In short, KBr pellets are used because potassium bromide (KBr) is transparent to the infrared light used in FTIR spectroscopy. By grinding a small amount of a solid sample with KBr powder and pressing it into a thin disc, you create a uniform medium that holds the sample in the instrument's light path without interfering with the measurement. This allows for clear, reliable analysis of solids that would otherwise be difficult to measure.
The core principle is to make the sample "invisible" to the instrument in a physical sense, while keeping it "visible" in a chemical one. KBr acts as a perfect, non-interfering window, allowing the spectrometer to measure only the infrared absorption of the sample itself.

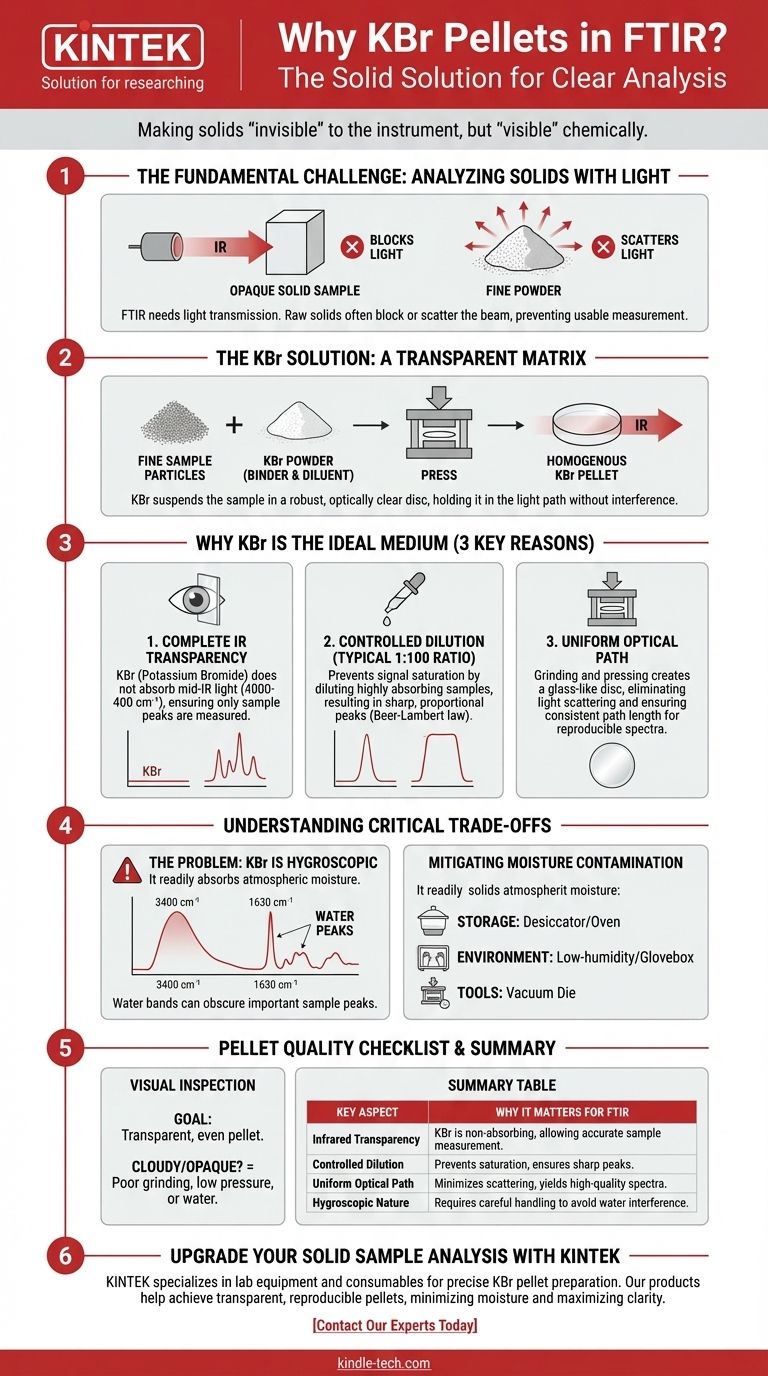
The Fundamental Challenge: Analyzing Solids with Light
FTIR (Fourier-Transform Infrared) spectroscopy is a transmission technique. It works by passing a beam of infrared light through a substance and measuring which wavelengths of light are absorbed. This absorption pattern provides a unique chemical fingerprint of the material.
Why Solids are Difficult
Analyzing a raw solid sample directly is often impossible. A chunk of material is typically opaque, meaning it blocks the light beam entirely. A fine powder scatters the light in all directions instead of letting it pass through in a straight line. Both scenarios prevent a usable measurement.
The KBr Solution
The KBr pellet method solves this by suspending the fine particles of the sample in a solid, transparent matrix. The KBr acts as a binding agent and a diluent, creating a homogenous disc that is physically robust and optically clear.
Why Potassium Bromide (KBr) is the Ideal Medium
KBr is not the only material that can be used, but it is the most common for several key reasons.
