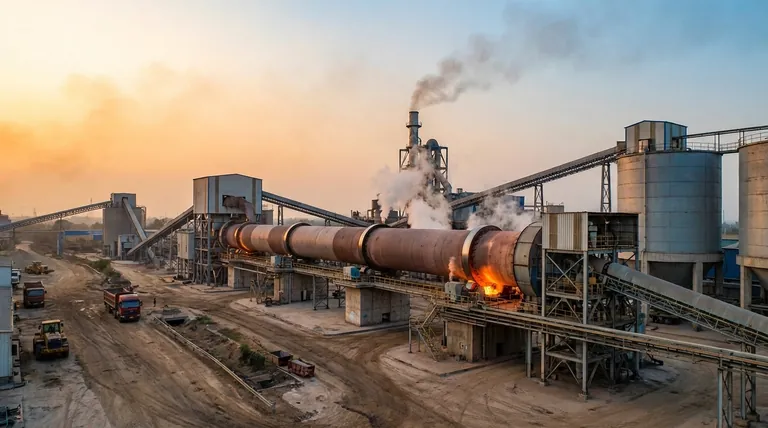
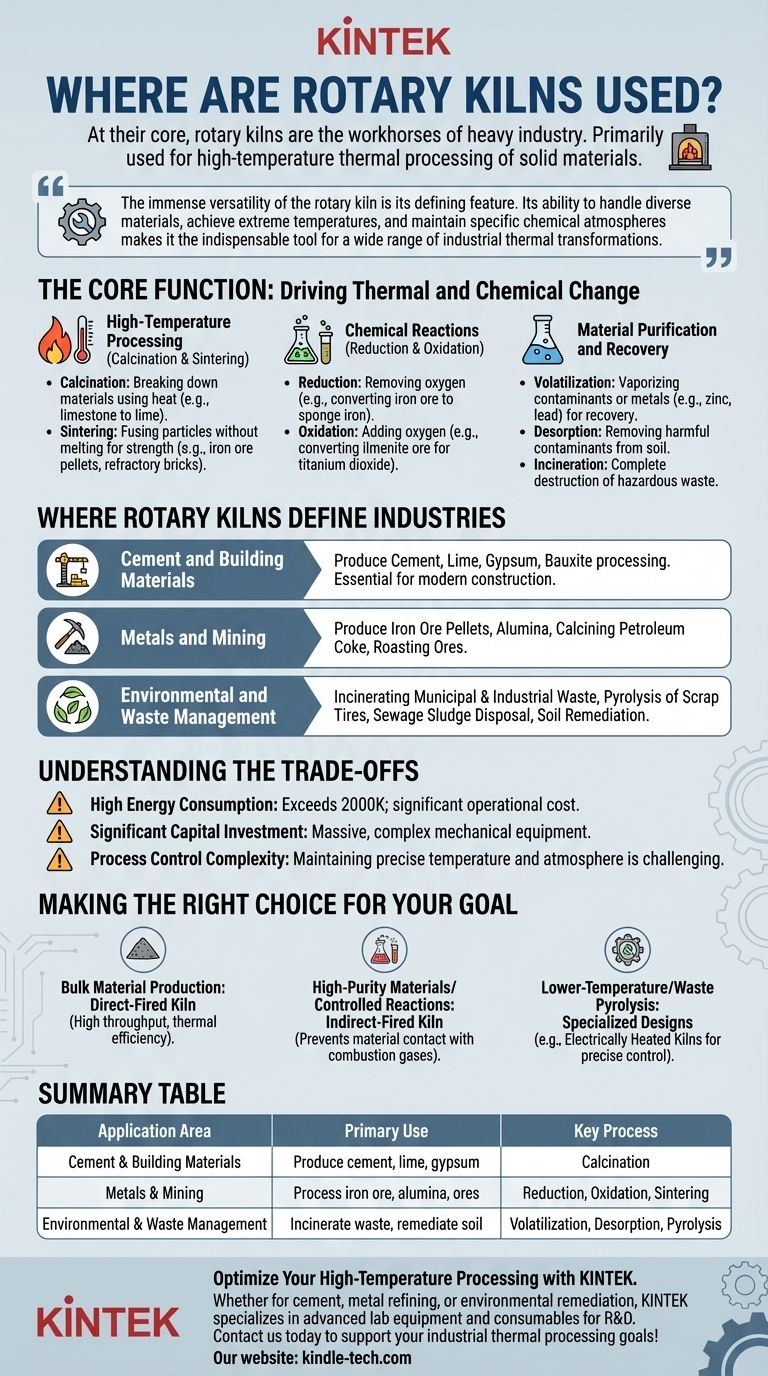
At their core, rotary kilns are the workhorses of heavy industry. They are primarily used for the high-temperature thermal processing of solid materials. You will find them at the heart of manufacturing for cement, lime, and various metals, as well as in critical environmental applications like waste incineration and soil remediation.
