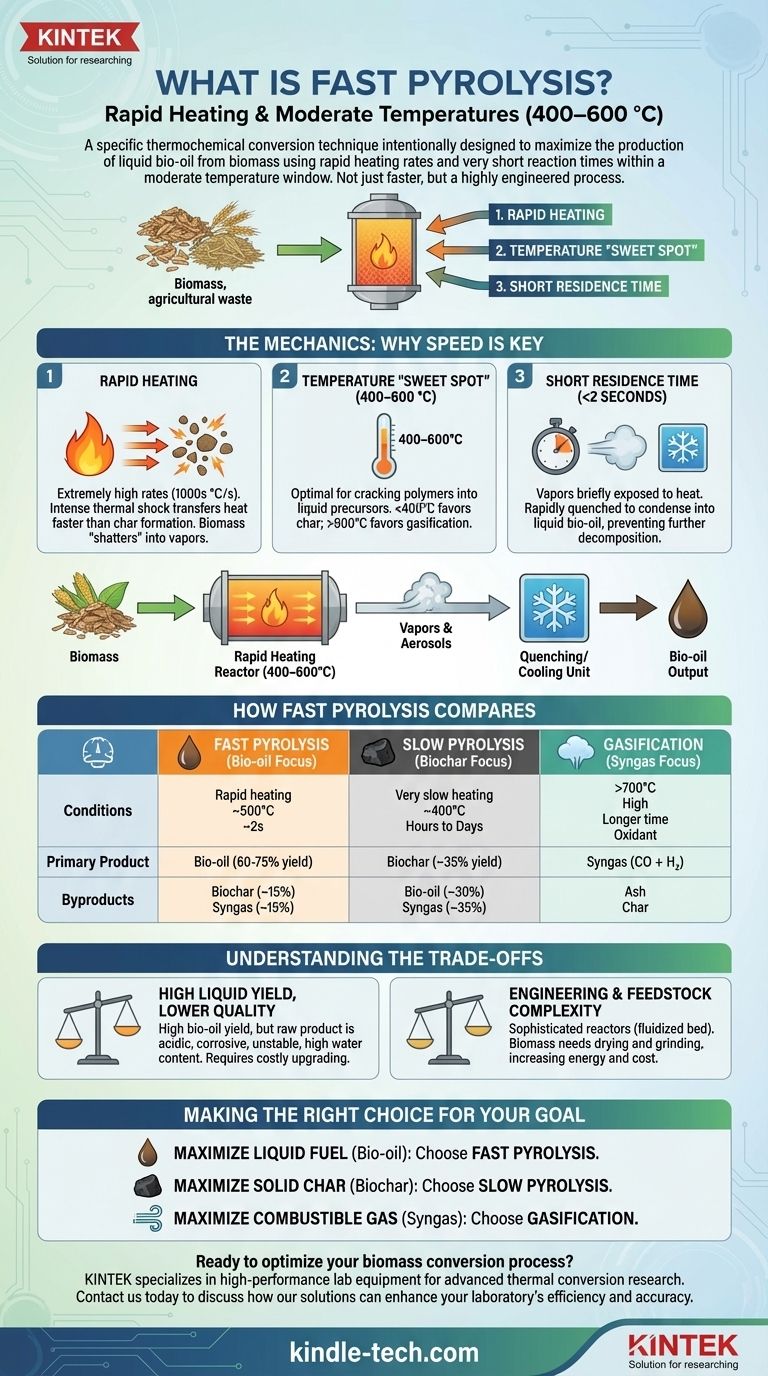
The process you're describing is known as fast pyrolysis. It is a specific thermochemical conversion technique intentionally designed to maximize the production of liquid bio-oil from biomass by using rapid heating rates and very short reaction times within a moderate temperature window.
Fast pyrolysis is not simply a faster version of traditional pyrolysis; it is a highly engineered process designed to vaporize biomass and rapidly cool those vapors into liquid bio-oil before they can decompose further into char and gas.

The Mechanics of Fast Pyrolysis: Why Speed is Key
The success of fast pyrolysis hinges on precise control over three interconnected variables: heating rate, temperature, and reaction time. The goal is to rapidly fracture the complex polymers in biomass (like cellulose and lignin) into smaller, condensable vapor molecules.
The Critical Role of Rapid Heating
Extremely high heating rates (often thousands of degrees Celsius per second) are the defining characteristic of this process. This intense thermal shock transfers heat to the biomass particles faster than they can undergo the slower chemical reactions that form solid char.
The biomass essentially "shatters" into vapors and aerosols before it has time to cook into charcoal.
The Temperature "Sweet Spot" (400–600 °C)
This temperature range is optimal for cracking the biomass polymers into the desired liquid precursors.
