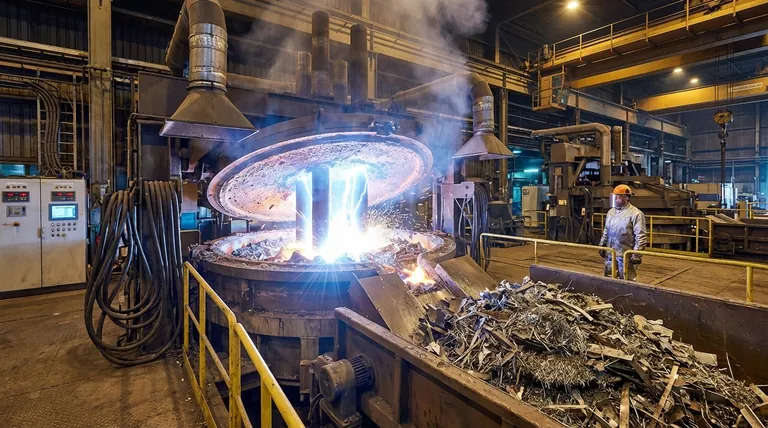
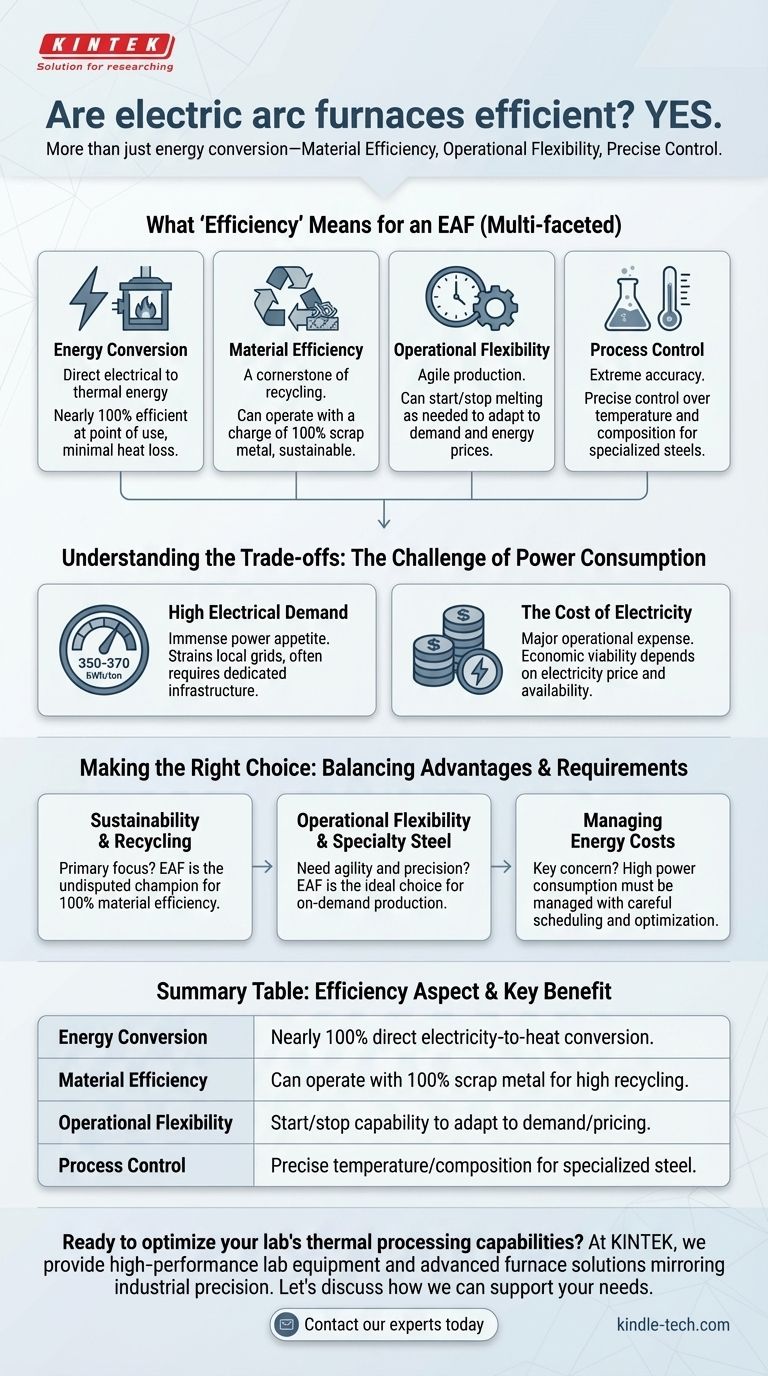
Yes, Electric Arc Furnaces (EAFs) are highly efficient, but the term "efficiency" in this context refers to more than just energy conversion. While the process of turning electricity directly into heat is nearly 100% efficient at the point of use, the true value of an EAF lies in its exceptional material efficiency, operational flexibility, and precise process control.
