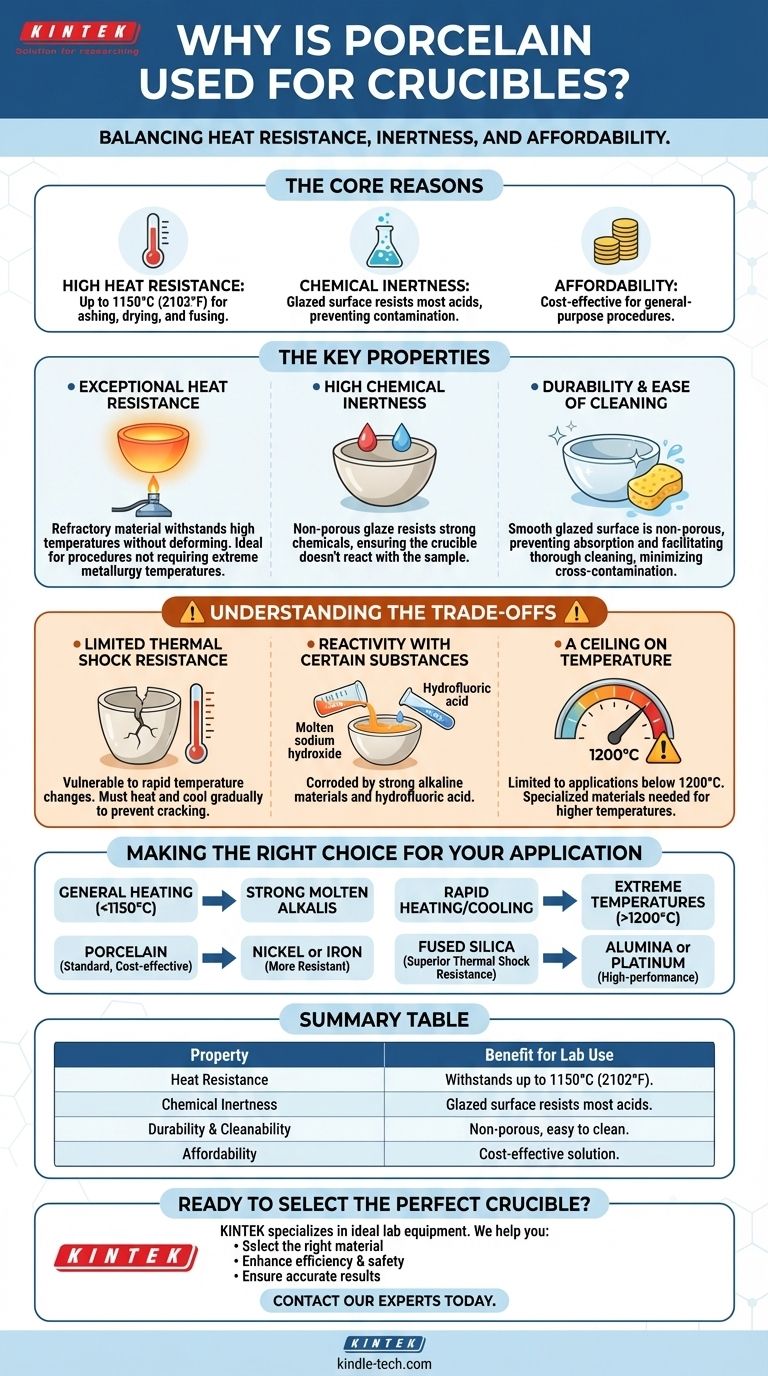
In short, porcelain is used for crucibles because it offers an excellent balance of high heat resistance, chemical inertness, and affordability. This combination makes it a reliable and cost-effective workhorse for a wide range of common laboratory heating procedures where extreme conditions are not a factor.
The core reason for porcelain's prevalence is not that it's the best material in any single category, but that it provides the most practical combination of thermal, chemical, and economic properties for general-purpose scientific work.

The Key Properties of Porcelain for Crucible Use
To understand why porcelain is so common, we need to examine its specific material characteristics. Each property solves a distinct problem encountered during high-temperature lab work.
Exceptional Heat Resistance
Porcelain is a refractory material, meaning it can withstand high temperatures without deforming or melting. A typical porcelain crucible can be safely heated to temperatures up to 1150°C (2102°F).
This allows for common procedures like ashing organic compounds, drying precipitates, or fusing mixtures that don't require the extreme temperatures needed for metallurgy.
