disadvantages and uses of sheet metal? The Ultimate Guide to Material Selection
- How does hardness change with temperature? Understand the Inverse Relationship to Prevent Failure
- What is titanium disadvantages and advantages? Weighing Performance vs. Cost for Your Project






