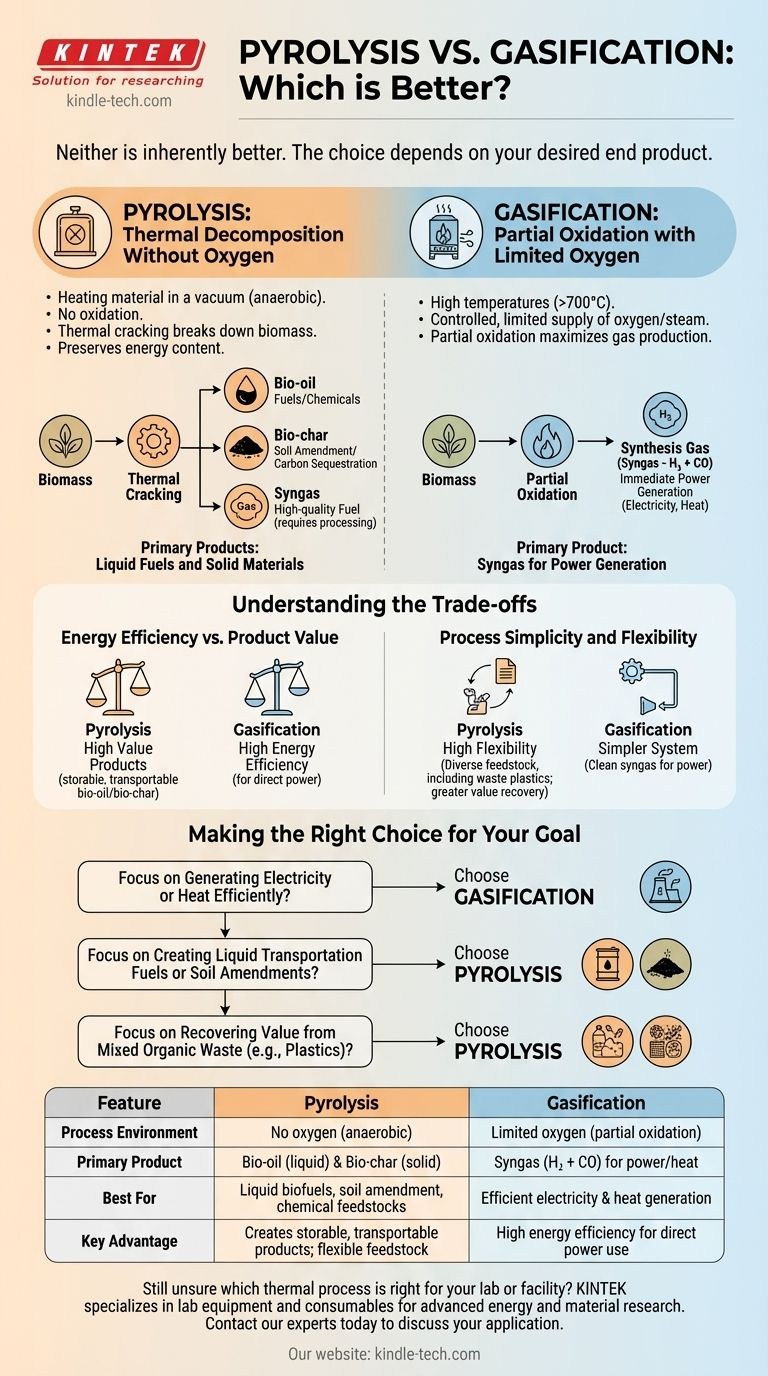
Neither process is inherently better. The superior choice depends entirely on your desired end product. Gasification is generally more efficient for generating electricity and heat, while pyrolysis excels at creating liquid biofuels and valuable solid materials like bio-char.
The decision between pyrolysis and gasification is not a matter of which technology is superior, but which is aligned with your goal. Gasification is optimized to convert biomass into a combustible gas for power, whereas pyrolysis is designed to deconstruct biomass into a spectrum of valuable liquid and solid products.

The Core Difference: The Role of Oxygen
The fundamental distinction between these two thermal processes is the environment in which they occur. This single factor dictates the end products and their applications.
Pyrolysis: Thermal Decomposition Without Oxygen
Think of pyrolysis as heating material in a vacuum. It is a thermochemical decomposition of organic material at elevated temperatures in the complete absence of oxygen.