Temperatures below 400°C are too low for rapid decomposition, favoring the slow reactions that produce char. Temperatures above 600°C begin to favor secondary cracking, where the valuable vapor molecules break down further into simple, non-condensable gases like carbon monoxide and methane (a process called gasification).
The Necessity of Short Residence Time
The vapors created during the initial thermal shock are only allowed to remain in the hot reactor zone for a very short period, typically less than two seconds.
This brief exposure is just enough time for the primary decomposition to occur but prevents the secondary reactions that would reduce the liquid yield. Immediately after leaving the reactor, these hot vapors are rapidly cooled, or "quenched," to condense them into the liquid product known as bio-oil.
How Fast Pyrolysis Compares to Other Methods
Understanding the specific conditions of fast pyrolysis is clearest when compared to other thermal conversion processes. Each is optimized for a different primary product.
Fast Pyrolysis (Bio-oil Focus)
- Conditions: Rapid heating, moderate temperature (~500°C), short residence time (~2s).
- Primary Product: Bio-oil (yields often 60-75% by weight).
- Byproducts: Biochar (~15%) and syngas (~15%).
Slow Pyrolysis (Biochar Focus)
- Conditions: Very slow heating, lower temperature (~400°C), long residence time (hours to days).
- Primary Product: Biochar, or charcoal (yields often ~35%).
- Byproducts: Bio-oil (~30%) and syngas (~35%).
Gasification (Syngas Focus)
- Conditions: High temperature (>700°C), controlled introduction of an oxidant (like air or oxygen), longer residence times.
- Primary Product: Syngas—a mixture of carbon monoxide (CO) and hydrogen (H₂).
- Byproducts: Ash and some char.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While fast pyrolysis is highly effective at producing liquid fuel, it comes with significant technical challenges and trade-offs that must be considered.
High Liquid Yield, Lower Quality
The primary advantage is the high yield of bio-oil. However, this raw bio-oil is not a drop-in replacement for conventional fossil fuels.
It is highly acidic, corrosive, contains a significant amount of water (15-30%), and is chemically unstable over time. It requires substantial and often costly upgrading to be used as a stable transportation fuel.
Engineering and Feedstock Complexity
Achieving rapid heating requires sophisticated reactor designs, such as fluidized bed or ablative reactors, which are more complex and capital-intensive than simple kilns used for slow pyrolysis.
Furthermore, the process requires that the biomass feedstock be dried and ground into very fine particles to ensure rapid heat transfer, adding energy and cost to the overall process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The selection of a thermal conversion technology depends entirely on the desired end product.
- If your primary focus is maximizing liquid fuel (bio-oil) production: Fast pyrolysis is the most established and effective method for converting biomass into a high-yield liquid intermediate.
- If your primary focus is producing a stable, solid soil amendment or solid fuel (biochar): Slow pyrolysis is the superior choice, as its conditions are optimized for char formation rather than liquid.
- If your primary focus is generating combustible gas (syngas) for power or chemical synthesis: Gasification, which operates at much higher temperatures, is the correct thermal conversion pathway.
Choosing the right process is about aligning the specific conditions of temperature and time with the chemical product you intend to create.
Summary Table:
| Pyrolysis Type | Primary Goal | Temperature Range | Heating Rate | Residence Time | Main Product |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fast Pyrolysis | Maximize Liquid Yield | 400-600°C | Very High (100s-1000s °C/s) | < 2 seconds | Bio-oil (60-75% yield) |
| Slow Pyrolysis | Maximize Char Yield | ~400°C | Very Slow | Hours to Days | Biochar (~35% yield) |
| Gasification | Maximize Gas Yield | >700°C | High | Longer | Syngas (CO + H₂) |
Ready to optimize your biomass conversion process?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables for advanced thermal conversion research, including pyrolysis and gasification. Whether you're developing new bio-oil production methods or optimizing biochar yields, our reliable tools help you achieve precise temperature control and rapid heating rates.
Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your laboratory's efficiency and accuracy. Let's work together to advance your sustainable energy research.
Get in touch with our experts now!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Reactor for Hydrothermal Synthesis
- Mini SS High Pressure Autoclave Reactor for Laboratory Use
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the process of biomass fast pyrolysis? Turn Biomass into Bio-Oil in Seconds
- How is energy converted into biomass? Harnessing Nature's Solar Power for Renewable Energy
- What are the reactions involved in pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock the Chemistry for Tailored Bio-Products
- What are the advantages of pyrolysis technology? Turn Waste into Profit and Reduce Emissions
- What are the components of biomass pyrolysis? A Complete Guide to the System, Products, and Process



















