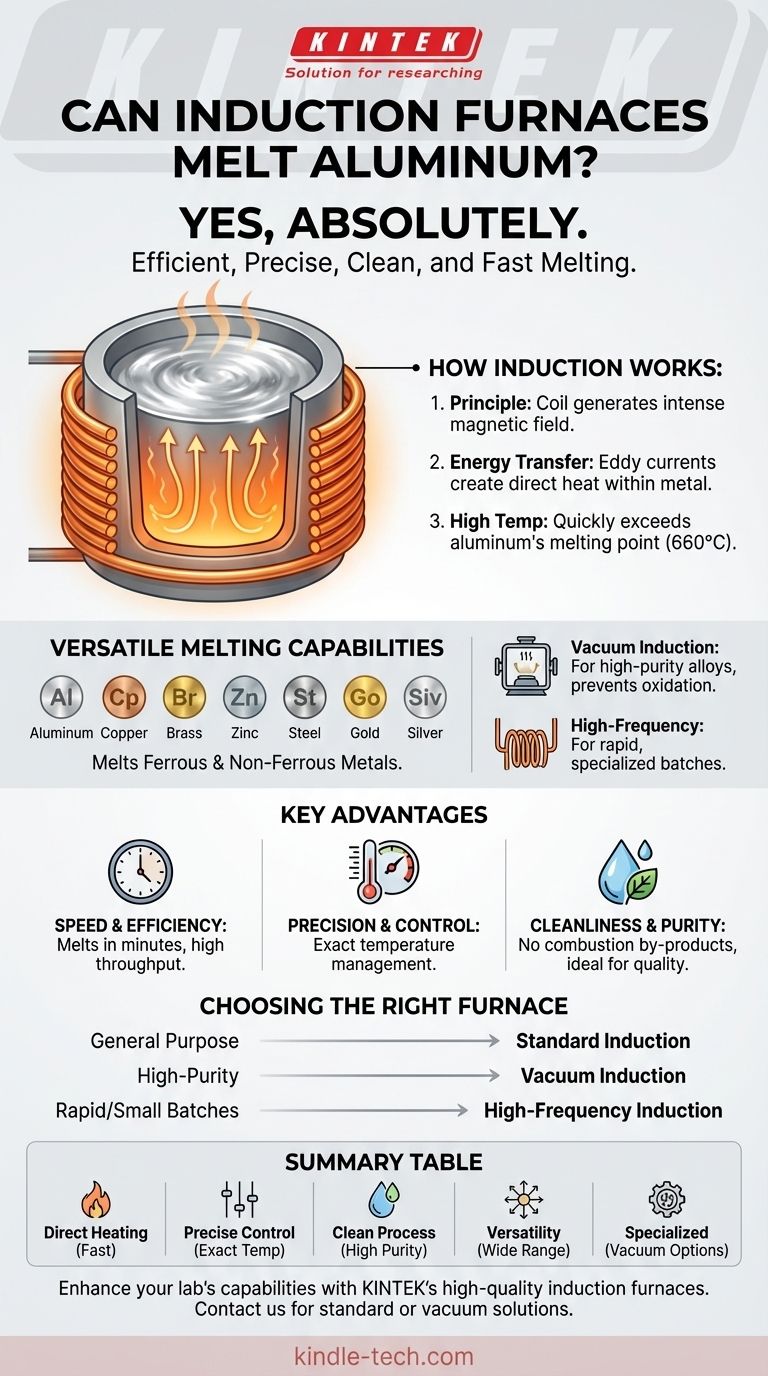
Yes, absolutely. An induction furnace is not only capable of melting aluminum but is a highly effective and widely used tool for the process. This technology is designed to melt a vast range of both ferrous and non-ferrous metals, including aluminum and its alloys, with significant efficiency and precision.
The core principle of induction melting—using an electromagnetic field to generate intense heat directly within the metal—makes it an exceptionally clean, fast, and controllable method for melting aluminum and many other industrial metals.

How Induction Furnaces Melt Metals
The Principle of Induction Heating
An induction furnace operates without any external flame or heating element touching the metal. It uses a coil, typically made of copper, through which a powerful alternating electrical current is passed.
