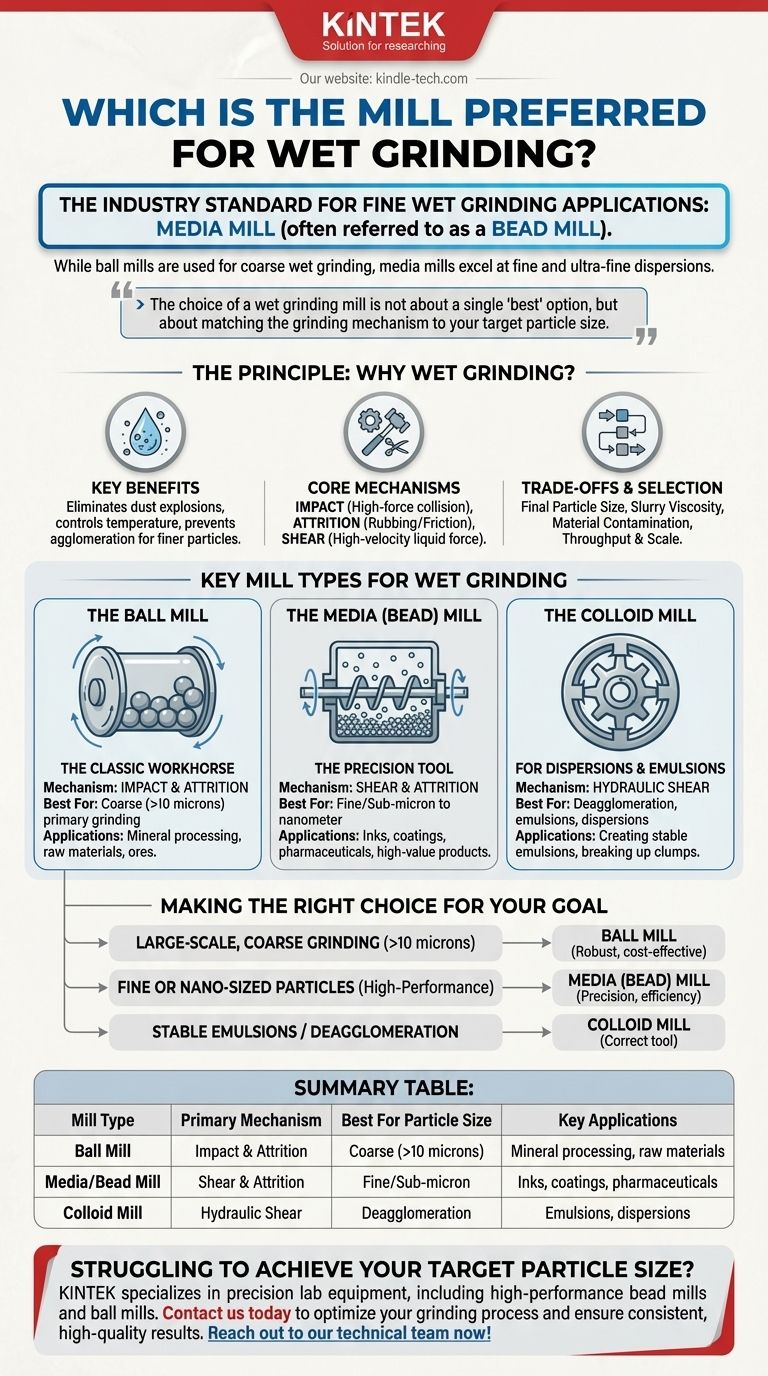
For fine wet grinding applications, the industry standard is the media mill, often specifically referred to as a bead mill. While traditional ball mills are also used for wet grinding, they are typically preferred for coarser particle sizes, whereas media mills excel at producing the fine and ultra-fine dispersions required for high-performance products like inks, coatings, and pharmaceuticals.
The choice of a wet grinding mill is not about a single "best" option, but about matching the grinding mechanism to your target particle size. The fundamental trade-off is between the large-scale, coarse grinding of a ball mill and the precise, fine grinding of a media mill.

The Principle: Why Wet Grinding?
Before selecting a mill, it's essential to understand the advantages of the wet grinding process itself. This context clarifies why certain mill designs are more effective than others.
Key Benefits of the Wet Process
Wet grinding involves milling solid particles suspended in a liquid medium. This method is often preferred over dry grinding for several critical reasons.
It eliminates the risk of dust explosions, controls temperature more effectively, and prevents material agglomeration, allowing for the production of much finer particles.
The Core Grinding Mechanisms
All mills reduce particle size through a combination of three forces, but the dominant force defines the mill's primary function.
- Impact: This is a high-force collision, like a hammer striking a rock. It's effective for breaking down large, brittle particles.
- Attrition: This is a rubbing or friction-based action, where particles are ground down by being scraped against each other and the grinding media.
