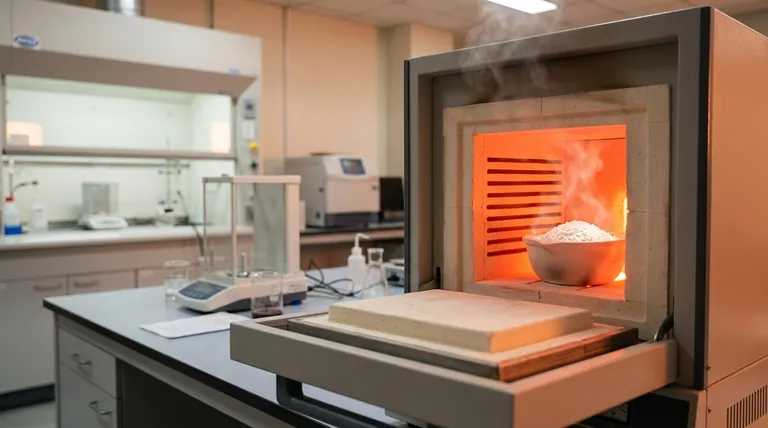
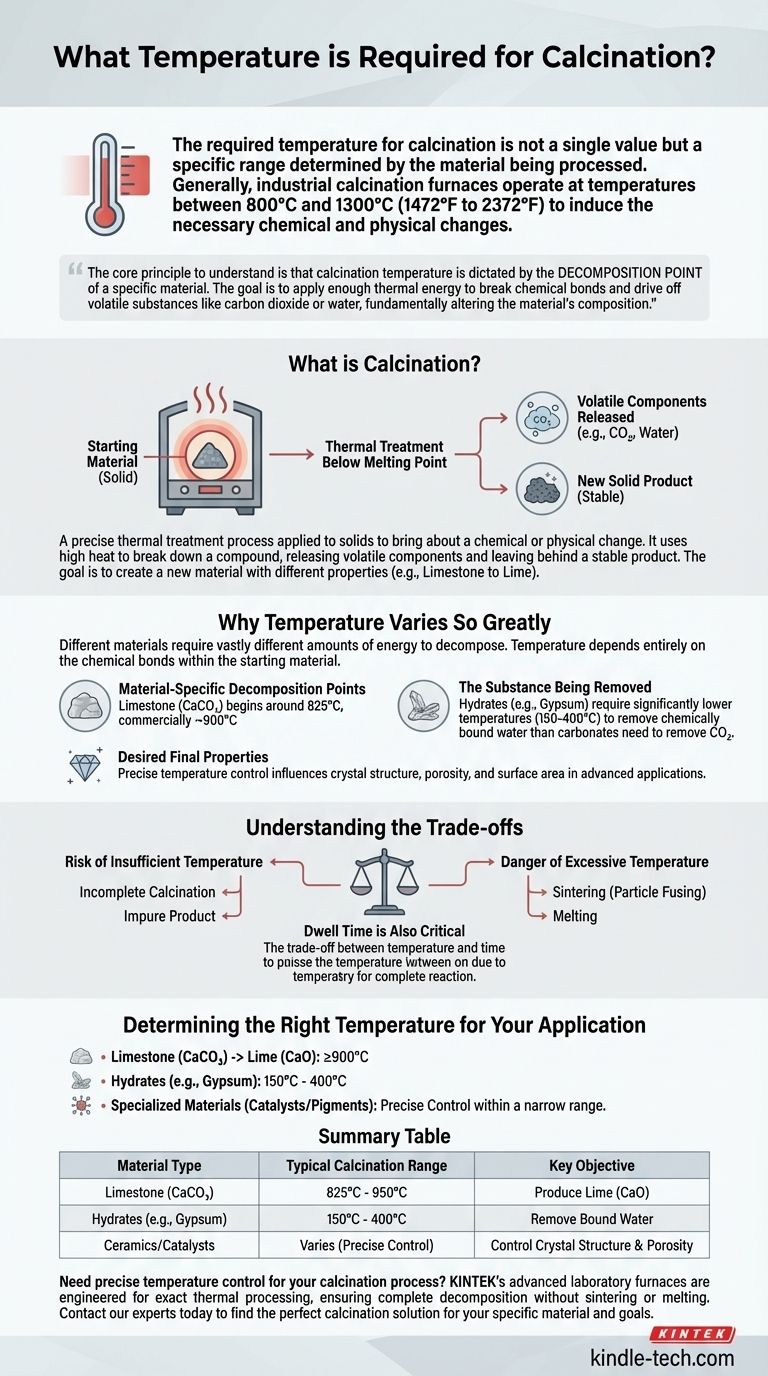
The required temperature for calcination is not a single value but a specific range determined by the material being processed. Generally, industrial calcination furnaces operate at temperatures between 800°C and 1300°C (1472°F to 2372°F) to induce the necessary chemical and physical changes.
