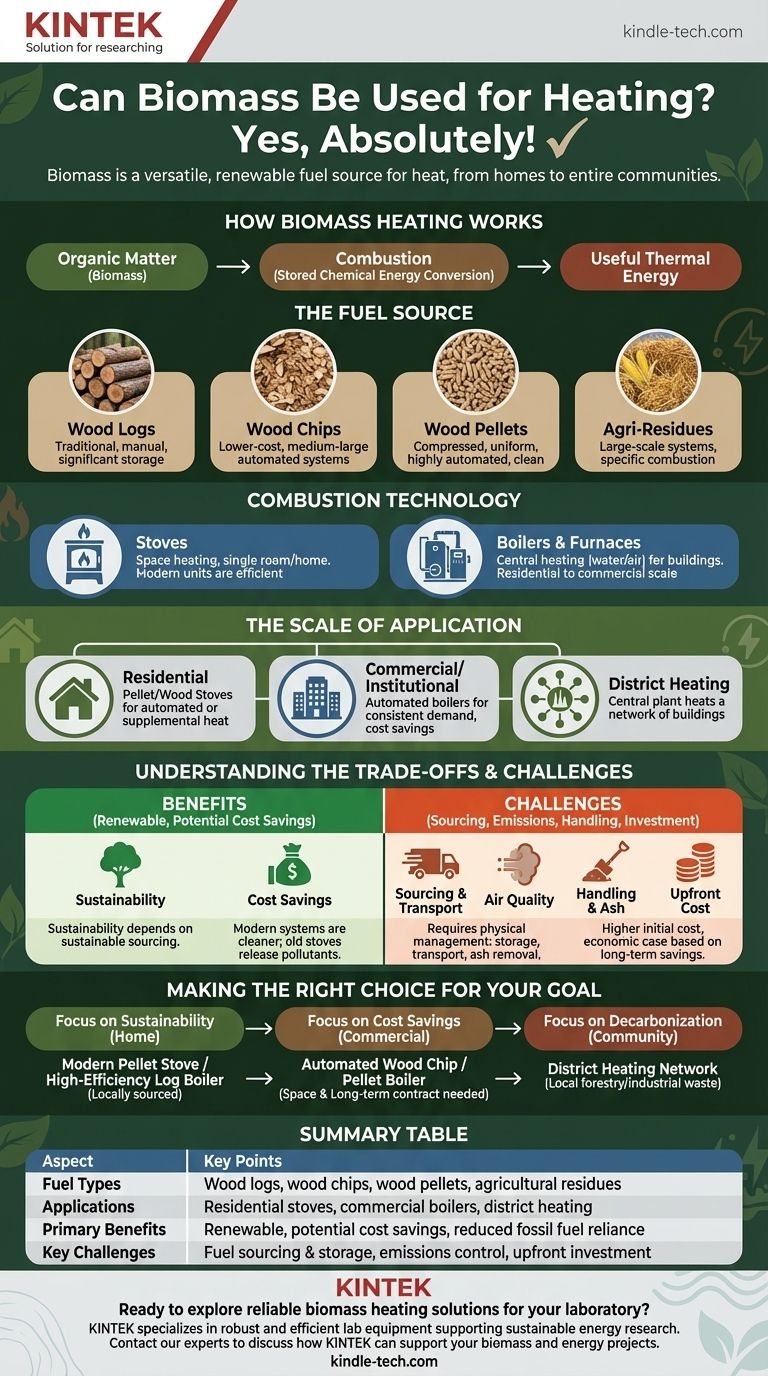
Yes, absolutely. Biomass is a well-established and highly versatile fuel source for generating heat. It is used across a vast range of applications, from simple wood-burning stoves in individual homes to sophisticated, automated boilers for commercial buildings and large-scale power plants that provide district heating for entire communities.
Biomass heating offers a renewable alternative to fossil fuels, but its environmental and economic viability is not automatic. Success depends entirely on the sustainability of the fuel source, the efficiency of the combustion system, and the practicalities of fuel handling and storage.

How Biomass Heating Works
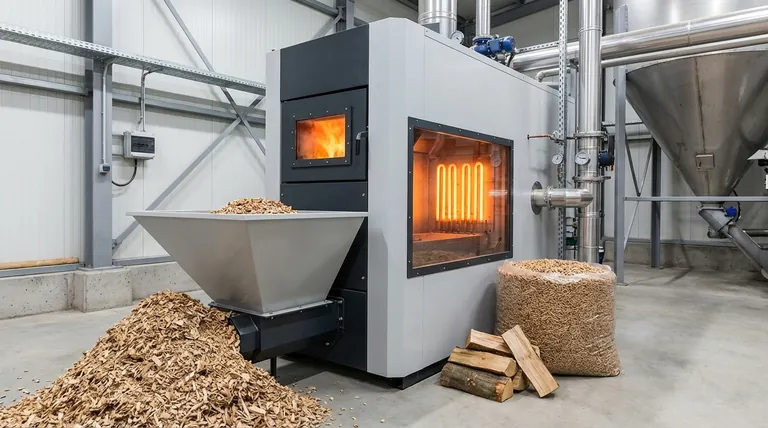
At its core, biomass heating is the process of converting the stored chemical energy in organic matter into useful thermal energy through combustion. This process can be adapted for vastly different needs and scales.
