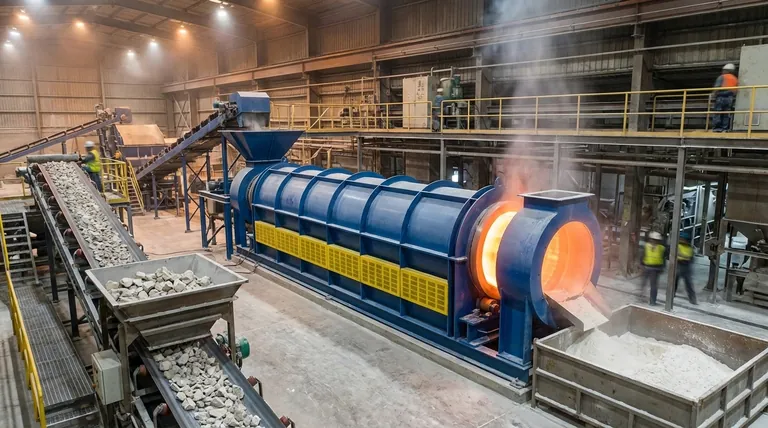
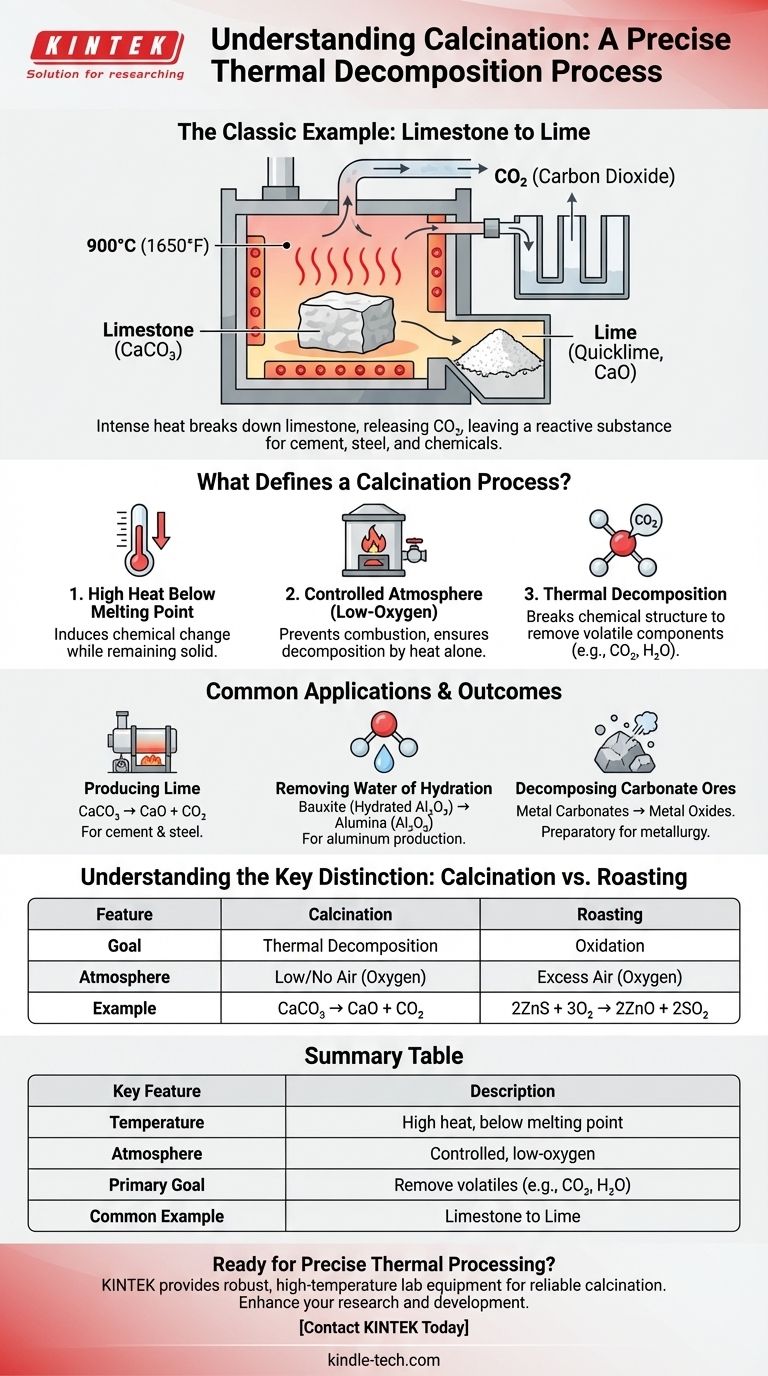
The classic example of calcination is the heating of limestone (calcium carbonate) to produce lime (calcium oxide). In this process, the intense heat breaks the limestone down, causing it to release carbon dioxide gas and leaving behind a powdery, more reactive substance. This is a foundational process used for centuries in the production of cement and other industrial materials.
