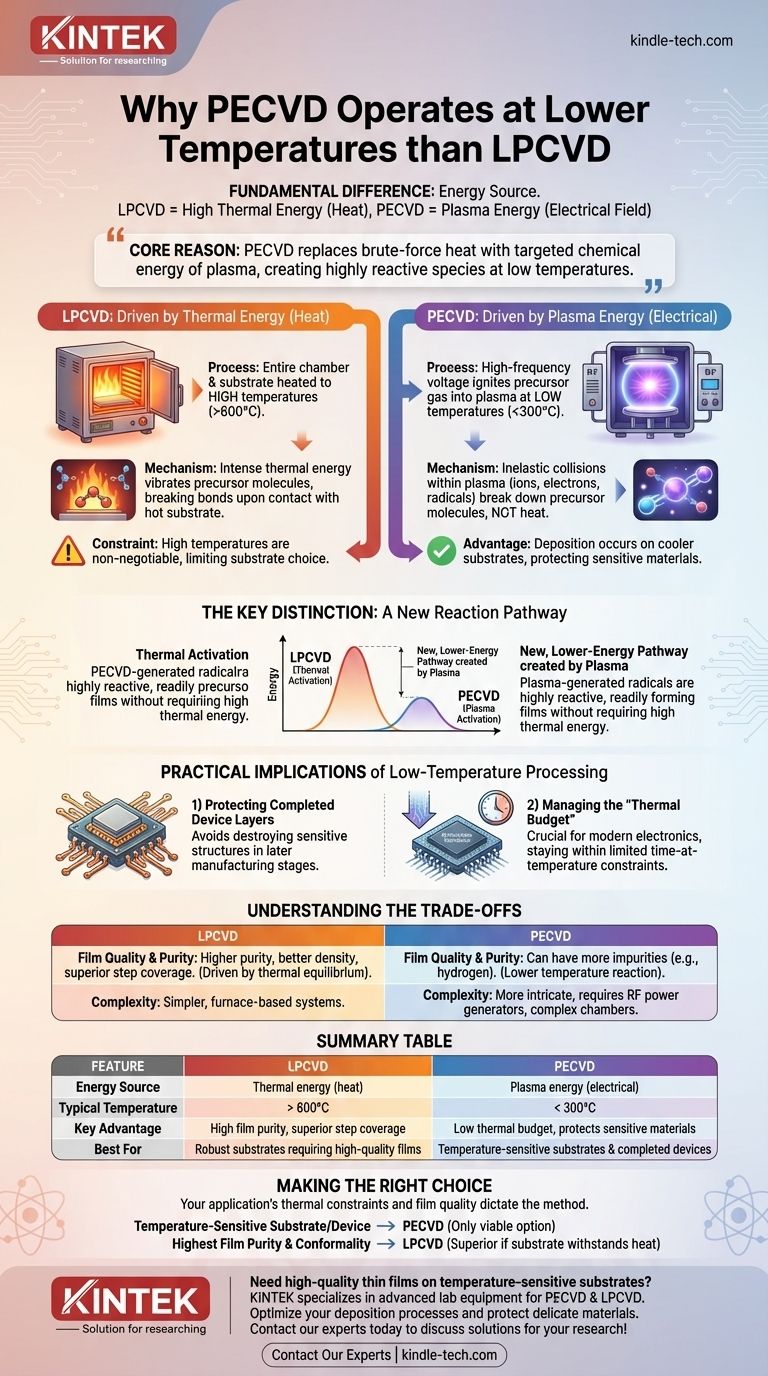
The fundamental difference is the energy source used to drive the chemical reaction. While traditional Low-Pressure Chemical Vapor Deposition (LPCVD) relies purely on high thermal energy (heat), Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD) uses an electrical field to generate a plasma, which provides the necessary energy to initiate the reaction at much lower substrate temperatures.
The core reason PECVD operates at lower temperatures is that it replaces the brute-force energy of heat with the targeted chemical energy of a plasma. This plasma creates highly reactive gas molecules without needing to heat the entire system, allowing deposition to occur on temperature-sensitive materials.