The Fuel Source: From Raw Logs to Processed Pellets
The term "biomass" covers a wide range of organic materials. The most common for heating include:
- Wood Logs: The most traditional fuel. Best suited for manual-fed stoves and boilers, requiring significant user effort and storage space.
- Wood Chips: A lower-cost fuel often produced from forestry residues. Chips are ideal for medium-to-large automated systems but require more storage space than pellets due to their lower density.
- Wood Pellets: Made from compressed sawdust and wood shavings. Their uniform size and density make them perfect for highly automated, efficient, and clean-burning residential and commercial systems.
- Agricultural Residues: Materials like straw, corn cobs, or cherry pits can also be used, typically in larger-scale systems designed to handle their specific combustion properties.
The Combustion Technology: Stoves, Boilers, and Furnaces
The technology used to burn the biomass is critical for efficiency and emissions.
- Stoves: Primarily used for space heating in a single room or smaller, well-insulated home. Modern pellet stoves are automated and relatively clean, while modern wood stoves are vastly more efficient and produce fewer emissions than older models.
- Boilers & Furnaces: These are central heating systems that burn biomass to heat water (boilers) or air (furnaces), which is then circulated throughout a building. They range from small residential units to large commercial systems that can heat schools, hospitals, or office buildings.
The Scale of Application: From One Room to an Entire District
Biomass heating is not a one-size-fits-all solution.
- Residential: The focus is typically on pellet stoves for automated heating or high-efficiency wood stoves for supplemental heat and ambiance.
- Commercial/Institutional: Automated wood chip or pellet boilers are a common choice for facilities with consistent heat demand, offering potential long-term cost savings.
- District Heating: In this model, a central plant burns biomass (often locally-sourced forestry or industrial wood waste) to produce hot water, which is then piped underground to heat a network of buildings in a neighborhood or town.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
While biomass has significant potential, an objective assessment requires acknowledging its challenges. Making an informed decision means understanding these trade-offs.
Fuel Sourcing and Sustainability
The carbon benefit of biomass hinges on sustainable sourcing. If forests are harvested faster than they can regrow, or if sensitive ecosystems are damaged, the system is not sustainable. The carbon footprint of transporting fuel over long distances can also erode its environmental advantage.
Air Quality and Emissions
Combustion releases pollutants. Old or poorly operated wood stoves are a significant source of fine particulate matter (PM2.5), which is harmful to human health. However, modern, automated biomass systems are engineered for high-efficiency, low-emission combustion and are dramatically cleaner than their predecessors.
Handling, Storage, and Ash
Unlike natural gas or oil, biomass is a solid fuel that requires physical management. You need a dry, dedicated space for storage, a method for moving fuel to the boiler (manual or automated), and a process for regularly removing and disposing of ash.
Upfront Investment Costs
The initial capital cost for a high-quality, automated biomass boiler system is typically higher than for a comparable fossil fuel system. The economic case often relies on long-term fuel cost savings to offset the initial investment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To determine if biomass is the right solution, you must align the technology with your specific objective.
- If your primary focus is sustainability in a single home: A modern pellet stove or a high-efficiency log boiler, fueled by locally and sustainably sourced wood, is an excellent choice.
- If your primary focus is cost savings for a commercial building: An automated wood chip or pellet boiler can provide significant operational savings, provided you have the space for fuel storage and can secure a reliable, long-term fuel contract.
- If your primary focus is decarbonizing a community: A district heating network powered by biomass from local forestry or industrial waste is one of the most effective and proven strategies available.
By matching the right technology and fuel source to your specific needs, biomass heating can serve as a reliable and responsible cornerstone of your energy strategy.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Points |
|---|---|
| Fuel Types | Wood logs, wood chips, wood pellets, agricultural residues |
| Applications | Residential stoves, commercial boilers, district heating |
| Primary Benefits | Renewable, potential cost savings, reduced fossil fuel reliance |
| Key Challenges | Fuel sourcing & storage, emissions control, upfront investment |
Ready to explore reliable biomass heating solutions for your laboratory?
KINTEK specializes in providing robust and efficient lab equipment, including systems that support sustainable energy research and development. Whether you're testing biomass fuel properties or developing new combustion technologies, our expertise can help you achieve precise and reliable results.
Contact our experts today to discuss how KINTEK's laboratory equipment and consumables can support your biomass and energy projects.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) Thermal Elements Electric Furnace Heating Element
- Cylindrical Lab Electric Heating Press Mold for Laboratory Applications
- Infrared Heating Quantitative Flat Plate Press Mold
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
People Also Ask
- What is the role of ultrasonic cleaning equipment in the surface modification of biomedical materials? Boost Adhesion
- Is it economically viable to recycle plastic? The Harsh Economic Reality of Plastic Recycling
- What safety feature do most ULT freezers have to protect stored samples? Redundancy and Alarm Systems
- What does the centrifuge do to the solution? Separate Components with High-Speed Centrifugal Force
- What are the advantages of a batch furnace? Achieve Unmatched Flexibility and Control
- What is the environmental significance of XRF? Rapid, On-Site Detection of Hazardous Contaminants
- What are the advantages of biomass? Unlock Renewable Power from Waste and Crops
- How to start a lab-grown diamonds business? Choose Your Path to Success