1. Complete Infrared Transparency
The primary requirement for a matrix material is that it does not absorb light in the region of interest. KBr is an ionic salt with a simple crystal lattice that has no molecular vibrations in the mid-infrared range (4000-400 cm⁻¹). This is the region where the vibrations of most organic and inorganic functional groups occur.
Because KBr is transparent, any absorption peaks seen in the final spectrum can be confidently attributed to the sample, not the matrix.
2. Controlled and Consistent Dilution
Most solid samples are highly absorbing. If a pure sample were pressed into a pellet, it would absorb nearly 100% of the light across a wide range, resulting in a useless spectrum with flat-topped, saturated peaks.
Mixing the sample with KBr at a typical 1:100 ratio (by weight) dilutes it to the perfect concentration. This ensures the absorption peaks are sharp and well-defined, and their intensity is proportional to the concentration (obeying the Beer-Lambert law).
3. Creation of a Uniform Optical Path
Thoroughly grinding the sample with KBr powder breaks down particles and distributes them evenly. When pressed under high pressure (typically around 10 tonnes), the KBr powder flows and fuses, forming a solid, glass-like disc.
This process eliminates the light-scattering issues associated with powders and creates a consistent path length for the IR beam to travel through, leading to high-quality, reproducible spectra.
Understanding the Critical Trade-offs
While the KBr method is powerful, it is not without challenges. Success depends on understanding and mitigating its primary weakness.
The Problem: KBr is Hygroscopic
The most significant issue with KBr is that it is hygroscopic—it readily absorbs moisture from the atmosphere. Water has very strong and broad absorption bands in the infrared spectrum (a large, broad peak around 3400 cm⁻¹ and a sharp bend around 1630 cm⁻¹).
If your KBr is contaminated with water, these water peaks can overlap with and obscure important peaks from your sample, especially N-H and O-H stretching vibrations.
Mitigating Moisture Contamination
To get a clean spectrum, you must minimize water exposure.
- Storage: Always store KBr powder in a desiccator or drying oven.
- Environment: For best results, prepare pellets in a low-humidity environment, such as inside a glovebox.
- Tools: Using a vacuum die, which pulls a vacuum on the powder as it's being pressed, is highly effective at removing adsorbed moisture.
Pellet Quality and Pressure
The physical quality of the pellet is crucial. A cloudy or opaque pellet indicates poor grinding, insufficient pressure, or particle sizes that are too large, which will cause light scattering and a sloping, noisy baseline. An even, transparent pellet is the goal.
Making the Right Choice for Your Analysis
Preparing a KBr pellet is a technique that requires care and attention to detail for reliable results.
- If your primary focus is quantitative accuracy: You must strictly control the sample-to-KBr ratio and pellet weight, and take every precaution to eliminate water contamination by using a glovebox or vacuum die.
- If your primary focus is qualitative identification: Consistency is still key, but a small amount of water contamination may be acceptable if it does not interfere with the key fingerprint region of your sample.
- If you see a poor-quality spectrum: First, visually inspect your pellet. If it's cloudy, remake it with more grinding. If the pellet looks good, check your spectrum for the classic broad water peak around 3400 cm⁻¹, which signals moisture contamination.
Mastering the KBr pellet technique is a fundamental skill that transforms an otherwise difficult solid sample into a source of clear, publishable analytical data.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Why It Matters for FTIR |
|---|---|
| Infrared Transparency | KBr does not absorb IR light, allowing only sample peaks to be measured. |
| Controlled Dilution | A 1:100 sample-to-KBr ratio prevents signal saturation and ensures sharp peaks. |
| Uniform Optical Path | Pressing creates a clear disc that minimizes light scattering for high-quality spectra. |
| Hygroscopic Nature | KBr absorbs moisture, which can interfere with results—proper handling is critical. |
Upgrade Your Solid Sample Analysis with KINTEK
Struggling with inconsistent FTIR results from solid samples? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables that support precise KBr pellet preparation. Our products help you achieve transparent, reproducible pellets for reliable spectral data—minimizing moisture contamination and maximizing clarity.
Ready to enhance your lab's capabilities? Contact our experts today to find the right solutions for your laboratory needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
- kbr pellet press 2t
- Automatic Laboratory Hydraulic Pellet Press Machine for Lab Use
- Laboratory Manual Hydraulic Pellet Press for Lab Use
- Automatic Laboratory Hydraulic Press for XRF & KBR Pellet Press
People Also Ask
- What is the pellet technique in IR? Master Solid Sample Preparation for Clear Spectroscopy
- What is the use of KBr? Master Sample Prep for Accurate IR Spectroscopy
- What is the pressed powder pellet method? A Guide to Accurate FTIR Sample Preparation
- Why use KBr for IR? Achieve Clear, Unobstructed Spectra for Solid Samples
- Are hydraulic presses powered by water? Discover the critical role of hydraulic oil.



















