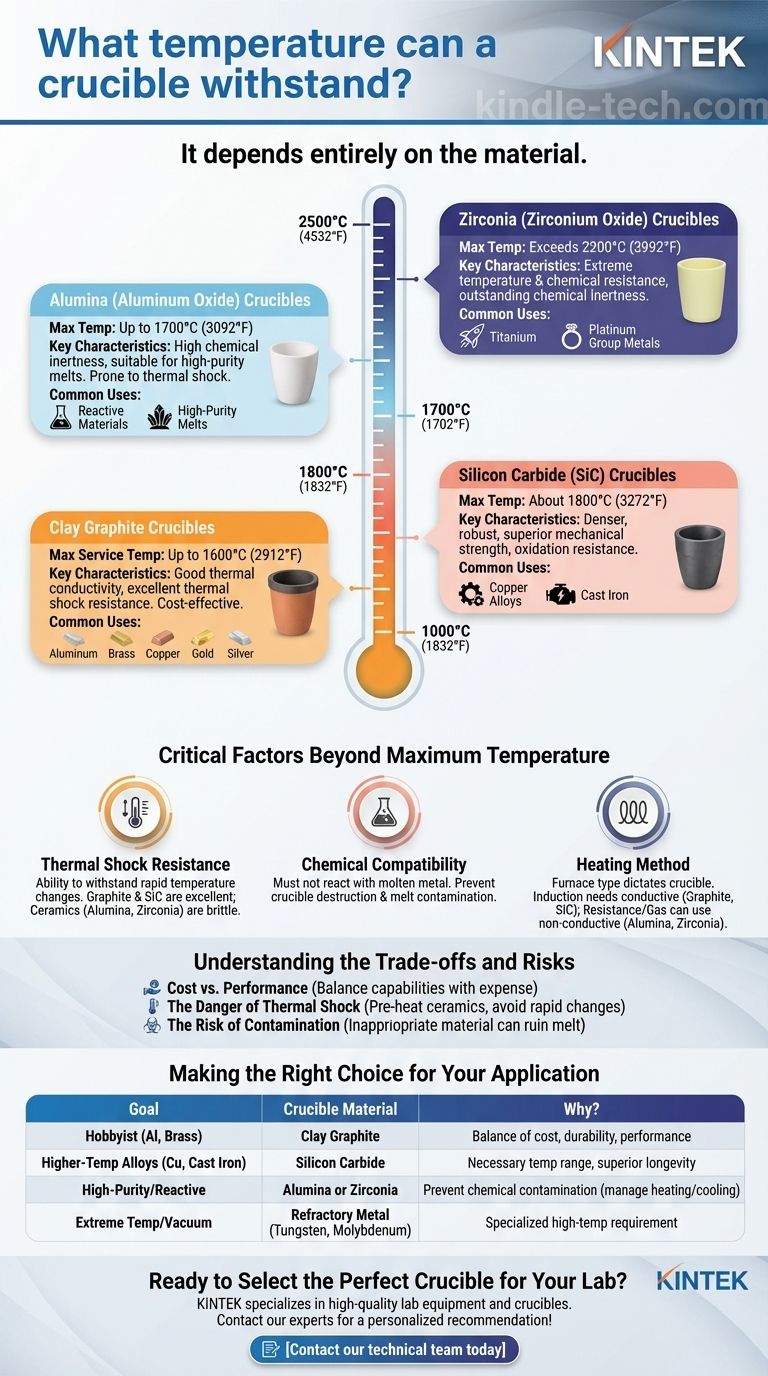
The temperature a crucible can withstand depends entirely on its material. A common clay graphite crucible for hobbyists might handle up to 1600°C (2912°F), whereas a specialized zirconia or tungsten crucible used in industrial or research settings can exceed 2400°C (4352°F). The correct choice is determined not just by the melting point of your target material, but also by chemical compatibility and your heating method.
Selecting a crucible is about more than preventing a meltdown. The right material must resist thermal shock from rapid heating, avoid chemical reactions that contaminate your final product, and be compatible with your furnace type.

A Guide to Common Crucible Materials
The material of a crucible dictates its performance characteristics, from its maximum service temperature to its durability. Understanding these options is the first step in making an informed decision.
Clay Graphite Crucibles
This is the most common and cost-effective choice, especially for hobbyists and small foundries. They are a composite of clay, graphite, and other materials.
Their maximum service temperature is typically around 1600°C (2912°F). They offer good thermal conductivity and excellent resistance to thermal shock, making them forgiving to use. They are ideal for melting non-ferrous metals like aluminum, brass, copper, gold, and silver.
Silicon Carbide (SiC) Crucibles
Silicon carbide crucibles represent a significant step up in durability and performance. They are denser and more robust than their clay graphite counterparts.
With a maximum temperature of about 1800°C (3272°F), they offer superior mechanical strength and resistance to oxidation. This makes them an excellent choice for melting copper alloys and cast iron in demanding, high-volume environments.
Alumina (Aluminum Oxide) Crucibles
Alumina is a high-purity ceramic material valued for its chemical stability. These crucibles are typically white and are used when melt purity is a primary concern.
They can withstand temperatures up to 1700°C (3092°F) but are much more susceptible to thermal shock than graphite-based crucibles. Their key feature is high chemical inertness, making them suitable for working with reactive materials or when contamination must be minimized.
