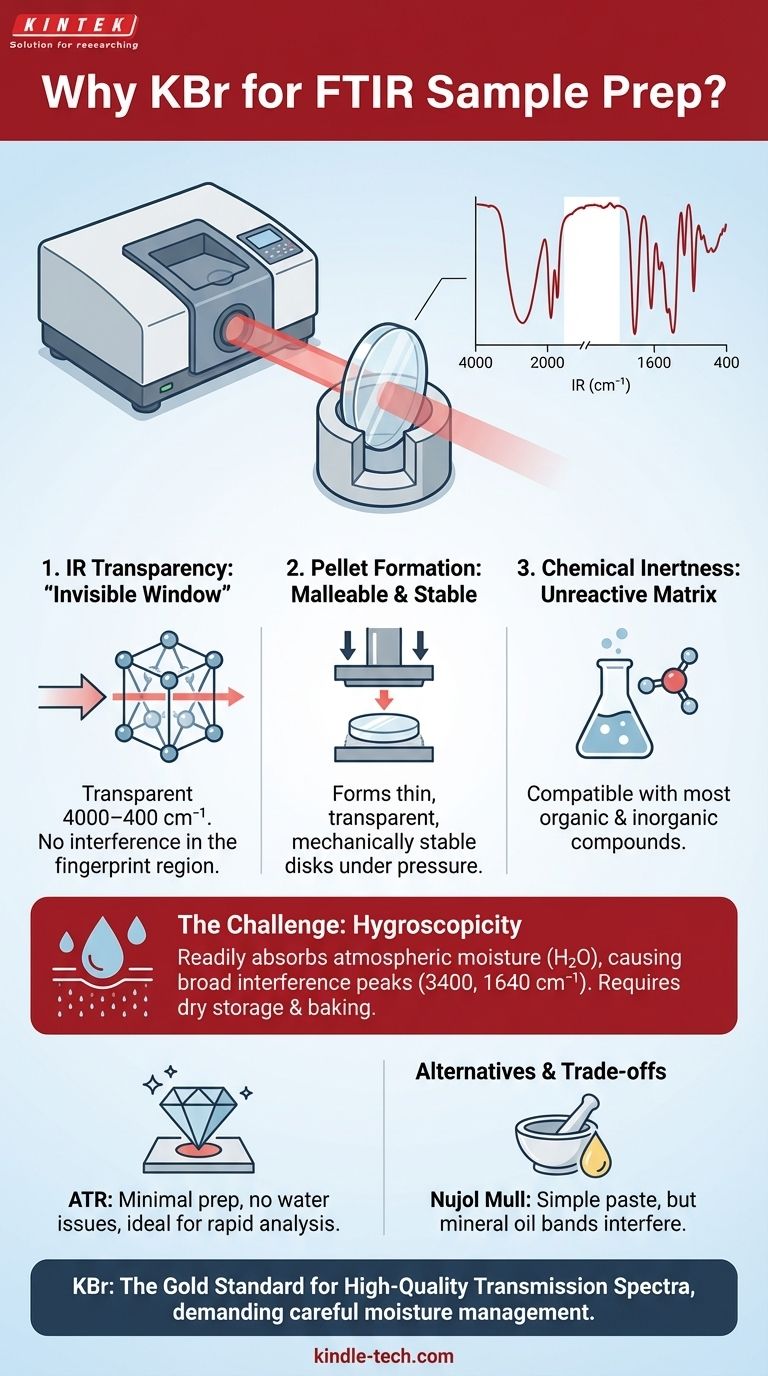
In Fourier-Transform Infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy, potassium bromide (KBr) is the most common material used to prepare solid samples because it is transparent to infrared light across the most useful frequency range (4000–400 cm⁻¹). Furthermore, its crystalline structure allows it to be pressed under high pressure into a thin, glass-like, transparent disk that immobilizes the sample, allowing the IR beam to pass through it for analysis.
The choice of a sample matrix in FTIR is not arbitrary; it's a search for a material that acts as an invisible window for the infrared beam. KBr is the standard because it uniquely combines near-perfect IR transparency with the physical property of forming a stable, solid disk, though its strong affinity for water presents a critical and persistent challenge.

The Fundamental Requirements of an FTIR Matrix
To understand why KBr is used, we must first establish what makes any material suitable for holding a sample for IR analysis. The primary goal is to measure the sample, not the material holding it.
Infrared Transparency: The "Invisible Window"
FTIR spectroscopy works by detecting the vibrations of molecular bonds, such as C-H, O-H, and C=O. These bonds absorb infrared light at specific frequencies, creating a unique spectral fingerprint.
The matrix material—the substance mixed with the sample—must not have any of its own vibrations in this analytical region. KBr is an ionic salt (K⁺Br⁻). Its ionic lattice vibrations occur at very low frequencies, well below the 400 cm⁻¹ cutoff of most mid-IR spectrometers. This makes it effectively invisible to the IR beam in the region of interest.
Physical Malleability Under Pressure
For solid samples, the goal is to create a thin, uniform medium for the IR beam to pass through, minimizing scattering of the light.
KBr has a soft, plastic-like quality under extreme pressure. When finely ground KBr is pressed in a die at several tons of force, its crystals fuse together and flow, forming a solid, semi-transparent pellet that is mechanically stable.
Chemical Inertness
The matrix material should not react with the sample. KBr is a stable salt that is generally unreactive with the vast majority of organic and inorganic compounds analyzed via FTIR, ensuring the spectrum collected is purely that of the analyte.