This current generates a strong, rapidly changing magnetic field around the coil and, more importantly, within the crucible holding the metal.
Energy Transfer to the Metal
When the conductive metal, like aluminum, is placed inside this magnetic field, the field induces powerful electrical currents (eddy currents) directly within the metal itself. The inherent electrical resistance of the aluminum causes these currents to generate immense heat.
This process transfers energy directly to the material you want to melt, making it highly efficient.
Reaching and Exceeding Melting Points
This direct heating allows the furnace to reach very high temperatures quickly and in a controlled manner. It can easily surpass the melting points of metals ranging from aluminum and copper to high-temperature materials like steel, which melts at 1370°C (2500°F).
The Versatility of Induction Technology
A Broad Range of Metals
Induction furnaces are valued for their flexibility. They are used to melt a wide spectrum of materials beyond just aluminum.
This includes other non-ferrous metals like copper, brass, zinc, lead, gold, and silver, as well as ferrous metals like iron and steel.
Specialized Furnace Designs
Different types of induction furnaces are optimized for specific tasks. For example, a high-frequency induction furnace can melt a wide array of materials, including precious metals and even gold dust or tin slag.
For metals like aluminum that have a high affinity for oxygen, a vacuum induction melting furnace is ideal. It operates under a vacuum to prevent oxidation and contamination from atmospheric gases, resulting in higher purity alloys.
Handling By-Products
Beyond primary melting, induction furnaces are also designed to efficiently process by-products. This includes melting and recovering valuable metal from materials like dross, which is a common occurrence in aluminum processing.
Understanding the Advantages
Speed and Efficiency
The direct heating method is incredibly fast. A small induction furnace can melt an entire batch of metal in as little as three minutes. This speed translates directly to higher operational efficiency and throughput.
Precision and Control
Because the heat is generated by a controllable magnetic field, operators have very precise control over the temperature of the melt. This is critical when working with specific aluminum alloys that have narrow temperature windows for casting.
Cleanliness and Purity
Since there is no combustion involved, the melting process is exceptionally clean. There are no by-products of fuel to contaminate the metal. This, combined with the capabilities of a vacuum furnace, ensures a high-purity final product.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Choosing the right induction furnace depends entirely on the specific requirements of your application.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose melting: A standard induction furnace provides a reliable and efficient solution for melting aluminum, copper, and other common metals.
- If your primary focus is high-purity aluminum alloys: A vacuum induction furnace is the correct choice to prevent oxidation and ensure the highest material quality.
- If your primary focus is rapid melting of small or specialized batches: A high-frequency induction furnace offers unparalleled speed and versatility.
Ultimately, induction technology provides a powerful, precise, and adaptable solution for nearly any metal melting requirement.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit for Aluminum Melting |
|---|---|
| Direct Heating | Energy is transferred directly into the metal, ensuring fast and efficient melting. |
| Precise Temperature Control | Allows for exact control over the melt, crucial for specific aluminum alloys. |
| Clean Process | No combustion by-products, resulting in high-purity aluminum with minimal contamination. |
| Versatility | Capable of melting a wide range of metals, including aluminum, copper, brass, and precious metals. |
| Specialized Options | Vacuum furnaces available to prevent oxidation for high-purity aluminum alloys. |
Ready to enhance your lab's metal melting capabilities? KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment, including induction furnaces designed for precise and efficient melting of aluminum and other metals. Whether you need a standard furnace for general use or a vacuum model for high-purity applications, we have the right solution for your laboratory needs. Contact us today to discuss how our equipment can boost your productivity and ensure superior results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the technical value of using a quartz tube reaction chamber for static corrosion testing? Achieve Precision.
- What materials are used for the tubes in tube furnaces? A Guide to Selecting the Right Tube for Your Process
- How does a quartz tube vacuum furnace contribute to the crystallization process of Ag-doped Li-argyrodite electrolytes?
- What role does a quartz tube furnace play in hBN synthesis? Optimize Your Chemical Vapor Deposition Results
- What is a tubular furnace used for? Precision Heating for Material Synthesis & Analysis



















