To be direct, neither CVD nor HPHT is universally "better." Both are advanced, legitimate methods for creating high-quality, lab-grown diamonds that are physically, chemically, and optically identical to natural diamonds. The "better" method depends entirely on the specific characteristics desired in the final stone, as each process imparts unique, albeit subtle, traits.
The question is not which method is superior, but which one produces a diamond with the specific qualities you value most. CVD excels at creating large, high-clarity stones, while HPHT mimics the earth's natural process, resulting in diamonds with their own distinct growth characteristics.

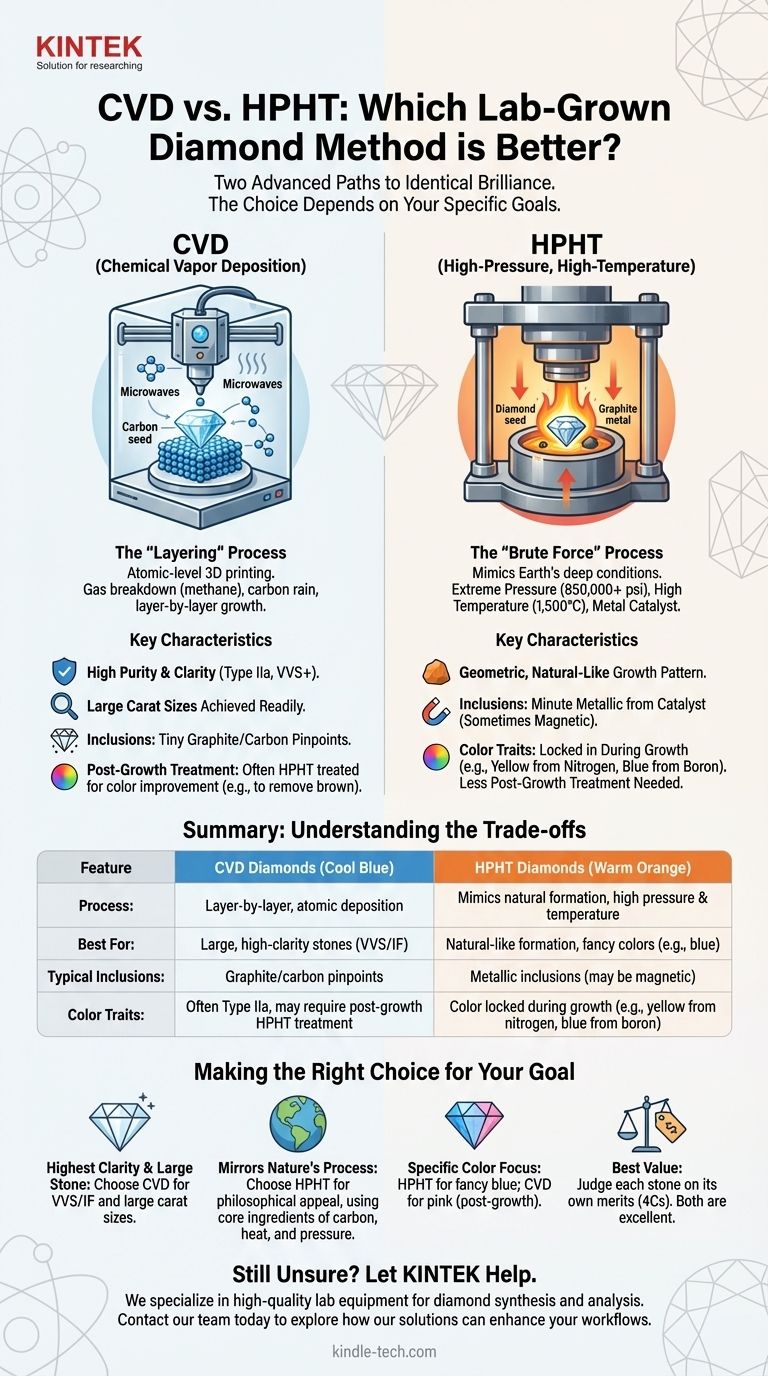
What is CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition)?
The CVD method is often compared to a sophisticated form of 3D printing, but at an atomic level. It is a process of addition and layering.
The "Layering" Process
In this method, a tiny diamond "seed" is placed inside a vacuum chamber. This chamber is then filled with carbon-rich gases (like methane) and heated.
Microwave energy is used to break down the gas molecules, causing pure carbon atoms to rain down and deposit onto the diamond seed, growing the diamond layer by painstaking layer.
Key Characteristics of CVD Diamonds
The primary advantage of CVD is the high degree of control it offers, as noted in process engineering. This translates into high-purity diamonds, often classified as Type IIa, a category that includes only 2% of the world's natural diamonds.