Why Potassium Bromide (KBr) Excels
KBr meets all the fundamental requirements for a solid transmission matrix, making it the historical and educational standard.
A Wide and Unobstructed Spectral Window
KBr offers a clear, unobstructed view from 4000 cm⁻¹ down to 400 cm⁻¹. This covers the entire "fingerprint region" and functional group region that are essential for identifying unknown compounds and characterizing materials.
Formation of a Homogeneous Pellet
When the sample is ground intimately with KBr powder, the sample particles become dispersed within the KBr matrix. Pressing this mixture creates a solid solution or a highly uniform dispersion.
This homogeneity is critical for producing a high-quality spectrum with a flat baseline and repeatable, quantifiable absorption peaks.
Cost and Availability
Potassium bromide is a common chemical that is relatively inexpensive and readily available in the high purity required for spectroscopic use.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Common Pitfalls
While KBr is the standard, it is not without significant challenges. A skilled analyst must know how to manage its primary weakness.
The Critical Issue: Hygroscopicity
KBr is hygroscopic, meaning it readily absorbs moisture from the atmosphere. Water (H₂O) is a very strong IR absorber, producing two characteristic peaks: a very broad absorption around 3400 cm⁻¹ (O-H stretching) and a sharper band around 1640 cm⁻¹ (H-O-H bending).
If your KBr is "wet," these large water peaks can obscure important sample peaks, rendering your spectrum useless. For this reason, spectroscopy-grade KBr must be stored in a desiccator and often baked in an oven before use to drive off any absorbed water.
The Importance of Particle Size
If the sample particles are too large relative to the wavelength of the IR light, it can cause significant light scattering. This phenomenon, known as the Christiansen effect, results in a distorted, sloping baseline that makes the spectrum difficult to interpret.
To prevent this, the sample must be ground to a fine powder (particle size < 2 µm) using an agate mortar and pestle before being mixed with the KBr.
Alternative Solid Matrices
Other alkali halides like potassium chloride (KCl) and cesium iodide (CsI) can also be used. CsI is more expensive but extends the usable spectral range to a lower frequency (~200 cm⁻¹), which can be useful for studying certain inorganic compounds.
Choosing the Right Sample Preparation Method
The KBr pellet method is a classic transmission technique, but it is not the only option. Modern labs often rely on easier, faster methods.
Attenuated Total Reflectance (ATR)
ATR is now the most common FTIR technique. It involves pressing a sample directly against a high-refractive-index crystal (often diamond or zinc selenide). The IR beam reflects internally within the crystal, but a small portion of its energy (an "evanescent wave") penetrates a few micrometers into the sample.
ATR requires virtually no sample preparation and completely avoids the issues with KBr and water, making it ideal for rapid analysis.
Nujol Mull
In this technique, the solid sample is ground with a few drops of mineral oil (Nujol) to create a thick paste or "mull." A thin film of this paste is then smeared between two salt plates (often NaCl or KBr).
The downside is that the mineral oil itself has C-H absorption bands that will always be present in the spectrum, potentially obscuring sample information in those regions.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your choice of sample preparation should be driven by your analytical needs, the nature of your sample, and the equipment available.
- If your primary focus is obtaining the highest quality reference spectra for a pure, solid compound: A carefully prepared KBr pellet remains the gold standard for transmission spectroscopy.
- If your primary focus is rapid analysis, quality control, or analyzing difficult samples (e.g., polymers, pastes, liquids): Attenuated Total Reflectance (ATR) is the superior, modern method that requires minimal sample preparation.
- If your sample is sensitive to pressure or you lack a pellet press: A Nujol mull provides a classic, low-cost alternative to the KBr pellet, provided you can accept the inherent spectral interference from the oil.
Understanding these principles of sample preparation is the key to generating clean, reliable, and interpretable FTIR spectra.
Summary Table:
| Property | Why It Matters for FTIR |
|---|---|
| IR Transparency | Transparent from 4000-400 cm⁻¹; provides clear spectral window. |
| Pellet Formation | Presses into stable, transparent disks under high pressure. |
| Chemical Inertness | Generally unreactive with most organic/inorganic samples. |
| Hygroscopicity | Absorbs water, which can cause interfering peaks in the spectrum. |
Ready to achieve superior FTIR results? KINTEK specializes in high-purity lab equipment and consumables, including spectroscopy-grade KBr and reliable pellet presses. Our products are designed to help you prepare perfect samples, minimizing issues like moisture interference and ensuring accurate, reproducible spectra. Let our experts support your laboratory's success—contact us today to find the right solution for your FTIR needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Manual Hydraulic Pellet Press for Lab Use
- Metallographic Specimen Mounting Machine for Laboratory Materials and Analysis
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Hollow Cleaning Basket and Rack Carrier
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Centrifuge Tubes
- Infrared Heating Quantitative Flat Plate Press Mold
People Also Ask
- What is the principle of wiped film molecular still? Preserve and Purify Heat-Sensitive Compounds
- Can sintered parts be machined? How to Overcome the Challenges of Porosity
- What is the difference between RF sputtering and DC sputtering? Choose the Right Method for Your Material
- What are the basic characteristics requirements in heat treatment? Master Temperature, Time, and Cooling
- What is surface sputtering? A Guide to Precision Thin Film Deposition & Etching
- What does a heat treatment do? Unlock Your Material's Full Potential
- How does a water bath work? Master Precise and Gentle Heating for Your Lab
- What can you test with a diamond tester? Accurately Identify Genuine Diamonds from Fakes



