Zirconia (Zirconium Oxide) Crucibles
For extremely high-temperature applications, Zirconia is a top-tier ceramic choice. It is used in highly specialized industrial and scientific work.
Zirconia crucibles can operate at temperatures exceeding 2200°C (3992°F). They possess outstanding chemical inertness and are one of the few materials suitable for melting highly reactive metals like titanium or platinum group metals.
Critical Factors Beyond Maximum Temperature
Simply choosing a crucible with a higher temperature rating than your metal's melting point is not enough. Other factors are equally critical for a successful and safe melt.
Thermal Shock Resistance
This is a material's ability to withstand rapid changes in temperature without cracking.
Graphite and silicon carbide have excellent thermal shock resistance. Ceramic crucibles like alumina and zirconia are much more brittle and require slow, controlled heating and cooling cycles to prevent catastrophic failure.
Chemical Compatibility
The crucible material must not react with the molten metal inside it. A chemical reaction can destroy the crucible and, just as importantly, contaminate your melt.
For example, using an oxide-based ceramic crucible (like alumina) to melt a material that aggressively reduces oxides can lead to failure. Always verify that your crucible material is inert to your target metal at its melting temperature.
Heating Method
Your furnace dictates which crucible materials are viable.
Induction furnaces require an electrically conductive crucible to function. This makes graphite and silicon carbide ideal choices, as the crucible itself heats up directly in the magnetic field.
Resistance-heated or gas-fired furnaces heat the environment around the crucible. For these, non-conductive ceramic crucibles like alumina and zirconia are perfectly suitable.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Risks
Every crucible choice involves balancing performance, cost, and operational requirements. Being aware of the potential pitfalls is crucial for safety and success.
Cost vs. Performance
There is a direct correlation between a crucible's performance capabilities and its cost. A Zirconia crucible can be orders of magnitude more expensive than a clay graphite one. Over-specifying a crucible for a simple task is an unnecessary expense.
The Danger of Thermal Shock
The most common cause of crucible failure is thermal shock. Never place a cool crucible into a red-hot furnace or expose a hot crucible to a cold surface. Always pre-heat your crucible according to the manufacturer's guidelines, especially for brittle ceramic types.
The Risk of Contamination
Even if a crucible doesn't melt or crack, it can still ruin your work. Using an inappropriate material can leach impurities into your melt, altering the chemical properties and performance of your final casted object.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your goal determines the right tool for the job. Use this guide to select the appropriate starting point for your work.
- If you are a hobbyist melting non-ferrous metals like aluminum or brass: A clay graphite crucible offers the best balance of cost, durability, and performance for your needs.
- If you are working with higher-temperature alloys like copper or cast iron: A silicon carbide crucible provides the necessary temperature range and superior longevity for more demanding work.
- If your primary focus is high-purity melts or reactive materials: An alumina or zirconia crucible is required to prevent chemical contamination, but you must carefully manage its heating and cooling rates.
- If you are operating in extreme temperatures within a vacuum furnace: A specialized crucible made from a refractory metal like tungsten or molybdenum is necessary.
By understanding that material properties—not just a single temperature rating—define a crucible's suitability, you can ensure the safety, purity, and success of your work.
Summary Table:
| Crucible Material | Max Service Temperature | Key Characteristics & Common Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Clay Graphite | Up to 1600°C (2912°F) | Cost-effective, good thermal shock resistance. Ideal for aluminum, brass, copper, gold, silver. |
| Silicon Carbide (SiC) | Up to 1800°C (3272°F) | Durable, high mechanical strength. Suitable for copper alloys, cast iron. |
| Alumina (Al₂O₃) | Up to 1700°C (3092°F) | High chemical inertness, prone to thermal shock. Best for high-purity or reactive melts. |
| Zirconia (ZrO₂) | Exceeds 2200°C (3992°F) | Extreme temperature & chemical resistance. For reactive metals like titanium, platinum. |
Ready to Select the Perfect Crucible for Your Lab?
Choosing the right crucible is critical for the safety, purity, and success of your work. KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including a full range of crucibles tailored for specific materials and temperatures.
Our experts can help you navigate the critical factors of thermal shock resistance, chemical compatibility, and heating method to ensure you get a crucible that performs reliably.
Let KINTEK be your partner in precision. Contact our technical team today to discuss your specific application needs and get a personalized recommendation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible Semicircle Boat with Lid for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Al2O3 Crucible With Lid Cylindrical Laboratory Crucible
- Arc-Shaped Alumina Ceramic Crucible High Temperature Resistant for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Crucibles (Al2O3) for Thermal Analysis TGA DTA
- Engineering Advanced Fine Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible for Laboratory Muffle Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of selecting an alumina crucible for TGA? Ensure High-Precision Thermal Analysis Data
- Why is the use of high-purity alumina crucibles necessary for NMC powders? Ensure Purity in Cathode Synthesis
- What is the function of alumina crucibles in Na3V2(PO4)2F3 synthesis? Ensure Purity in NVPF Production
- What are the functional advantages of using high-purity alumina crucibles? Achieve Precise Oxidation Data
- What role does an Alumina Crucible play in the high-temperature solid-state synthesis of Na3OBr? Ensure Sample Purity



















