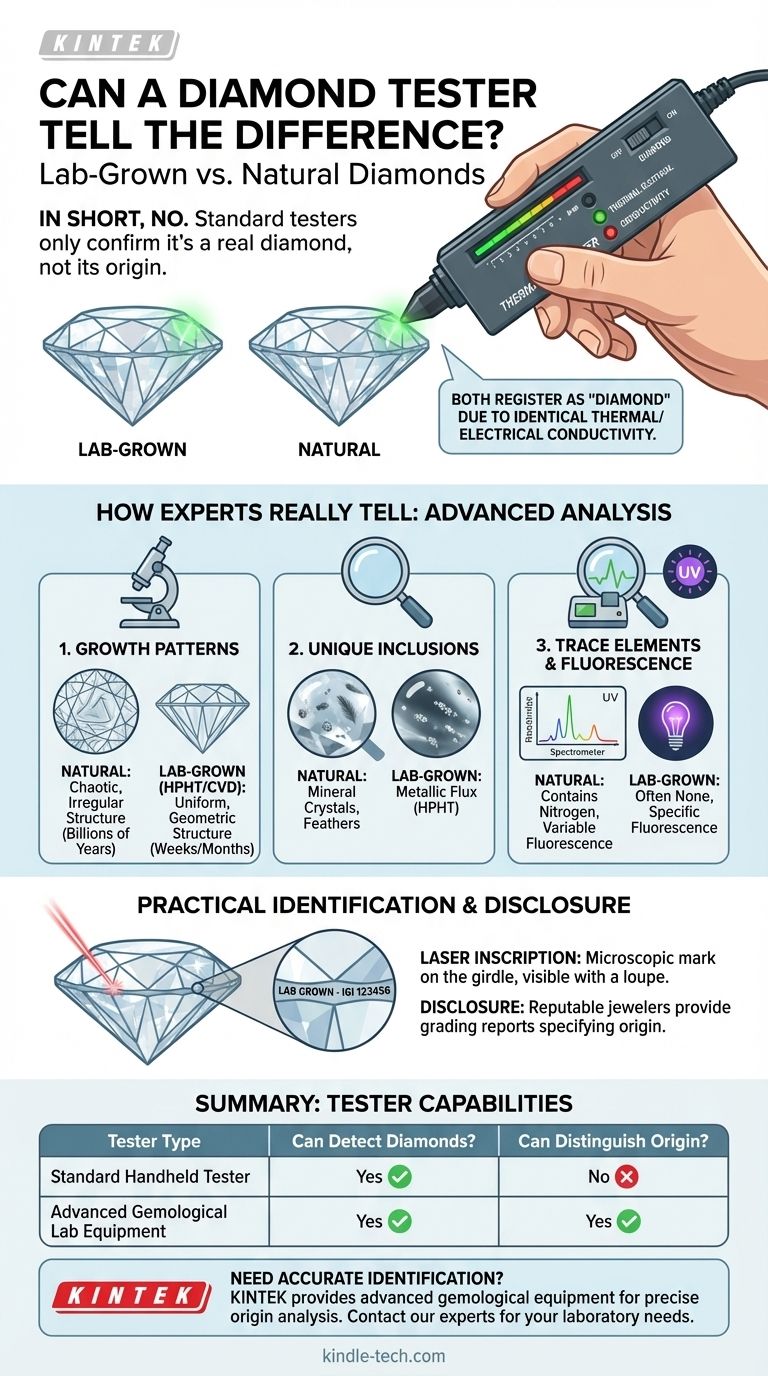
In short, no. A standard, handheld diamond tester cannot distinguish between a lab-grown diamond and a natural one. These devices are designed to differentiate true diamonds from simulants like cubic zirconia by testing for thermal or electrical conductivity. Since lab-grown diamonds possess the exact same chemical composition and physical properties as natural diamonds, they will both correctly register as "diamond" on these testers.
A basic diamond tester confirms a stone is a real diamond, but it cannot determine its origin. Distinguishing a lab-grown diamond from a natural one requires analyzing subtle differences in their growth structure, a task that demands highly specialized gemological equipment.

Why Standard Testers Identify Both as "Diamond"
What a Diamond Tester Actually Measures
Most common diamond testers are thermal conductivity meters. They work by touching a small metal tip to the stone and measuring how quickly heat dissipates from the tip.
Diamonds, both natural and lab-grown, are exceptional thermal conductors. Common simulants like cubic zirconia or glass are thermal insulators. A tester simply detects this fundamental property and indicates whether the stone is a diamond or not.
