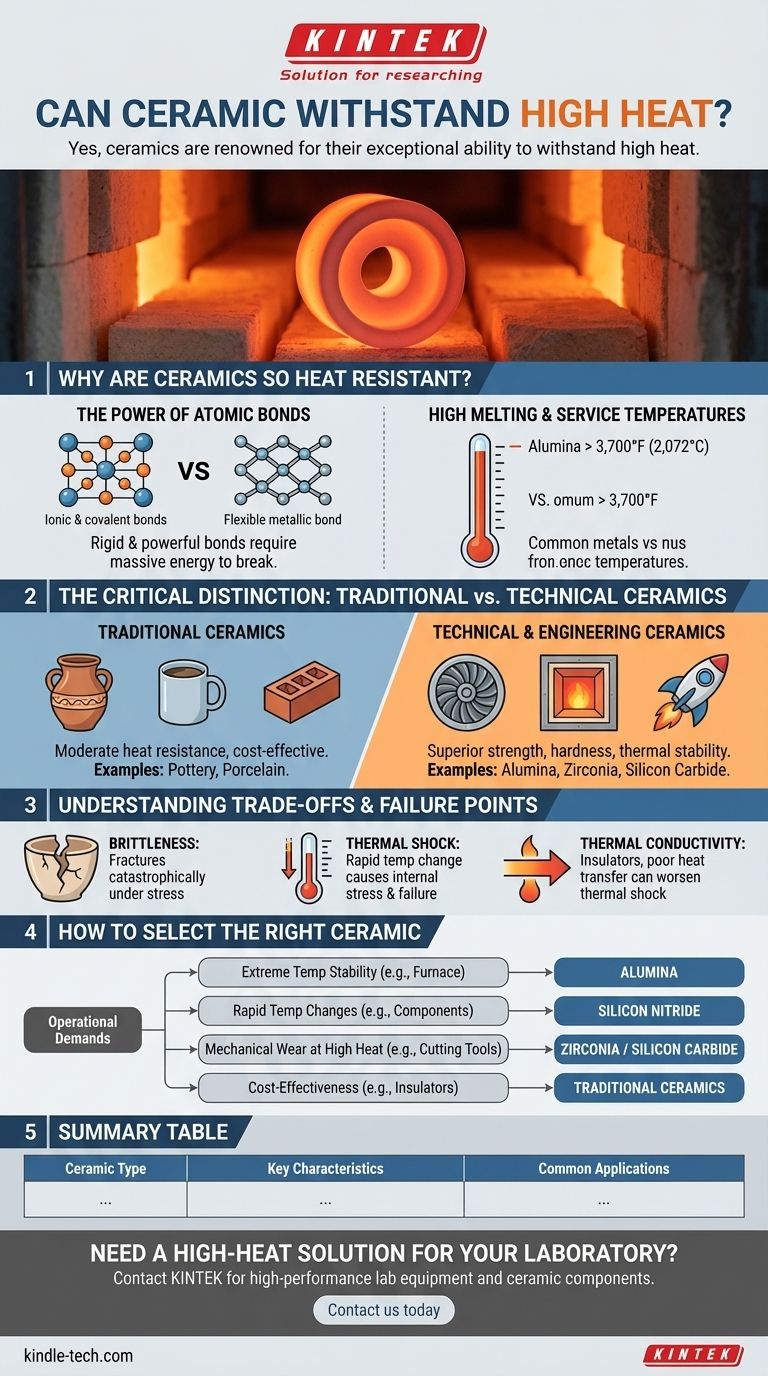
Yes, ceramics are renowned for their exceptional ability to withstand high heat. In fact, high-temperature stability is one of their most defining engineering characteristics. However, the term "ceramic" covers a vast range of materials, from simple earthenware pottery to advanced composites used in jet engines. The degree and nature of their heat resistance vary dramatically across this spectrum.
The critical insight is not if ceramics can handle heat, but rather understanding that each type of ceramic is engineered for a specific thermal environment. Your focus should be on matching the right ceramic to the application's temperature, rate of temperature change, and mechanical stress.

Why Are Ceramics So Heat Resistant?
The ability of ceramics to endure extreme temperatures is not an accident; it is a direct result of their fundamental atomic structure. Unlike metals, which are characterized by a flexible "sea" of shared electrons, ceramics are built on much more rigid and powerful bonds.
The Power of Atomic Bonds
Most technical ceramics are held together by ionic and covalent bonds. These are extremely strong chemical links that require a massive amount of energy—in the form of heat—to break apart. This inherent stability is what gives ceramics their characteristically high melting points.