The immense versatility of the rotary kiln is its defining feature. Its ability to handle diverse materials, achieve extreme temperatures, and maintain specific chemical atmospheres makes it the indispensable tool for a wide range of industrial thermal transformations.

The Core Function: Driving Thermal and Chemical Change
A rotary kiln's fundamental purpose is to heat materials to a specific temperature for a specific time to cause a physical or chemical change. This capability is applied across three main categories of processes.
High-Temperature Processing (Calcination & Sintering)
Calcination is a process that uses heat to break down materials and drive off a component, such as removing carbon dioxide from limestone to create lime.
Sintering uses heat to fuse particles together without melting them, which is critical for creating strong materials like iron ore pellets or durable refractory bricks. The cement industry relies almost entirely on rotary kilns for the calcination stage of clinker production.
Chemical Reactions (Reduction & Oxidation)
Rotary kilns act as large-scale chemical reactors where the atmosphere can be tightly controlled.
Reduction processes, which remove oxygen, are used to convert iron ore into sponge iron. Oxidation processes, which add oxygen, are used for tasks like converting ilmenite ore in the production of titanium dioxide.
Material Purification and Recovery
Heat is a powerful tool for purification. Rotary kilns can volatilize, or turn into vapor, contaminants or valuable metals like zinc, lead, and mercury, allowing for their separation and recovery.
This same principle is used in environmental applications for desorbing harmful contaminants from soil or for incinerating hazardous waste at temperatures that ensure complete destruction.
Where Rotary Kilns Define Industries
The processes above are the building blocks for countless products and industrial activities. The kiln is rarely the final step, but it is almost always the most critical one.
Cement and Building Materials
This is the most well-known application. Rotary kilns are essential for producing cement, lime, and for processing gypsum and bauxite. Their ability to handle huge volumes of raw material makes modern construction possible.
Metals and Mining
The metals industry uses kilns extensively. Key applications include producing iron ore pellets, calcining petroleum coke for aluminum smelting, creating alumina from bauxite, and roasting a wide variety of ores to prepare them for further processing.
Environmental and Waste Management
Modern environmental regulations have driven significant innovation in kiln technology. They are now central to incinerating municipal and industrial waste, recycling scrap tires through pyrolysis, disposing of sewage sludge, and remediating contaminated soil.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While incredibly versatile, rotary kilns are not a universal solution. Their selection requires understanding their inherent limitations.
High Energy Consumption
Achieving temperatures that can exceed 2000 K requires an immense amount of energy, typically from natural gas, coal, or other fuels. This makes them one of the most significant operational costs in any plant.
Significant Capital Investment
Rotary kilns are massive, complex pieces of mechanical equipment. The initial purchase, installation, and commissioning of a kiln system represent a major capital expenditure.
Process Control Complexity
While a key advantage, maintaining a precise temperature profile and chemical atmosphere along the length of a continuously rotating, 100-meter-long tube is a complex control challenge that requires significant expertise.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The specific design of a rotary kiln is always tailored to its intended purpose. Whether it's heated directly by a flame or indirectly through the shell determines its capabilities.
- If your primary focus is bulk material production (e.g., cement, lime): A large, direct-fired kiln is the industry standard for its high throughput and thermal efficiency.
- If your primary focus is high-purity materials or controlled reactions: An indirect-fired kiln is superior, as it prevents the material from contacting combustion gases.
- If your primary focus is lower-temperature processing or waste pyrolysis: Specialized designs, including electrically heated kilns, provide the precise control needed for these sensitive applications.
Understanding these core applications and principles allows you to identify why this technology remains fundamental to the modern industrial landscape.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Primary Use | Key Process |
|---|---|---|
| Cement & Building Materials | Produce cement, lime, gypsum | Calcination |
| Metals & Mining | Process iron ore, alumina, ores | Reduction, Oxidation, Sintering |
| Environmental & Waste Management | Incinerate waste, remediate soil | Volatilization, Desorption, Pyrolysis |
Optimize Your High-Temperature Processing with KINTEK
Whether you're in cement production, metal refining, or environmental remediation, the right thermal processing equipment is critical to your success. KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables for industrial research and development, helping you test and scale your processes with precision.
Let our experts help you select the ideal solutions for your specific needs. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your laboratory and industrial thermal processing goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the products of pyrolysis of wood? A Guide to Biochar, Bio-oil, and Syngas Yields
- What is the difference between calcining and roasting? A Guide to High-Temperature Processing
- What are the zones in rotary kiln in cement production? Master the Core Process for High-Quality Clinker
- What are the types of pyrolysis reactors used in industry? Choose the Right Technology for Your Product
- What equipment is used in pyrolysis? Choosing the Right Reactor for Your Feedstock and Products



