High Chemical Inertness
The surfaces of most porcelain crucibles are coated with a hard, non-porous glaze. This glaze is highly resistant to the action of most chemicals, including strong acids.
This inertness is critical for ensuring that the crucible itself does not react with the sample being heated, which would contaminate the results of the experiment.
Durability and Ease of Cleaning
The glazed surface is not only chemically resistant but also smooth and non-porous. This prevents chemicals from being absorbed into the crucible body.
As a result, porcelain crucibles are easy to clean thoroughly, minimizing cross-contamination between different experiments and extending the usable life of the equipment.
Understanding the Trade-offs: When Porcelain Isn't the Right Choice
While versatile, porcelain is not invincible. Understanding its limitations is just as important as knowing its strengths. Choosing the wrong crucible can ruin an experiment or even create a safety hazard.
Limited Thermal Shock Resistance
This is porcelain's most significant weakness. Rapid changes in temperature, such as placing a hot crucible on a cold surface, can easily cause it to crack or shatter.
Heating and cooling must be done gradually to prevent this. For applications requiring rapid temperature cycling, a material like fused silica is a superior choice.
Reactivity with Certain Substances
While resistant to most chemicals, porcelain can be attacked by a few specific substances. Strong alkaline materials, like molten sodium hydroxide, will corrode the glaze and the underlying ceramic.
Hydrofluoric acid is another chemical that will damage porcelain, as it attacks the silica components within the ceramic matrix.
A Ceiling on Temperature
Porcelain is excellent for many applications, but it has a clear temperature limit. For experiments requiring temperatures above 1200°C, more specialized and expensive materials are necessary.
Materials like alumina, zirconia, or even platinum are used for very high-temperature applications where porcelain would fail.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct crucible material is fundamental to achieving accurate and reliable results. Your decision should be based directly on the requirements of your specific procedure.
- If your primary focus is general heating of chemical compounds below 1150°C: Porcelain is the standard, most cost-effective, and reliable choice.
- If your primary focus is working with strong molten alkalis (bases): You must use a crucible made of a more resistant material, such as nickel or iron.
- If your primary focus involves extremely rapid heating and cooling cycles: Choose a fused silica crucible, which has superior thermal shock resistance.
- If your primary focus is reaching temperatures well above 1200°C: You will need to invest in a high-performance ceramic crucible like alumina or a platinum crucible.
Understanding your material's limits is the first step toward successful and safe experimentation.
Summary Table:
| Property | Benefit for Lab Use |
|---|---|
| Heat Resistance | Withstands temperatures up to 1150°C (2102°F) for ashing, drying, and fusing. |
| Chemical Inertness | Glazed surface resists most acids, preventing sample contamination. |
| Durability & Cleanability | Non-porous, glazed surface is easy to clean and minimizes cross-contamination. |
| Affordability | Cost-effective solution for general-purpose heating applications. |
Ready to select the perfect crucible for your lab's needs?
Porcelain crucibles are the reliable, cost-effective workhorses for countless applications, but choosing the right material is critical for your results. The experts at KINTEK specialize in providing the ideal lab equipment, including a full range of crucibles for every requirement.
We help you:
- Select the right crucible material (porcelain, alumina, quartz, platinum, and more) based on your specific temperature and chemical exposure needs.
- Enhance lab efficiency and safety with equipment tailored to your procedures.
- Ensure accurate, contamination-free results with high-quality, durable consumables.
Don't let the wrong crucible compromise your work. Let KINTEK, your trusted partner in laboratory equipment and consumables, provide the solution you need.
Contact our experts today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Engineering Advanced Fine Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible for Laboratory Muffle Furnace
- Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible Semicircle Boat with Lid for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Arc-Shaped Alumina Ceramic Crucible High Temperature Resistant for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Custom Machined and Molded PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer with PTFE Crucible and Lid
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Al2O3 Crucible With Lid Cylindrical Laboratory Crucible
People Also Ask
- What temperature can alumina crucible withstand? A Guide to High-Temperature Stability and Safety
- What is the temperature range of alumina crucibles? Key Factors for Safe High-Temp Use
- What is a crucible material for a furnace? A Guide to Choosing the Right High-Temperature Container
- What is a crucible porcelain? Choosing the Right High-Temperature Lab Vessel
- What is the function of an alumina crucible in NaSICON synthesis? Ensure Purity in High-Temperature Reactions



