Calcination is not merely heating; it is a precise thermal decomposition process. It uses high temperatures below the material's melting point in a controlled, low-oxygen atmosphere to remove volatile components like carbon dioxide or water.

What Defines a Calcination Process?
To truly identify calcination, you must look beyond the simple application of heat. Three specific conditions define the process and separate it from other heat treatments like roasting or drying.
The Role of High Heat
Calcination involves heating a solid material to a very high temperature. Critically, this temperature is maintained below the material's melting point.
The goal is to induce a chemical change or decomposition while the material remains in its solid state, often making it brittle or porous.
A Controlled Atmosphere
The process is conducted in the absence or a very limited supply of air (oxygen). This is a key differentiator from other thermal processes.
By restricting oxygen, calcination prevents combustion or significant oxidation. The primary goal is decomposition driven by heat alone, not by reaction with the air.
The Goal: Thermal Decomposition
The fundamental purpose of calcination is to break down the chemical structure of a substance.
This decomposition results in the removal of a volatile component from the solid. The part that is driven off is typically a gas, such as carbon dioxide (CO2) from carbonates or water vapor (H2O) from hydrated minerals.
Common Applications and Outcomes
While producing lime is the textbook case, calcination is used across various industries to transform materials.
Producing Lime from Limestone
This is the most common example. Limestone (CaCO₃) is heated to temperatures around 900°C (1650°F). It decomposes into quicklime (CaO) and releases carbon dioxide gas.
This lime is a crucial ingredient in manufacturing cement, steel, and certain chemicals.
Removing Water of Hydration
Calcination is widely used to remove chemically bound water from hydrated minerals.
For instance, bauxite ore, a hydrated form of aluminum oxide, is calcined to drive off water and produce pure alumina (Al₂O₃), the primary raw material for producing aluminum metal.
Decomposing Carbonate Ores
Similar to limestone, other metal carbonate ores are calcined to convert them into their oxide forms.
This is often a preparatory step in metallurgy, as metal oxides are generally easier to reduce to pure metal than their original carbonate forms.
Understanding the Key Distinctions
A common point of confusion is differentiating calcination from a similar process called roasting. The distinction is critical and lies entirely in the goal and the atmosphere used.
Calcination vs. Roasting
Calcination aims for thermal decomposition in the absence of air. Think of it as "baking" a mineral to break it down. An example is CaCO₃ → CaO + CO₂.
Roasting, in contrast, is heating a mineral in an excess of air (oxygen). The goal is oxidation, often to convert sulfide ores into oxides. An example is 2ZnS + 3O₂ → 2ZnO + 2SO₂.
Why Control the Atmosphere?
Limiting air during calcination is essential to prevent unwanted side reactions. If oxygen were present when heating limestone, for example, it wouldn't fundamentally change the primary reaction, but for other materials, it could lead to undesirable oxidation.
Controlling the atmosphere ensures that thermal decomposition is the dominant and intended transformation.
How to Identify a Calcination Process
Based on these principles, you can easily identify if a process is an example of calcination.
- If your focus is decomposing a carbonate ore: Heating limestone, dolomite, or other carbonates to drive off CO₂ and form an oxide is a definitive example of calcination.
- If your focus is removing chemically bound water: Heating a hydrated mineral like bauxite or gypsum to produce its anhydrous (water-free) form is another primary application of calcination.
- If the key distinction is the atmosphere: A process involving heating a solid below its melting point in little to no air to cause a chemical breakdown is calcination.
Recognizing these conditions allows you to distinguish calcination as a fundamental tool of chemical and materials engineering.
Summary Table:
| Key Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Temperature | High heat, but below the material's melting point. |
| Atmosphere | Controlled, low-oxygen or no-oxygen environment. |
| Primary Goal | Thermal decomposition to remove volatile components (e.g., CO₂, H₂O). |
| Common Example | Heating limestone (CaCO₃) to produce lime (CaO). |
Ready to Achieve Precise Thermal Processing in Your Lab?
Calcination is a fundamental process for transforming materials, from decomposing carbonates to dehydrating minerals. KINTEK specializes in providing the robust, high-temperature lab equipment—like advanced furnaces with precise atmosphere control—that you need to execute these processes reliably and safely.
Whether you are in materials science, metallurgy, or chemical engineering, our solutions are designed to meet the rigorous demands of your research and development. Let us help you enhance your lab's capabilities.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific thermal processing needs and discover the right equipment for your application.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between calcining and roasting? A Guide to High-Temperature Processing
- What equipment is used in pyrolysis? Choosing the Right Reactor for Your Feedstock and Products
- What are the types of pyrolysis reactors used in industry? Choose the Right Technology for Your Product
- What are the products of pyrolysis of wood? A Guide to Biochar, Bio-oil, and Syngas Yields
- What are the industrial applications of pyrolysis? Transform Waste into Energy and Valuable Products



















