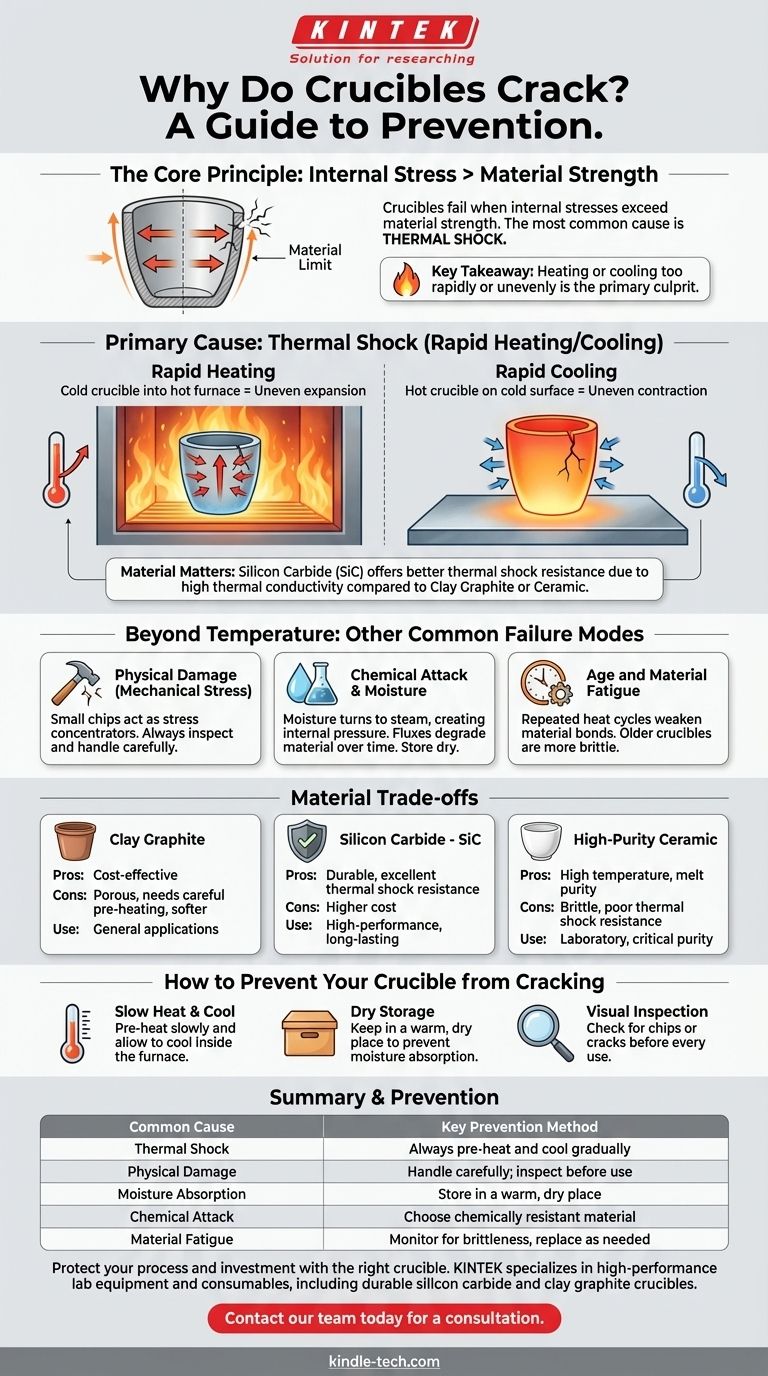
Yes, a crucible can absolutely crack. In fact, cracking is one of the most common failure modes for any crucible, regardless of its material. This failure is rarely random; it is almost always the result of specific, and often preventable, stresses placed upon the material during use.
The core principle to understand is that crucibles fail when internal stresses exceed the material's strength. The most common cause of this stress is thermal shock—heating or cooling the crucible too rapidly or unevenly.
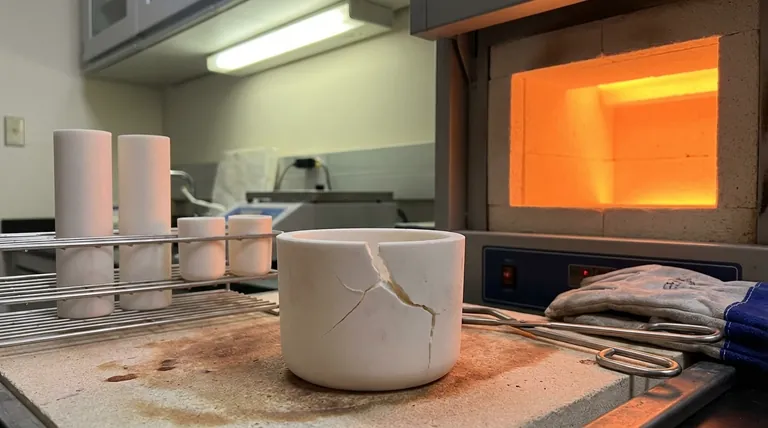

The Primary Cause of Cracking: Thermal Shock
Thermal shock is the single greatest threat to the integrity of your crucible. Understanding how it works is the first step toward preventing catastrophic failure.
What is Thermal Shock?