High Melting and Service Temperatures
Because of these strong bonds, many technical ceramics melt at temperatures far exceeding those of even high-performance metal alloys. For example, alumina (aluminum oxide), a common technical ceramic, has a melting point of over 3,700°F (2,072°C), allowing it to be used reliably in applications where most metals would have failed.
The Critical Distinction: Traditional vs. Technical Ceramics
Not all ceramics are created equal. The difference in performance between the ceramic in a coffee mug and the ceramic in a turbine blade is immense.
Traditional Ceramics
These are the materials most people think of, such as pottery, porcelain, and brick. They are typically clay-based and fired at high temperatures to achieve hardness and stability. While they are heat-resistant enough for applications like cookware and building materials, they are not suited for extreme industrial or aerospace environments.
Technical & Engineering Ceramics
This is a class of highly purified and precisely manufactured materials designed for extreme performance. They offer superior strength, hardness, and thermal stability. Common examples include:
- Alumina (Aluminum Oxide): Excellent for furnace linings and electrical insulators due to its high melting point and stability.
- Zirconia (Zirconium Dioxide): Known for its exceptional fracture toughness at high temperatures, used in engine components and cutting tools.
- Silicon Carbide (SiC): Maintains its strength at very high temperatures and is used for parts like car brakes and rocket nozzles.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Failure Points
While thermally resilient, ceramics are not invincible. Their unique properties come with specific vulnerabilities that are critical to understand for any high-heat application.
Brittleness and Fracture
The primary trade-off for a ceramic's hardness and heat resistance is its brittleness. Unlike a metal that will bend or deform under stress, a ceramic will typically fracture catastrophically once its limit is reached. This must be a central consideration in any design.
The Threat of Thermal Shock
This is the most common failure mode for ceramics in high-heat environments. Thermal shock occurs when a material experiences a rapid change in temperature, causing different parts of it to expand or contract at different rates. This creates immense internal stress that can easily cause cracks and complete failure.
Thermal Conductivity
Most ceramics are thermal insulators, meaning they do not transfer heat well. This is often a desirable property, for example, in furnace linings. However, this low conductivity can worsen their susceptibility to thermal shock, as it allows sharp temperature gradients to build up within the material.
How to Select the Right Ceramic
Your choice depends entirely on the operational demands of your application. To make an informed decision, you must move beyond the general question of heat resistance and evaluate the specific environment.
- If your primary focus is extreme temperature stability (e.g., furnace linings, crucibles): You need a technical ceramic with a very high melting point, like Alumina (Aluminum Oxide).
- If your primary focus is surviving rapid temperature changes (e.g., components that are quickly heated and cooled): Look for materials engineered for thermal shock resistance, such as certain grades of Silicon Nitride or Fused Silica.
- If your primary focus is mechanical wear at high temperatures (e.g., cutting tools, engine parts): Zirconia or Silicon Carbide offer a superior combination of hardness, toughness, and heat resistance.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness in moderate heat (e.g., consumer goods, basic insulators): Traditional ceramics like porcelain or stoneware are often the most practical choice.
Understanding the specific type of ceramic and its inherent trade-offs is the key to successfully leveraging its remarkable thermal properties.
Summary Table:
| Ceramic Type | Key Characteristics | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Traditional Ceramics (e.g., pottery, brick) | Moderate heat resistance, cost-effective | Cookware, building materials |
| Alumina (Aluminum Oxide) | High melting point (>3,700°F), excellent stability | Furnace linings, electrical insulators |
| Zirconia (Zirconium Dioxide) | Exceptional fracture toughness at high temperatures | Engine components, cutting tools |
| Silicon Carbide (SiC) | Maintains strength at very high temperatures | Rocket nozzles, car brakes |
Need a High-Heat Solution for Your Laboratory?
Choosing the right ceramic material is critical for the success and safety of your high-temperature processes. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including ceramic components engineered for extreme thermal environments. Our experts can help you select the perfect material to ensure durability, efficiency, and precision in your applications.
Contact us today to discuss your specific needs and discover how KINTEK's solutions can enhance your laboratory's capabilities!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Precision Machined Zirconia Ceramic Ball for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Head Tweezers with Pointed Elbow Zirconia Ceramic Tip
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Conductive Boron Nitride BN Ceramics Composite for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of using high-hardness zirconia grinding balls? Ensure Purity & Power in Electrolyte Milling
- Why are zirconia grinding balls preferred for NiCrAlY-Mo-Ag powders? Ensure Maximum Purity and Durability
- What are the advantages of using zirconia milling jars for sulfide electrolytes? Enhance Purity and Conductivity
- Why are ZrO2 grinding jars and balls required for sulfide solid electrolytes? Ensure Purity & Performance
- What are the applications of zirconia ceramics? Unlock High-Performance Solutions for Extreme Environments



















