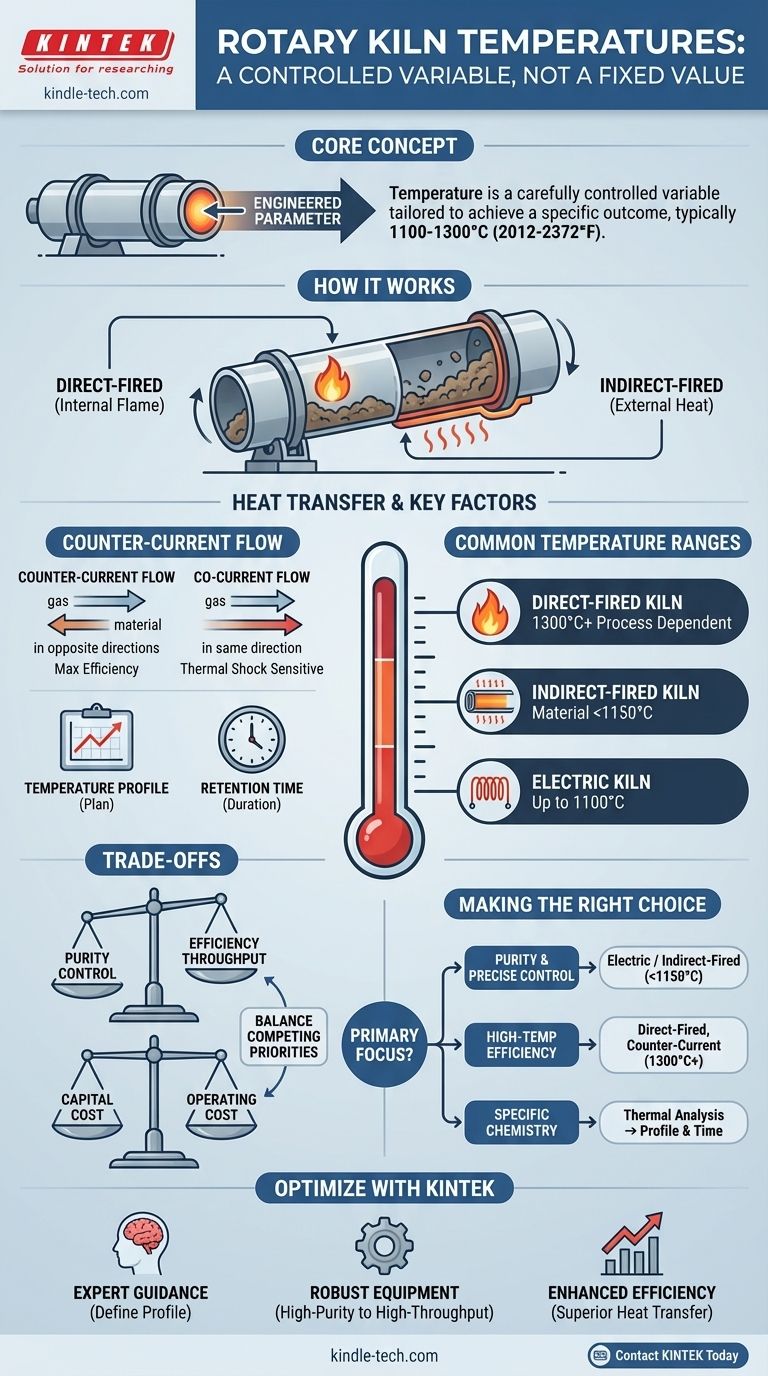
In practice, a rotary kiln's operating temperature is not a single value but a highly controlled variable tailored to a specific industrial process. While many applications operate in the 1100 °C to 1300 °C (2012 °F to 2372 °F) range, the exact temperature depends entirely on the material being processed and the desired chemical or physical change.
The core concept to understand is that a rotary kiln is a tool for thermal processing. Its temperature is not a fixed specification of the machine itself, but rather a carefully engineered parameter set to achieve a specific outcome for a specific material.

How a Rotary Kiln Functions
A rotary kiln is fundamentally a large, rotating cylinder set at a slight angle. This design ensures that as the kiln turns, the solid material inside tumbles and mixes, guaranteeing even heat exposure as it gradually moves from the higher entry point to the lower exit.
The Role of the Heat Source
The method of heating is a primary factor influencing the kiln's capabilities. There are two main approaches.
Direct-fired kilns introduce a flame or hot gases directly into the cylinder to make contact with the material. This method is common for processes that require extremely high temperatures.
