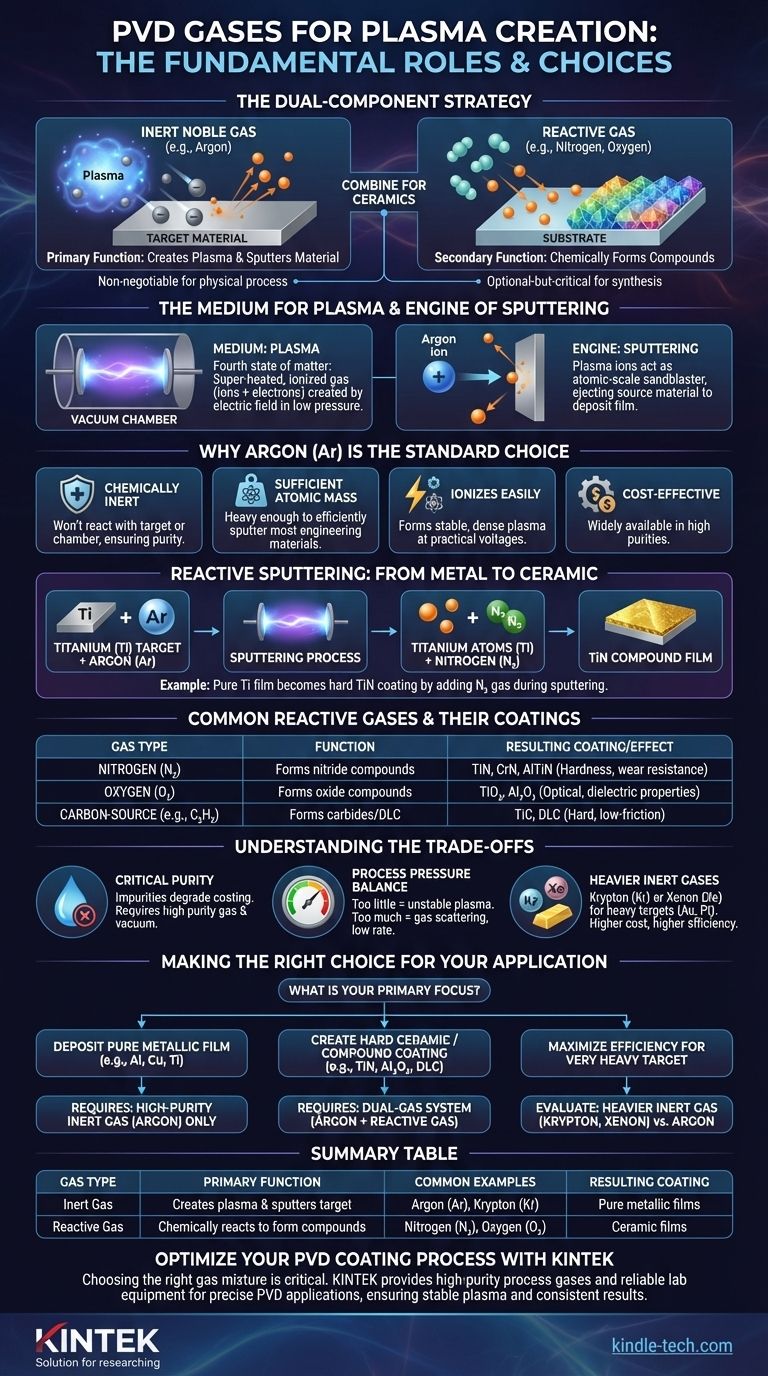
The primary gas required to create and sustain plasma in most Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) processes is an inert noble gas, with Argon (Ar) being the industry standard. While Argon is essential for the physical sputtering mechanism, other reactive gases like Nitrogen or Oxygen are often introduced intentionally, not to create the plasma, but to chemically form the desired coating on the substrate's surface.
The choice of gas in PVD is a dual-component strategy. An inert gas is non-negotiable for generating the plasma and physically ejecting source material, while a reactive gas is an optional-but-critical ingredient for synthesizing compound films like ceramics.
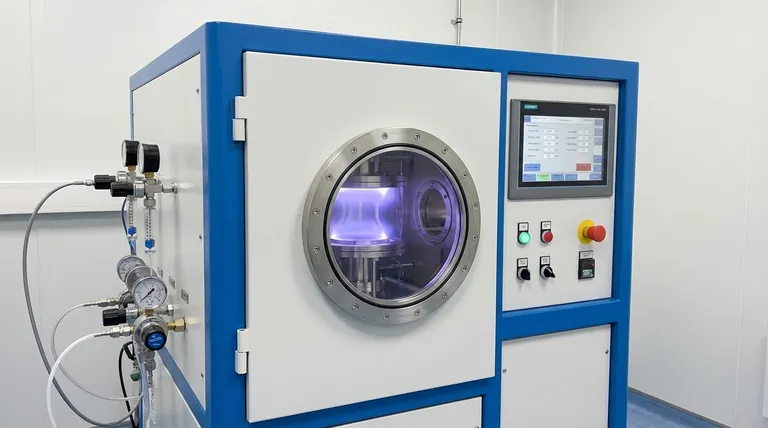

The Fundamental Roles of Gas in PVD
To understand why specific gases are chosen, we must first break down their two distinct functions within the PVD vacuum chamber: creating the plasma and dislodging the coating material.
The Medium for Plasma
Plasma is often called the fourth state of matter. It is a super-heated, ionized gas containing free-moving ions and electrons.