Imagine pouring boiling water into a thick, cold glass. The inner surface expands rapidly from the heat while the outer surface remains cold and contracted. This difference in expansion creates immense internal stress, often causing the glass to shatter.
A crucible experiences this same phenomenon on a much more extreme scale. Rapidly heating or cooling creates a significant temperature difference between its inner and outer walls, leading to stress that can easily fracture the material.
Critical Heating and Cooling Rates
The number one operational error leading to a cracked crucible is heating it too quickly. Placing a room-temperature crucible into a pre-heated, blazing-hot furnace is a recipe for disaster.
The same principle applies to cooling. Removing a glowing-hot crucible and placing it on a cold, conductive surface (like concrete or steel) will cause it to cool unevenly and crack. Gradual, controlled temperature changes are essential.
The Role of Material
Different crucible materials have varying resistance to thermal shock. A silicon carbide crucible, for instance, has excellent thermal conductivity, which helps distribute heat more evenly and reduces stress. A clay graphite or ceramic crucible may be more susceptible and require even more careful heating and cooling protocols.
Beyond Temperature: Other Common Failure Modes
While thermal shock is the primary culprit, other factors can weaken a crucible's structure, making it vulnerable to cracking even under normal heating conditions.
Physical Damage (Mechanical Stress)
Even a small chip or hairline fracture from being dropped or struck can become a critical failure point. These micro-cracks act as stress concentrators. When the crucible is heated, the stress of thermal expansion focuses on that weak point, causing the crack to propagate and split the crucible.
Always inspect your crucible for damage before every use. Handle it carefully with properly fitting tongs to avoid creating nicks and scrapes.
Chemical Attack and Moisture
Crucibles are porous and can absorb moisture from the air. If a damp crucible is heated too quickly, that moisture turns to steam, creating explosive internal pressure that can crack or spall the material from the inside.
Similarly, aggressive fluxes used in melting can chemically react with the binder in the crucible material. Over time, this degrades the crucible's structure, making it weak and brittle.
Age and Material Fatigue
Every heat cycle is a stress cycle. Over its lifespan, a crucible will expand and contract thousands of times, which gradually weakens the material bonds. An older crucible is inherently more brittle and susceptible to cracking than a new one.
Understanding the Trade-offs in Material Choice
The material you choose directly impacts its resistance to cracking and its ideal use case. There is no single "best" material, only the right one for a specific application.
Clay Graphite
This is a common and cost-effective choice. However, it is more porous and susceptible to moisture absorption and requires very careful pre-heating. It's also softer and more easily damaged by mishandling.
Silicon Carbide
Known for its durability and excellent thermal conductivity, "SiC" crucibles resist thermal shock much better than clay graphite. This makes them safer and longer-lasting, but they come at a higher cost.
High-Purity Ceramic
Materials like porcelain or alumina are used when melt purity is critical, such as in laboratory settings. They can withstand very high temperatures but are often extremely brittle and have poor thermal shock resistance, requiring a highly controlled heating and cooling process.
How to Prevent Your Crucible from Cracking
Applying the right operational discipline is key to ensuring safety and maximizing the life of your equipment.
- If your primary focus is safety and longevity: Always pre-heat your crucible slowly and allow it to cool down gradually, ideally inside the furnace.
- If you are concerned about contamination: Store your crucible in a warm, dry place to prevent moisture absorption, which is a leading cause of internal stress failure.
- If you want to maximize your investment: Before every use, perform a quick visual inspection for any chips or cracks, as these are the starting points for catastrophic failure.
By understanding that a crucible is a high-performance tool subject to immense stress, you can prevent cracks before they ever start.
Summary Table:
| Common Cause of Cracking | Key Prevention Method |
|---|---|
| Thermal Shock (Rapid Heating/Cooling) | Always pre-heat and cool gradually |
| Physical Damage (Chips, Fractures) | Handle carefully; inspect before each use |
| Moisture Absorption | Store in a warm, dry place |
| Chemical Attack from Fluxes | Choose a chemically resistant crucible material |
| Material Fatigue (Age) | Monitor for brittleness and replace as needed |
Protect your processes and investment with the right crucible. Cracking is a preventable failure. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including durable silicon carbide and clay graphite crucibles designed for excellent thermal shock resistance. Our experts can help you select the perfect crucible for your specific application to ensure safety, purity, and longevity. Contact our team today for a consultation and let us help you prevent crucible failure.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Al2O3 Crucible With Lid Cylindrical Laboratory Crucible
- Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible Semicircle Boat with Lid for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Arc-Shaped Alumina Ceramic Crucible High Temperature Resistant for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Crucibles (Al2O3) for Thermal Analysis TGA DTA
- Engineering Advanced Fine Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible for Laboratory Muffle Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is a crucible material for a furnace? A Guide to Choosing the Right High-Temperature Container
- What is the temperature range of alumina crucibles? Key Factors for Safe High-Temp Use
- Why use high-purity alumina crucibles for RPPO calcination? Ensure Stoichiometric Purity at 1150°C
- What precautions should be taken when using a crucible? Essential Steps for Safety and Accuracy
- What is the purpose of using an alumina crucible with a lid for g-C3N4 synthesis? Optimize Your Nanosheet Production



