Indirect-fired kilns, including electric models, heat the kiln shell from the outside. The heat then transfers through the wall to the material inside. This provides a more controlled atmosphere, free from combustion byproducts.
Material Flow and Heat Transfer
The direction of the hot gas flow relative to the material is critical for thermal efficiency.
In a counter-current system, hot gases flow in the opposite direction of the material. This is highly efficient, as the hottest gases meet the most processed material, ensuring maximum heat transfer before the material exits.
In a co-current system, the gases and material move in the same direction. This is less common but can be useful for materials that are sensitive to thermal shock.
Temperature Profiles and Retention Time
Achieving a peak temperature is only part of the process. The kiln is programmed with a specific temperature profile—a plan for how the material's temperature should change over time.
This is combined with retention time, the duration the material spends inside the kiln. These two factors are precisely controlled to ensure the desired chemical reaction or physical change is fully completed.
Common Temperature Ranges by Type
While process-dependent, different kiln types are generally suited for certain temperature brackets.
Indirect and Electric Kilns
These kilns are ideal for processes requiring high purity and precise control, such as specialized chemical reactions or calcination.
An electric rotary kiln can typically reach up to 1100 °C (2012 °F).
An indirect-fired rotary kiln can achieve furnace tube temperatures of 1200-1300 °C (2192-2372 °F), resulting in material temperatures just below that, often less than 1150 °C (2102 °F).
Direct-Fired Kilns
These workhorses are used for large-scale industrial processes like cement manufacturing or waste incineration, where achieving the highest possible temperatures is the primary goal. The temperatures are dictated by the needs of the reaction, which can often exceed the ranges of indirect kilns.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a kiln and temperature profile involves balancing competing priorities.
Purity vs. Heat Efficiency
Direct firing is very energy-efficient but risks contaminating the product with combustion byproducts. Indirect firing protects product purity but is limited by the heat-transfer capability of the kiln shell material.
Control vs. Throughput
Achieving a precise temperature profile and long retention time often requires slower rotation and a reduced feed rate. This enhances process control at the expense of overall material throughput.
Capital Cost vs. Operating Cost
Electric kilns can offer the finest control but may have higher operating costs depending on electricity prices. Large, direct-fired kilns are massive capital investments but are often the most effective solution for high-volume, high-temperature processing.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The ideal temperature is determined by your material's specific transformation requirements.
- If your primary focus is process purity and precise temperature control: An electric or indirect-fired kiln operating up to 1150 °C is your best choice.
- If your primary focus is achieving a high-temperature reaction efficiently: A direct-fired, counter-current kiln is the industry standard for reaching temperatures necessary for processes like clinker formation.
- If your primary focus is a specific chemical transformation (e.g., oxidation or reduction): You must work from a thermal analysis of your material to define the exact temperature profile and retention time needed.
Ultimately, the kiln's temperature is a tool engineered to serve the specific chemistry of your material.
Summary Table:
| Kiln Type | Typical Maximum Temperature | Key Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Electric Rotary Kiln | Up to 1100°C (2012°F) | High-purity chemical reactions, precise calcination |
| Indirect-Fired Kiln | 1200-1300°C (Tube Temp) | Controlled atmosphere processing, material temperatures <1150°C |
| Direct-Fired Kiln | 1300°C+ (Process Dependent) | Cement production, waste incineration, high-throughput processes |
Optimize Your Thermal Processing with KINTEK
Selecting the right rotary kiln and temperature profile is critical to your product's quality and process efficiency. Whether your priority is extreme purity, maximum temperature, or precise control, KINTEK's expertise in lab and industrial equipment can guide you to the ideal solution.
We provide:
- Expert Guidance: Our team helps you define the exact temperature profile and retention time for your specific material transformation.
- Robust Equipment: From high-purity electric kilns to high-throughput direct-fired systems, we have the tools for your application.
- Enhanced Efficiency: Achieve superior heat transfer and process control to improve your bottom line.
Ready to engineer the perfect thermal process for your materials? Contact KINTEK today to discuss your project requirements and discover how our specialized equipment can meet your laboratory and production needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the zones in rotary kiln in cement production? Master the Core Process for High-Quality Clinker
- What equipment is used in pyrolysis? Choosing the Right Reactor for Your Feedstock and Products
- What is the principle of rotary kiln? Mastering Continuous Thermal Processing
- What are the industrial applications of pyrolysis? Transform Waste into Energy and Valuable Products
- What are the products of pyrolysis of wood? A Guide to Biochar, Bio-oil, and Syngas Yields



















