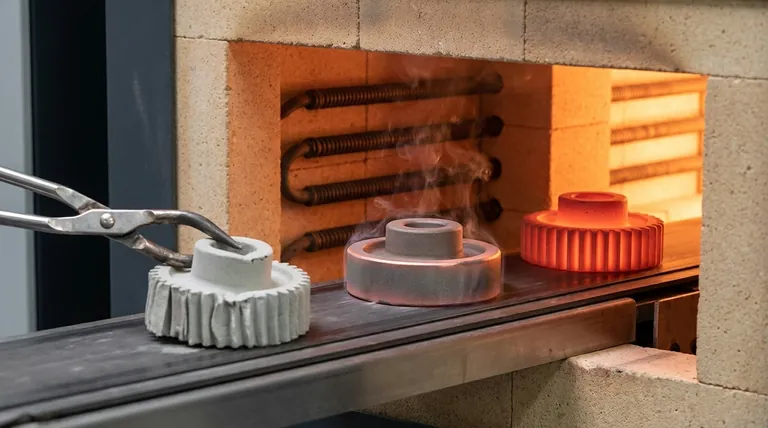
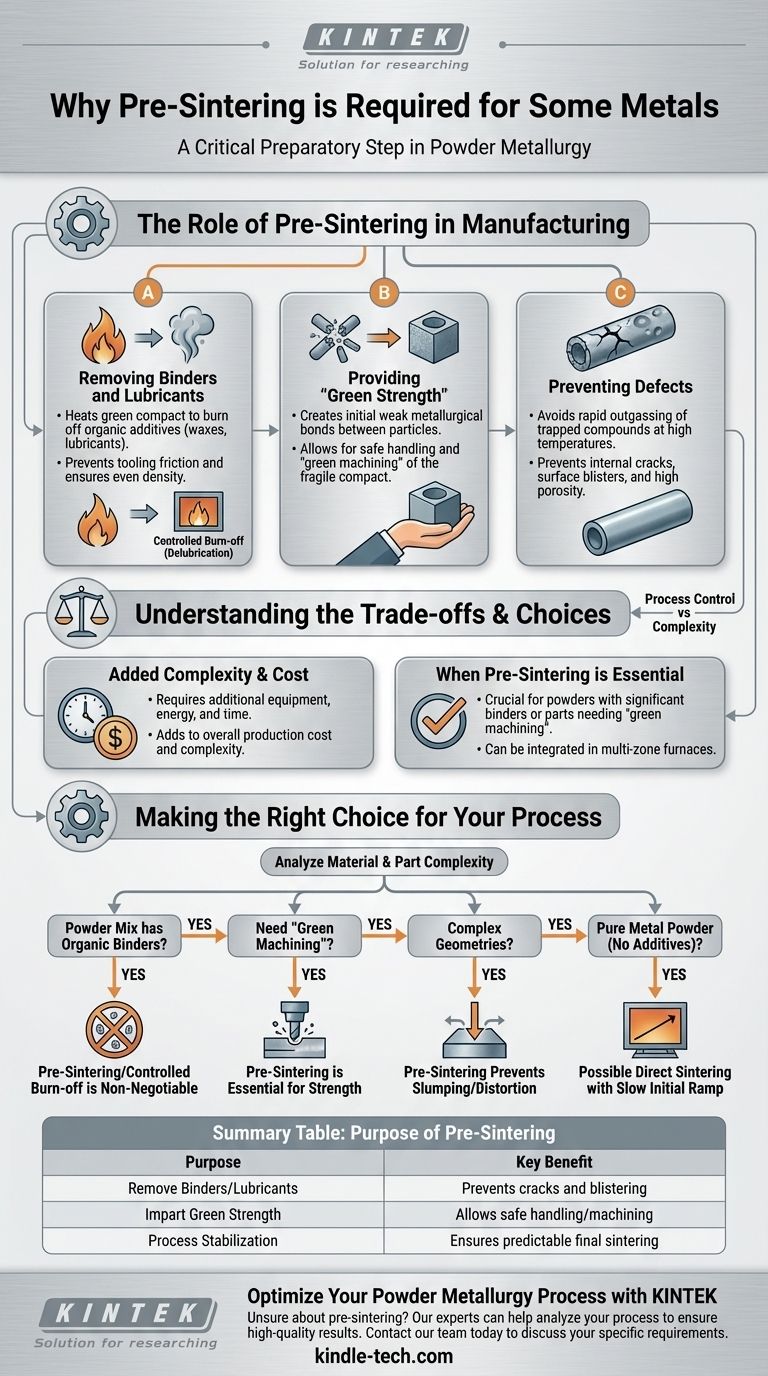
Pre-sintering is required for some metals as a critical preparatory step to remove additives like lubricants or binders and to impart initial strength to the fragile "green" compact. This lower-temperature heating cycle ensures the part can be handled or machined before the final, high-temperature sintering, and it prevents defects like cracks or blistering that would otherwise occur.