This process breaks down biomass not through burning, but through thermal cracking. Because there is no oxidation, the energy content of the original material is largely preserved and distributed among its valuable outputs.
Gasification: Partial Oxidation with Limited Oxygen
Gasification involves exposing biomass to very high temperatures (often above 700°C) with a controlled, limited supply of oxygen or steam. It is not complete combustion.
This partial oxidation provides just enough energy to break down the organic material into its simplest gaseous components. The primary goal is to maximize the production of a specific gas mixture.
Comparing the Outputs and Their Uses
Your choice hinges on whether you need a gas for immediate energy use or a set of storable, transportable products.
Pyrolysis Products: Liquid Fuels and Solid Materials
Pyrolysis yields three primary products:
- Bio-oil: A liquid, also known as pyrolysis oil, that can be upgraded into transportation fuels or used as a feedstock for specialty chemicals.
- Bio-char: A stable, carbon-rich solid similar to charcoal. It is highly effective as a soil amendment to improve fertility and acts as a method of carbon sequestration.
- Syngas: A mixture of gases, including hydrocarbons, that requires further processing (like catalytic reforming) to be cleaned for use as a high-quality fuel.
Gasification Product: Syngas for Power Generation
Gasification is designed to produce one primary output with maximum efficiency:
- Synthesis Gas (Syngas): A mixture composed primarily of hydrogen (H₂) and carbon monoxide (CO). This gas is a clean, combustible fuel that can be used immediately to power engines or turbines for electricity and heat generation.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Each process comes with distinct advantages and complexities that must be weighed against your operational goals and available resources.
Energy Efficiency vs. Product Value
Gasification is widely considered more energy-efficient for the direct production of electricity and heat from biomass. The process is optimized to convert the maximum amount of the feedstock's chemical energy into a usable gas.
Pyrolysis, being an endothermic process, retains more of the feedstock's energy within the high-value products themselves. The value is not in immediate power generation but in the creation of storable, transportable goods like bio-oil and bio-char.
Process Simplicity and Flexibility
The syngas from gasification is relatively clean and ready for immediate use in power generation systems. This can simplify the overall system architecture if electricity is the only goal.
Pyrolysis is highly flexible and can process a wide range of organic materials, including waste plastics and rubber. While its outputs can be more complex to handle and may require refinement, this flexibility allows for greater material and value recovery from diverse waste streams.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your objective dictates the correct technology. Use these guidelines to make a clear decision.
- If your primary focus is generating electricity or heat efficiently: Choose gasification. Its direct conversion of biomass to clean-burning syngas is optimized for power production.
- If your primary focus is creating liquid transportation fuels or soil amendments: Choose pyrolysis. It is the only one of the two that produces bio-oil and bio-char as primary outputs.
- If your primary focus is recovering value from mixed organic waste (like plastics): Choose pyrolysis. Its ability to create valuable chemical feedstocks and materials from diverse inputs is a significant advantage.
Ultimately, the "better" process is the one that transforms your specific feedstock into the exact output your objective requires.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Pyrolysis | Gasification |
|---|---|---|
| Process Environment | No oxygen (anaerobic) | Limited oxygen (partial oxidation) |
| Primary Product | Bio-oil (liquid fuel) & Bio-char (solid) | Syngas (H₂ + CO) for power/heat |
| Best For | Liquid biofuels, soil amendment, chemical feedstocks | Efficient electricity & heat generation |
| Key Advantage | Creates storable, transportable products; flexible feedstock | High energy efficiency for direct power use |
Still unsure which thermal process is right for your lab or facility? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables for advanced energy and material research. Whether you're developing pyrolysis for bio-oil or optimizing gasification for syngas, our expertise and reliable equipment can help you achieve precise, repeatable results. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application and find the ideal solution for your laboratory needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
People Also Ask
- What are the types of pyrolysis reactors used in industry? Choose the Right Technology for Your Product
- What equipment is used in pyrolysis? Choosing the Right Reactor for Your Feedstock and Products
- What is the purpose of a calciner? Boost Efficiency in High-Temperature Processing
- What are the industrial applications of pyrolysis? Transform Waste into Energy and Valuable Products
- What are the zones in rotary kiln in cement production? Master the Core Process for High-Quality Clinker



