The Role of Energy in Deposition
To deposit a thin film from a gas, the precursor molecules must be given enough energy to break their chemical bonds and react on the substrate surface. This is known as the activation energy. LPCVD and PECVD simply provide this energy in different ways.
How Thermal Energy Drives LPCVD
In an LPCVD process, the entire chamber, including the substrate, is heated to high temperatures, often well above 600°C.
This intense thermal energy causes the precursor gas molecules to vibrate and move rapidly, eventually providing enough energy to break them apart upon contact with the hot substrate.
The reaction is driven entirely by heat, which is why high temperatures are non-negotiable for this method.
How Plasma Energy Drives PECVD
PECVD uses a high-frequency voltage to ignite the precursor gas, transforming it into a plasma.
A plasma is a state of matter containing ionized gas, free electrons, and highly reactive neutral species called radicals.
It is the inelastic collisions within this plasma that break down the precursor gas molecules—not high heat. These reactive species are then free to deposit onto the much cooler substrate, which can be kept below 300°C.
The Key Distinction: A New Reaction Pathway
LPCVD relies on thermal activation to overcome the energy barrier for a reaction to occur.
PECVD uses the plasma to create an entirely new, lower-energy reaction pathway. The plasma-generated radicals are so reactive that they readily form a film on the substrate without requiring high thermal energy.
Practical Implications of Low-Temperature Processing
The ability to deposit high-quality films without high heat is not just a minor advantage; it is a critical enabler for modern electronics manufacturing.
Protecting Completed Device Layers
Modern integrated circuits are built in many layers. In the later stages of manufacturing, metal interconnects and other sensitive structures are already present.
Exposing these completed layers to the high temperatures of LPCVD would destroy them. PECVD allows for the deposition of insulating dielectrics between these metal layers without causing damage.
Managing the "Thermal Budget"
As device geometries shrink, the amount of time a component can spend at a high temperature—its "thermal budget"—is severely limited.
PECVD's low-temperature nature is crucial for staying within this budget, preserving the material properties and electrical characteristics of the nanoscale components.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While its low-temperature operation is a major advantage, PECVD is not a universal replacement for LPCVD. The choice involves clear trade-offs.
Film Quality and Purity
Because the reaction occurs at lower temperatures, PECVD films can sometimes have more impurities, such as incorporated hydrogen from the precursor gases.
LPCVD, driven by thermal equilibrium at high temperatures, often produces films with higher purity, better density, and superior step coverage (conformality).
Process and Equipment Complexity
PECVD reactors require RF power generators and complex chamber designs to generate and contain the plasma.
This makes the equipment more intricate and potentially more expensive to maintain than the simpler, furnace-based systems used for LPCVD.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your application's thermal constraints and film quality requirements will dictate the best method.
- If your primary focus is depositing on a temperature-sensitive substrate or a completed device: PECVD is the only viable option due to its low thermal impact.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest possible film purity and conformality on a robust substrate: LPCVD is often the superior choice, provided the material can withstand the heat.
Ultimately, the decision rests on choosing the right energy source to achieve your specific material and integration goals.
Summary Table:
| Feature | LPCVD | PECVD |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Source | Thermal energy (heat) | Plasma energy (electrical) |
| Typical Temperature | > 600°C | < 300°C |
| Key Advantage | High film purity, superior step coverage | Low thermal budget, protects sensitive materials |
| Best For | Robust substrates requiring high-quality films | Temperature-sensitive substrates and completed devices |
Need to deposit high-quality thin films on temperature-sensitive substrates? KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables for cutting-edge semiconductor and materials research. Our expertise in PECVD and LPCVD technologies can help you optimize your thin film deposition processes while protecting your delicate materials. Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your research and development workflow!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
People Also Ask
- How do PECVD systems improve DLC coatings on implants? Superior Durability and Biocompatibility Explained
- Can plasma enhanced CVD deposit metals? Why PECVD is rarely used for metal deposition
- What are different types of thin films? A Guide to Function, Material, and Deposition Methods
- What is the difference between plasma CVD and thermal CVD? Choose the Right Method for Your Substrate
- What is the process of PECVD in semiconductor? Enabling Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition



















