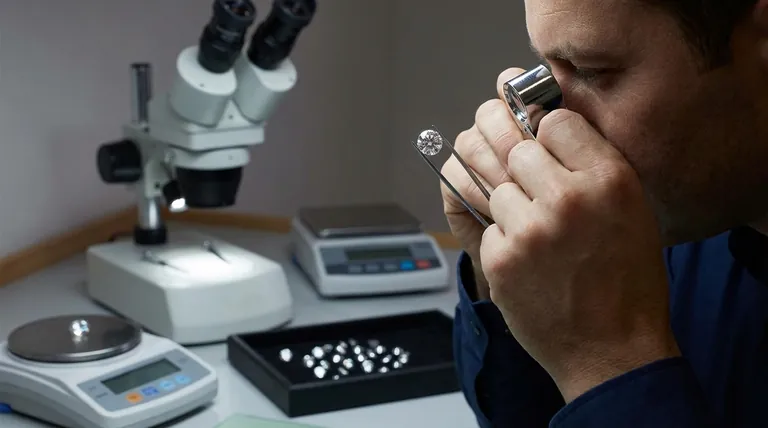
The essential tool for checking diamond quality is a jeweler's loupe, a small, high-powered magnifying glass. While other specialized equipment exists, the 10x magnification loupe is the universally accepted standard for examining the characteristics that determine a diamond's grade and value. For official grading reports, gemological labs use a binocular microscope, which offers more stability and control for detailed analysis.
A loupe doesn't determine a diamond's quality on its own. Instead, it is the instrument through which an expert evaluates the diamond against the established framework of the "4Cs"—Cut, Color, Clarity, and Carat Weight. Understanding this framework is the true key to assessing quality.
The Standard Tool: The 10x Jeweler's Loupe
The loupe is the most fundamental piece of equipment in the gem trade. It is used by everyone from miners and cutters to jewelers and appraisers for quick but detailed inspection.
What is a Loupe?
A loupe is a simple, portable magnifier designed for close examination of small objects. A "triplet" loupe, which contains three lenses bonded together to correct for distortion and color fringing, is the preferred type for professional use.
Why 10x Magnification is the Standard
The entire international diamond grading system is based on what is visible at 10x magnification. Any inclusions or blemishes that are not visible at this power are considered non-existent for grading purposes.
Using a higher magnification can be misleading for a consumer. You might spot minuscule imperfections that have no impact on the diamond's official clarity grade, leading you to undervalue an otherwise excellent stone.
How Quality is Truly Assessed: The 4Cs
The loupe is not a magic wand; it is a window. Its purpose is to allow a clear view of the specific attributes that are measured and graded to define a diamond's quality.
Assessing Clarity
This is the most direct application of a loupe. Clarity refers to the presence of internal flaws (inclusions) and external blemishes. A grader uses the loupe to identify the size, number, position, and nature of these characteristics to assign a grade on a scale from Flawless (FL) to Included (I3).
Evaluating Cut
A diamond's cut is arguably the most important factor for its brilliance and fire. A loupe helps an expert examine the precision of the cut, including the symmetry of the facets, the sharpness of the facet junctions, and the quality of the polish on the surface. These factors determine how well the diamond handles light.
Judging Color
While a loupe can be used to look for color zoning, grading a diamond's color is primarily done with the naked eye. Graders place the diamond table-down on a pure white background and compare it to a set of pre-graded "master stones." This allows for a precise assessment of the subtle presence of yellow or brown hues.
Determining Carat Weight
Carat is a measure of weight, not size, and it is not measured with a loupe. This is done using a highly precise and calibrated digital scale that can measure to the thousandth of a carat.
Understanding the Limitations
While a loupe is indispensable, it has clear limitations. Relying on visual inspection alone without understanding its context can lead to poor decisions.
The Loupe vs. A Grading Report
A personal loupe inspection should be used to verify a diamond against its official grading report, not to create a new grade from scratch. For example, you can use the loupe to find a specific inclusion plotted on a GIA or AGS report diagram to confirm you are looking at the correct stone. The report is the definitive legal and financial assessment.
Lab-Grown vs. Natural Diamonds
A loupe alone cannot reliably distinguish a natural diamond from a lab-grown one. While some lab-grown diamonds may have tell-tale inclusions, confirming origin requires specialized equipment found only in gemological laboratories.
Detecting Advanced Treatments
Many modern treatments, such as fracture filling or certain types of color enhancement, are designed to be invisible under a 10x loupe. Identifying these treatments also requires advanced testing by a professional lab.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your approach to using these tools should align with your specific objective.
- If you are a diamond buyer: Use a 10x loupe to confirm the diamond's identity against its grading report and to appreciate its characteristics, not to second-guess the lab's grade.
- If you are learning about gemology: A loupe is your best friend. Use it to practice identifying different types of inclusions and to understand the visual differences between a well-cut and a poorly-cut stone.
- If you are concerned about authenticity: Always rely on a grading report from a top-tier laboratory (like GIA or AGS), as a loupe cannot definitively identify lab-grown diamonds or most treatments.
Ultimately, empowering yourself with knowledge of the 4Cs is far more valuable than simply owning the tool used to see them.
Summary Table:
| Tool | Primary Use | Key Limitation |
|---|---|---|
| 10x Jeweler's Loupe | Examining clarity, cut, and polish characteristics. | Cannot identify lab-grown diamonds or advanced treatments. |
| Binocular Microscope | Detailed analysis for official lab grading reports. | Not portable; requires professional expertise. |
| Digital Scale | Precisely measuring carat weight. | Does not assess visual quality. |
Empower Your Precision with KINTEK
Whether you're a professional jeweler, a gemology student, or a quality control lab, having the right tools is the first step to accurate analysis. KINTEK specializes in high-quality laboratory equipment and consumables, providing the reliable instruments you need to make informed decisions.
Let us help you equip your workspace for success. Contact our experts today to find the perfect tools for your specific diamond and gemological analysis needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Special Shape Press Mold for Lab
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Crucibles (Al2O3) for Thermal Analysis TGA DTA
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
People Also Ask
- What is the use of vibrating sieve machine? Achieve Precise Particle Size Analysis for Your Lab
- What does a vibrating sieve do? Automate Particle Size Analysis for Accurate Results
- What are the different types of sieving machines? Choose the Right Motion for Your Material
- What is the speed of a sieving machine? Optimize Vibration for Maximum Efficiency and Accuracy
- What are the components of a sieving machine? Unlock the Anatomy of Precision Particle Separation