- Shear: This force is created by the liquid slurry itself as it moves at high velocity, tearing particles apart. It is critical for dispersions and deagglomeration.
Key Mill Types for Wet Grinding
The two primary categories of mills used for wet grinding are tumbling mills (like ball mills) and agitated media mills (bead mills). They operate on different principles and are suited for different outcomes.
The Ball Mill: The Classic Workhorse
A ball mill is a large rotating cylinder partially filled with grinding media, typically ceramic or steel balls. As the cylinder tumbles, the media cascades down, crushing the material.
The dominant forces are impact and attrition. This makes ball mills excellent for primary, coarse grinding of hard materials like ores and minerals, often down to a range of 10-50 microns.
The Media Mill (Bead Mill): The Precision Tool
A media mill is a more advanced design where a shaft with agitator discs or pins spins at high speed within a stationary chamber filled with small grinding media (beads).
This high-energy agitation creates intense shear and attrition forces. By using very small beads (often less than 1 mm), these mills can efficiently grind particles down to the sub-micron or even nanometer scale. They are the go-to choice for high-value products.
The Colloid Mill: For Dispersions and Emulsions
It is important to distinguish colloid mills from the previous types. A colloid mill does not use grinding media.
Instead, it operates on a rotor-stator principle, subjecting the fluid to intense hydraulic shear. It is not designed for primary particle size reduction but is exceptional at deagglomerating clumps and creating stable emulsions and dispersions.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Selection Criteria
Choosing the right mill requires a clear understanding of your specific process variables and final product goals. An incorrect choice leads to inefficiency, poor product quality, and increased operational costs.
Final Particle Size Requirement
This is the most important factor. If your target is in the micron range, a ball mill may be sufficient. For sub-micron or nanoparticle targets, a bead mill is non-negotiable.
Slurry Viscosity
The viscosity of your liquid-solid mixture significantly impacts mill efficiency. High-viscosity slurries can "cushion" the impact in a ball mill, reducing its effectiveness. High-energy bead mills are generally better equipped to handle more viscous materials.
Material Contamination
Grinding media inevitably wears down, which can introduce contamination into your product. If product purity is critical (e.g., in pharmaceuticals or electronics), using high-purity ceramic media (like zirconia or yttria) in a bead mill is the standard solution.
Throughput and Scale
Ball mills are built for durability and massive throughput, making them ideal for large-scale, continuous industrial processes like mineral processing. Media mills can also operate continuously but are often used for smaller, higher-value batches where precision is paramount.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your decision should be driven by the specific requirements of your final product. There is no single mill that is best for every task.
- If your primary focus is large-scale, coarse grinding (>10 microns) of raw materials: A ball mill offers the most robust and cost-effective solution.
- If your primary focus is achieving fine or nano-sized particles for high-performance products: A media (bead) mill is the necessary instrument for precision and efficiency.
- If your primary focus is creating stable emulsions or breaking up agglomerates without significant size reduction: A colloid mill is the correct tool for the job.
Ultimately, selecting the correct mill is an investment in the quality and consistency of your final product.
Summary Table:
| Mill Type | Primary Mechanism | Best For Particle Size | Key Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ball Mill | Impact & Attrition | Coarse (>10 microns) | Mineral processing, raw materials |
| Media/Bead Mill | Shear & Attrition | Fine/Sub-micron | Inks, coatings, pharmaceuticals |
| Colloid Mill | Hydraulic Shear | Deagglomeration | Emulsions, dispersions |
Struggling to achieve your target particle size? The right wet grinding mill is critical for your product's performance and quality. KINTEK specializes in precision lab equipment, including high-performance bead mills for fine dispersions and ball mills for coarse grinding. Our experts will help you select the perfect mill for your application in inks, coatings, or pharmaceuticals. Contact us today to optimize your grinding process and ensure consistent, high-quality results. Reach out to our technical team now!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Single Horizontal Jar Mill
- Laboratory Horizontal Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine
- Laboratory Ten-Body Horizontal Jar Mill for Lab Use
- Laboratory Planetary Ball Mill Rotating Ball Milling Machine
- High Energy Vibratory Laboratory Ball Mill Double Tank Type
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of polyurethane ball mill jars for silicon nitride? Ensure Purity & Prevent Metal Contamination
- Why are zirconia (ZrO2) milling jars recommended for sulfide electrolytes? Ensure Purity in Li6PS5Cl Synthesis
- Why are excellent sealing and corrosion resistance required for WC-10Co ball milling? Ensure High-Purity Mixing Results
- How do stainless steel grinding jars and balls contribute to mechanical alloying? Optimize HEA Powder Synthesis
- Why is a ball mill jar lined with Y-ZrO2 required for Na3PS4 synthesis? Ensuring Purity in Sulfide Electrolytes



