Because of this controlled, layered growth, CVD diamonds are known for their potential to achieve very high clarity grades (VVS or better) and can be grown into large carat sizes more readily than with HPHT.
What is HPHT (High-Pressure, High-Temperature)?
The HPHT method is fundamentally different, relying on immense force to replicate the conditions deep within the Earth where natural diamonds form.
The "Brute Force" Process
HPHT begins with a diamond seed and a source of pure, solid carbon (like graphite). This material is placed in a large mechanical press capable of generating extreme conditions.
The press subjects the carbon to immense pressures (over 850,000 pounds per square inch) and high temperatures (around 1,500°C). A molten metal catalyst is used to dissolve the carbon and help it crystallize onto the diamond seed, simulating nature's own crucible.
Key Characteristics of HPHT Diamonds
HPHT diamonds grow in a geometric, cuboctahedral pattern, much like natural diamonds. Because of the metal catalyst used, they can sometimes contain tiny metallic inclusions.
This process can also introduce trace elements. For example, nitrogen can impart a slight yellowish tint, while boron can create a desirable blue hue. HPHT is also a common treatment method used to permanently improve the color of both lab-grown and natural diamonds.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Distinctions
While both methods produce real diamonds, gemologists can identify their origin based on subtle differences in their growth structure and typical inclusions.
Clarity and Inclusions
CVD diamonds are less likely to have metallic inclusions. If inclusions are present, they are often tiny, dark pinpoints of graphite or other carbon-based imperfections.
HPHT diamonds are more prone to having minute metallic inclusions from the catalyst. These are invisible to the naked eye but can be detected by gemologists and may make the stone slightly magnetic.
Color and Post-Growth Treatment
CVD diamonds are often very pure (Type IIa), but the growth process can sometimes result in a brownish color. To correct this, many CVD diamonds undergo an HPHT treatment after they are grown to permanently remove the brown and improve their color.
HPHT diamonds are less likely to require post-growth treatment for color. Any color they have is typically locked in during their initial formation.
Process Legacy
The CVD process leverages advanced material science, focusing on controlled deposition. It benefits from decades of research in semiconductor and coatings technology, allowing for excellent uniformity and purity.
The HPHT process is a triumph of raw power and engineering, more closely replicating the geological forces of nature. It was the first successful method for creating gem-quality diamonds in a lab.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Ultimately, you are not buying the process; you are buying the final stone. Both methods produce beautiful, durable diamonds that are certified based on their individual quality (the 4Cs).
- If your primary focus is the highest clarity in a large stone: CVD is often the more direct path to producing large, internally flawless (IF) or very, very slightly included (VVS) diamonds.
- If your primary focus is a process that mirrors nature: HPHT uses the same core ingredients as the earth—carbon, heat, and pressure—which may hold a philosophical appeal for you.
- If your primary focus is a specific color: HPHT is a well-established method for producing coveted fancy blue diamonds (due to boron), while CVD is capable of producing pink diamonds through post-growth treatment.
- If your primary focus is simply the best value: Judge each diamond on its own merits. A certified diamond from either method can be an excellent choice, so prioritize the stone that meets your standards for cut, color, clarity, and carat.
Focus on the individual diamond's certification and beauty, as both CVD and HPHT are simply different roads leading to the same brilliant destination.
Summary Table:
| Feature | CVD Diamonds | HPHT Diamonds |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Chemical vapor deposition, layer-by-layer growth | High pressure & temperature, mimics natural formation |
| Best For | Large, high-clarity stones (VVS/IF) | Natural-like formation, fancy colors (e.g., blue) |
| Typical Inclusions | Graphite/carbon pinpoints | Metallic inclusions (may be magnetic) |
| Color Traits | Often Type IIa, may require post-growth HPHT treatment | Color locked during growth (e.g., yellow from nitrogen, blue from boron) |
Still unsure which diamond growth method is right for your application?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables tailored to laboratory needs. Whether you're researching CVD or HPHT processes, our experts can help you select the right tools for precise, reliable results.
Let’s discuss your project: Contact our team today to explore how our solutions can enhance your diamond synthesis and analysis workflows.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
People Also Ask
- What is the process of vacuum vapor deposition? Mastering CVD and PVD Thin-Film Coating
- What are the steps of the CVD process? A Guide to Precision Thin Film Deposition
- What color diamonds are CVD? Understanding the Process from Brown Tint to Colorless Beauty
- What are the different types of thin films? A Guide to Optical, Electrical, and Functional Coatings
- How does PECVD work? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition



