Identical Chemical and Physical Properties
A lab-grown diamond is not a "fake" diamond; it is a real diamond created in a controlled environment. It is composed of pure carbon atoms arranged in the same crystal lattice structure as a natural diamond.
Because of this, they are visually identical and share the same hardness, brilliance, and thermal conductivity. For a device measuring only these physical properties, they are indistinguishable.
How Experts Really Tell the Difference
While a simple tester fails, a trained gemologist in a lab can reliably determine a diamond's origin. They do this by looking for telltale signs left behind by the diamond's unique creation process.
Analyzing Growth Patterns
Natural diamonds form over billions of years under immense, fluctuating pressure and heat deep within the Earth. This chaotic process creates distinct and often irregular internal growth patterns.
Lab-grown diamonds, created in just weeks or months via methods like HPHT (High Pressure, High Temperature) or CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition), have much more uniform and geometric growth patterns. Specialized imaging equipment can reveal these different structural signatures.
Identifying Unique Inclusions
Inclusions are tiny imperfections within a diamond. The types of inclusions often point to the stone's origin.
Natural diamonds may contain tiny crystals of other minerals or unique "feathers" formed under natural geological stress. In contrast, HPHT-grown diamonds may contain microscopic metallic flux inclusions from the growth chamber, something never found in natural stones.
The Role of Specialized Equipment
Gemological laboratories use sophisticated scientific instruments to make a definitive call. Tools like spectrometers and advanced microscopes can detect minute differences in trace elements and observe fluorescence patterns under ultraviolet light.
For example, most natural diamonds contain tiny amounts of nitrogen, while many lab-grown diamonds do not. These are atomic-level clues that are far beyond the capability of a handheld device.
The Practical Distinction: Disclosure and Inscription
While scientific analysis is the ultimate arbiter, the most common way to identify a lab-grown diamond is far simpler.
The Importance of Disclosure
Reputable jewelers are transparent about the origin of their diamonds. A lab-grown diamond will be clearly sold and documented as such, often accompanied by a grading report from a lab like GIA or IGI that specifies its origin.
The Telltale Laser Inscription
Most importantly, the vast majority of lab-grown diamonds over a certain size are microscopically laser-inscribed on their girdle (the thin edge of the stone).
This inscription is invisible to the naked eye but can be read with a jeweler's loupe. It often includes the term "LAB GROWN" and the corresponding grading report number, providing definitive identification.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding how diamonds are identified empowers you to make a confident purchase, whether you are buying or verifying.
- If your primary focus is verifying authenticity: A basic tester can confirm you have a real diamond, but to know its origin, you must rely on a grading report and check for a laser inscription.
- If your primary focus is choosing between lab and natural: Remember that both are physically and chemically real diamonds. The decision rests on factors like budget, environmental considerations, and personal preference, not on "real vs. fake."
Ultimately, the distinction between a lab-grown and natural diamond lies in its origin story, not in the stone you see before you.
Summary Table:
| Tester Type | Can Detect Diamonds? | Can Distinguish Lab-Grown vs. Natural? |
|---|---|---|
| Standard Handheld Tester | Yes | No |
| Advanced Gemological Lab Equipment | Yes | Yes |
Need to accurately identify your diamond's origin?
While a basic tester confirms authenticity, determining if a diamond is lab-grown or natural requires specialized expertise and equipment. KINTEK specializes in providing the advanced laboratory equipment and consumables needed for precise gemological analysis.
Our solutions help jewelers, gemologists, and laboratories accurately identify diamond origin through advanced spectroscopy and imaging techniques. Ensure confidence in your diamond verification process.
Contact our experts today to discuss the right equipment for your specific laboratory needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- CVD Diamond Cutting Tool Blanks for Precision Machining
- CVD Diamond Domes for Industrial and Scientific Applications
- Filter Testing Machine FPV for Dispersion Properties of Polymers and Pigments
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition and Lab Diamond Growth
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Head Tweezers with Pointed Elbow Zirconia Ceramic Tip
People Also Ask
- What are the raw materials for CVD diamonds? A seed, a gas, and the science of crystal growth.
- What are the environmental issues with diamond mining? Uncover the True Ecological and Human Cost
- Will CVD diamond change color? Discover the Science of Permanent, Stable Color
- What are 5 negative impacts of diamond mines on the environment? The Hidden Environmental Cost of Diamond Mining
- How is something diamond coated? A Guide to CVD Growth vs. Plating Methods