To create this state, a low-pressure gas is introduced into a vacuum chamber. A strong electric field is then applied, which energizes the gas atoms and strips them of their electrons, creating the positively charged ions and free electrons that constitute the plasma.
The Engine of Sputtering
In sputtering, one of the most common PVD methods, the plasma serves as a source of high-energy projectiles. The heavy, positively charged gas ions (like Argon) are accelerated by the electric field and directed at the source material, known as the target.
Think of this as an atomic-scale sandblaster. These ions slam into the target with enough force to knock off, or "sputter," atoms of the target material. These sputtered atoms then travel through the chamber and deposit onto your part, forming the thin film.
Why Argon is the Standard Choice
Argon is the workhorse of the PVD industry for several key reasons:
- It is chemically inert. It will not react with the target material or the components in the vacuum chamber, ensuring a pure deposition process.
- It has sufficient atomic mass. Argon is heavy enough to efficiently sputter most common engineering materials without being prohibitively expensive.
- It ionizes relatively easily. This allows for a stable and dense plasma to be formed at practical voltages and pressures.
- It is cost-effective and widely available in the high purities required for these processes.
Beyond Inert: The Role of Reactive Gases
While Argon handles the physical part of the process, reactive gases handle the chemical part. This process, known as reactive sputtering, is used to create hard, wear-resistant compound films.
From Metal to Ceramic
If you only sputter a Titanium (Ti) target with Argon, you will deposit a pure Titanium film. But to create the common, gold-colored, hard coating Titanium Nitride (TiN), a second gas is required.
In this case, a controlled amount of Nitrogen (N₂) gas is introduced into the chamber along with the Argon. The sputtered Titanium atoms travel from the target and react with the nitrogen in the plasma and on the substrate surface, forming a TiN compound film.
Common Reactive Gases and Their Coatings
This principle applies to a wide range of materials, allowing for the synthesis of highly engineered surfaces.
- Nitrogen (N₂) is used to form nitride coatings like TiN, CrN, and AlTiN, which are prized for their hardness and wear resistance.
- Oxygen (O₂) is used to form oxide coatings like Titanium Dioxide (TiO₂) and Aluminum Oxide (Al₂O₃), which are often used for optical or dielectric properties.
- Carbon-source gases (like Acetylene, C₂H₂) are used to form carbide coatings (e.g., TiC) or hard, low-friction Diamond-Like Carbon (DLC) films.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The choice and control of gas are critical to the success of a PVD coating, and several factors must be managed carefully.
The Critical Need for Purity
Any unintended impurity in the process gas—such as water vapor or residual air from a poor vacuum—can become incorporated into the growing film. This contamination can severely degrade the coating's adhesion, structure, and performance.
Process Pressure and Its Impact
The amount of gas in the chamber (the pressure) is a delicate balance. Too little gas, and the plasma may be unstable or too weak for efficient sputtering. Too much gas, and the sputtered atoms will collide with gas atoms too frequently, scattering them and preventing them from reaching the substrate, which kills the deposition rate.
Heavier Inert Gases for Niche Applications
For sputtering very heavy target materials like Gold (Au) or Platinum (Pt), Argon can be less efficient. In these cases, a heavier inert gas like Krypton (Kr) or Xenon (Xe) can provide a higher sputtering yield. The trade-off is significant, as these gases are substantially more expensive than Argon.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your choice of gas is dictated entirely by the final film you intend to create.
- If your primary focus is depositing a pure metallic film (e.g., Aluminum, Copper, Titanium): Your only requirement is a high-purity inert gas, which in almost all cases will be Argon.
- If your primary focus is creating a hard ceramic or compound coating (e.g., TiN, Al₂O₃, DLC): You will need a dual-gas system: high-purity Argon to run the sputtering process and a specific high-purity reactive gas to form the desired compound.
- If your primary focus is maximizing sputtering efficiency for a very heavy target element: You may need to evaluate the cost-benefit of using a more expensive, heavier inert gas like Krypton or Xenon instead of Argon.
Ultimately, selecting the right gas is about controlling both the physical mechanism of deposition and the final chemical composition of the film.
Summary Table:
| Gas Type | Primary Function | Common Examples | Resulting Coating/Effect |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inert Gas | Creates plasma & sputters target material | Argon (Ar), Krypton (Kr) | Pure metallic films (e.g., Ti, Al) |
| Reactive Gas | Chemically reacts to form compounds | Nitrogen (N₂), Oxygen (O₂) | Ceramic films (e.g., TiN, Al₂O₃) |
Optimize Your PVD Coating Process with KINTEK
Choosing the right gas mixture is critical for achieving the desired film properties, whether you need a pure metallic layer or a hard, wear-resistant ceramic coating. KINTEK specializes in providing high-purity process gases and reliable lab equipment tailored for precise PVD applications.
Our expertise ensures your laboratory can maintain stable plasma, control contamination, and achieve consistent, high-quality results. Let us help you enhance your deposition rate and coating performance.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific PVD gas and equipment needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- VHP Sterilization Equipment Hydrogen Peroxide H2O2 Space Sterilizer
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition and Lab Diamond Growth
People Also Ask
- What is an example of PECVD? RF-PECVD for High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What are the advantages of PECVD? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin-Film Deposition
- How does RF power create plasma? Achieve Stable, High-Density Plasma for Your Applications
- What are the benefits of PECVD? Achieve Superior Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What is plasma activated chemical vapour deposition method? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings



