The efficiency of an Electric Arc Furnace is best understood as a balance. It offers unparalleled efficiency in recycling materials and adapting to production demands, but this comes at the cost of extremely high electricity consumption that requires careful management.

What "Efficiency" Means for an Electric Arc Furnace
The concept of efficiency for an EAF is multi-faceted. It excels in several key areas that make it a cornerstone of modern steel production.
Energy Conversion
An EAF works by passing a high-power electric arc through metal, typically scrap steel. This method converts electrical energy directly into thermal energy within the target material.
Unlike a gas furnace where significant heat is lost through exhaust, nearly all the electricity is used to generate the heat needed for melting.
Material Efficiency
This is arguably the EAF's greatest strength. It is a primary technology for recycling ferrous scrap metal.
An EAF can operate using a charge of 100% scrap metal, making it a highly sustainable and resource-efficient method for producing new steel.
Operational Flexibility
EAFs offer a level of agility that traditional blast furnaces cannot match. Smelters can start and stop the melting process as needed.
This flexibility allows producers to adapt to fluctuating demand and even schedule operations to take advantage of off-peak electricity prices, a significant cost-efficiency measure.
Process Control and Versatility
The process is highly automated and mechanized. Operators can control the temperature and composition of the molten steel with extreme accuracy.
This precision allows for the production of a wide variety of carbon and alloy steels, reducing waste and ensuring high-quality, specialized products.
Understanding the Trade-offs: The Challenge of Power Consumption
The primary challenge and key trade-off for EAFs is their immense appetite for electricity.
High Electrical Demand
An EAF consumes a significant amount of power, often requiring 350 to 370 kWh of energy to process one ton of steel scrap.
This massive and rapid power draw can place a substantial strain on local electrical grids, often requiring dedicated power infrastructure.
The Cost of Electricity
While the furnace is efficient at converting power to heat, the cost of that electricity is a major operational expense.
The economic viability of an EAF is therefore heavily tied to the price and availability of electricity, making energy management a critical aspect of its operation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use an EAF hinges on balancing its powerful advantages against its significant energy requirements.
- If your primary focus is sustainability and recycling: The EAF is the undisputed champion for turning scrap metal into high-quality new steel with 100% material efficiency.
- If your primary focus is operational flexibility and specialty steel production: The EAF's precise control and ability to start and stop on demand make it the ideal choice.
- If your primary focus is managing energy costs: The high power consumption is a critical factor that must be managed through careful scheduling and optimization.
Ultimately, the electric arc furnace represents a modern, highly efficient approach to steelmaking, defined by its incredible recycling capability and operational agility.
Summary Table:
| Efficiency Aspect | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| Energy Conversion | Nearly 100% direct electricity-to-heat conversion |
| Material Efficiency | Can operate with 100% scrap metal, enabling high recycling rates |
| Operational Flexibility | Start/stop capability to adapt to demand and energy pricing |
| Process Control | Precise temperature and composition control for specialized steel production |
Ready to optimize your lab's thermal processing capabilities?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-performance lab equipment, including advanced furnace solutions that mirror the precision and control of industrial systems. Whether you're involved in materials research, metallurgy, or quality control, our products are designed to enhance your operational efficiency and deliver reliable results.
Let's discuss how we can support your laboratory needs. Contact our experts today to find the perfect equipment for your specific applications.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a high-purity alumina lining required for high-temperature tube furnaces? Ensure Accurate Biomass Research
- What is the pressure on a tube furnace? Essential Safety Limits for Your Lab
- What is a tubular furnace used for? Precision Heating for Material Synthesis & Analysis
- What is the ceramic tube high temperature? From 1100°C to 1800°C, Choose the Right Material
- Why is an Alumina Ceramic Tube Support Necessary for 1100°C Experiments? Ensure Data Accuracy and Chemical Inertness



