The core principle to understand is that calcination temperature is dictated by the decomposition point of a specific material. The goal is to apply enough thermal energy to break chemical bonds and drive off volatile substances like carbon dioxide or water, fundamentally altering the material's composition.

What is Calcination?
Calcination is a precise thermal treatment process applied to solids. Its purpose is to bring about a chemical or physical change, which almost always involves heating the material below its melting point.
A Process of Thermal Decomposition
At its heart, calcination uses high heat to break down a compound. This decomposition releases volatile components, such as carbon dioxide (CO₂) or chemically bound water (water of crystallization), leaving behind a solid, stable product.
The Goal: Creating a New Substance
The most common objective is to create a new material with different properties. A classic example is the calcination of limestone (calcium carbonate, CaCO₃) to produce lime (calcium oxide, CaO) and release carbon dioxide gas.
Why Temperature Varies So Greatly
The broad temperature range for calcination exists because different materials require vastly different amounts of energy to decompose. The specific temperature depends entirely on the chemical bonds within the starting material.
Material-Specific Decomposition Points
Every compound has a unique temperature at which it begins to break down. For limestone, this process begins around 825°C and is typically performed commercially closer to 900°C to ensure a complete and efficient reaction.
The Substance Being Removed
The temperature needed to drive off water of crystallization from a hydrate is often much lower than that needed to remove CO₂ from a carbonate. Carbonate compounds have stronger chemical bonds that require significantly more thermal energy to break.
Desired Final Properties
In advanced applications like creating ceramics or catalysts, temperature control is even more critical. The final temperature can influence the resulting material's crystal structure, porosity, and surface area, all of which are vital to its performance.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Simply heating a material is not enough; the temperature must be precisely controlled to avoid undesirable outcomes and ensure the process is efficient.
The Risk of Insufficient Temperature
If the temperature is too low, the calcination will be incomplete. This leaves behind unreacted starting material, resulting in an impure product that lacks the desired chemical or physical properties.
The Danger of Excessive Temperature
Overheating can be just as damaging. Exceeding the optimal temperature can lead to sintering, where particles begin to fuse. This can reduce the reactivity of the final product or, in the worst case, cause it to melt, destroying its intended structure.
Dwell Time is Also Critical
The duration the material is held at the target temperature, known as dwell time, is a crucial variable. A lower temperature may require a longer dwell time to achieve a complete reaction, while a higher temperature can shorten the time, creating a trade-off between energy consumption and throughput.
Determining the Right Temperature for Your Application
To identify the correct calcination temperature, you must first define your material and your goal.
- If your primary focus is producing lime from limestone: You will need to operate at or above 900°C to ensure the complete decomposition of calcium carbonate.
- If your primary focus is removing chemically bound water from hydrates (e.g., gypsum): The required temperature will be significantly lower, often in the range of 150°C to 400°C, well below carbonate decomposition temperatures.
- If your primary focus is creating specialized materials like catalysts or pigments: The temperature must be meticulously controlled within a narrow range specified by the material's chemistry to achieve the exact crystal phase and surface characteristics required.
Ultimately, mastering calcination is about understanding the chemistry of your specific material and applying heat with precision to achieve a controlled transformation.
Summary Table:
| Material Type | Typical Calcination Range | Key Objective |
|---|---|---|
| Limestone (CaCO₃) | 825°C - 950°C | Produce Lime (CaO) |
| Hydrates (e.g., Gypsum) | 150°C - 400°C | Remove Bound Water |
| Ceramics/Catalysts | Varies (Precise Control) | Control Crystal Structure & Porosity |
Need precise temperature control for your calcination process? KINTEK's advanced laboratory furnaces are engineered for exact thermal processing, ensuring complete decomposition without sintering or melting. Whether you're producing lime, dehydrating hydrates, or developing advanced materials, our equipment delivers the accuracy and reliability your lab demands. Contact our experts today to find the perfect calcination solution for your specific material and goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- Do different liquids melt at different rates? Unlock the Science of Melting Points and Material Properties
- How does heat treatment affect surface roughness? Minimize Surface Degradation for Precision Parts
- What is a furnace used in a chemistry lab? A Guide to High-Temperature Material Transformation
- What are the lab safety rules for heating substances? Essential Protocols to Prevent Accidents
- Does melting require increase in temperature? Understanding Latent Heat and Phase Changes



