The core purpose of pre-sintering is not to achieve the final density or strength of a part, but rather to ensure process control. It cleans and stabilizes the powdered metal compact, paving the way for a more successful and predictable final sintering stage.

The Role of Pre-Sintering in Manufacturing
Pre-sintering, sometimes called the "burn-off" or "delubrication" cycle, is an intermediate thermal process. It occurs after a metal powder has been pressed into shape (the green compact) but before the main high-temperature sintering that fuses the particles together.
Removing Binders and Lubricants
In powder metallurgy, organic materials like waxes are often mixed with the metal powder. These lubricants reduce friction during the compaction stage, protecting the tooling and ensuring even density.
These additives must be completely removed before the final sintering. Pre-sintering heats the part to a temperature high enough to burn off these organic compounds but low enough to avoid significant densification.
Providing "Green Strength"
A newly pressed part, or green compact, is extremely fragile and can be compared to a piece of chalk. It can easily crumble or break during handling.
Pre-sintering creates initial, weak metallurgical bonds between the metal particles. This provides just enough strength—known as "green strength"—to allow the part to be safely transported, handled, or even machined before it undergoes final sintering.
Preventing Defects in the Final Part
Heating a green compact directly to the high final sintering temperature would be disastrous. The trapped lubricants and binders would vaporize rapidly and violently.
This rapid outgassing can cause a host of defects, including internal cracks, surface blisters, and high porosity. A controlled, lower-temperature pre-sintering cycle allows these compounds to burn off slowly, preserving the part's structural integrity.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While beneficial, pre-sintering is an additional manufacturing step that introduces its own set of considerations. It is not universally required for every powder metallurgy application.
Added Process Complexity and Cost
A separate pre-sintering step requires additional equipment, energy, and time. This adds to the overall cost and complexity of the production line.
When Pre-Sintering is Essential
The need for pre-sintering is dictated by the material and the part's complexity. It is most critical for parts made with powder mixes containing a significant amount of organic binders or for those requiring "green machining"—shaping the part before it is fully hardened.
Integrating the Steps
In some modern furnaces, pre-sintering and final sintering can occur in a single, continuous process. The furnace is designed with distinct temperature zones that allow for a carefully controlled ramp-up, where the part is held at the burn-off temperature before moving into the high-heat sintering zone.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Deciding whether to implement a distinct pre-sintering step depends entirely on your material, part complexity, and final quality requirements.
- If your powder mix contains organic binders or lubricants: A pre-sintering or controlled burn-off cycle is non-negotiable to prevent defects.
- If you need to perform "green machining": Pre-sintering is essential to provide the necessary strength to machine the part without it crumbling.
- If you are working with complex geometries: Pre-sintering can impart enough stability to prevent slumping or distortion before full densification occurs.
- If you are using a pure metal powder with no additives: You may be able to proceed directly to sintering, using a single thermal cycle with a slow initial temperature ramp.
Ultimately, pre-sintering is a strategic investment in process control that ensures the integrity and quality of the final sintered component.
Summary Table:
| Purpose of Pre-Sintering | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| Remove Binders/Lubricants | Prevents cracks and blistering during final sintering |
| Impart Green Strength | Allows safe handling and machining of fragile compacts |
| Process Stabilization | Ensures a predictable and successful final sintering stage |
Optimize Your Powder Metallurgy Process with KINTEK
Unsure if your metal parts require a pre-sintering step? Our experts can help you analyze your material and process to prevent costly defects and ensure consistent, high-quality results. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing the thermal processing solutions you need for successful sintering.
Contact our team today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's specific powder metallurgy requirements.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the process of zirconium production? From Ore to High-Performance Metal & Ceramic
- How are composites processed using sintering? Engineered Material Solutions Through Advanced Thermal Bonding
- What are the process advantages of using a rotary tube furnace for WS2 powder? Achieve Superior Material Crystallinity
- At what temperature does wood pyrolysis begin? Control the Process for Biochar, Bio-Oil, or Syngas
- What is the function of a high-temperature furnace during burnout? Master Aluminum Foam Production with Precision



















