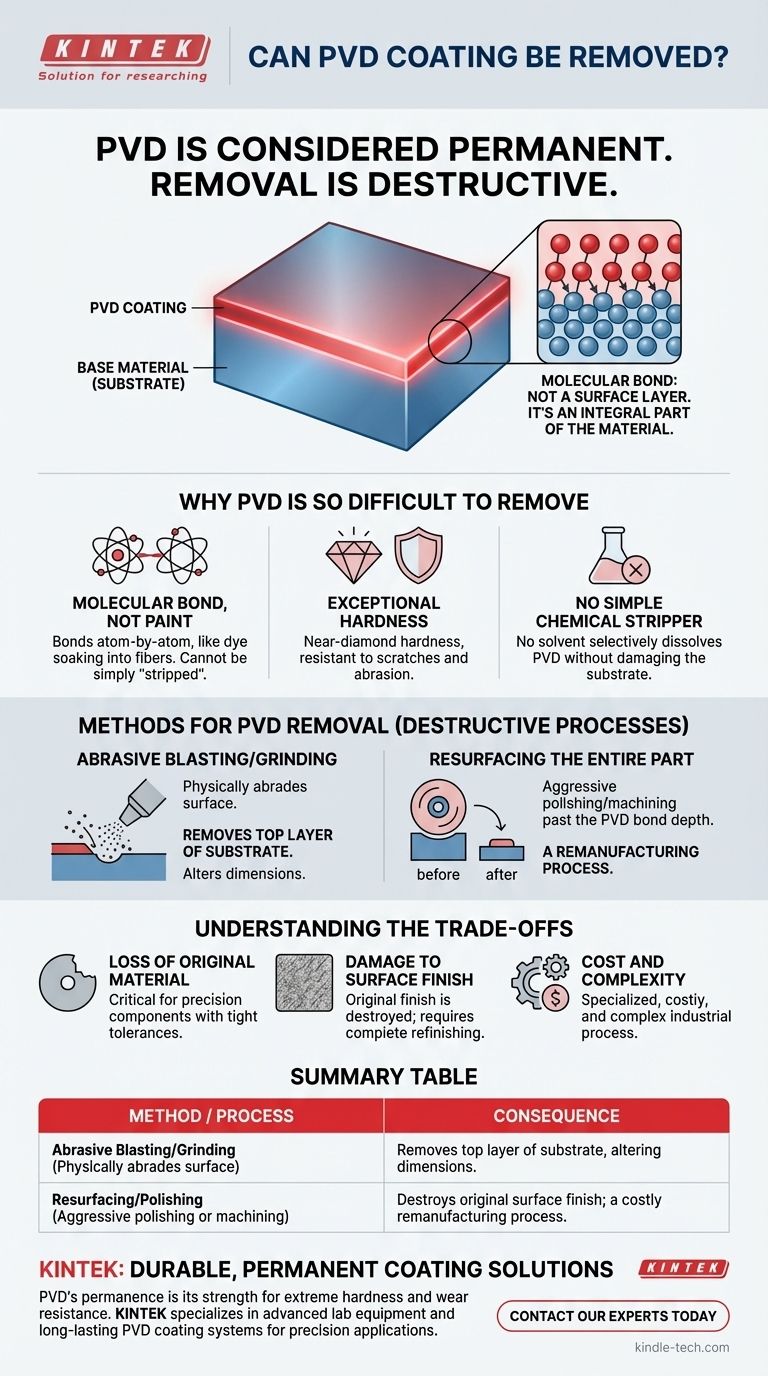
In practice, PVD coating is considered permanent. While it can be technically removed, the process is extremely difficult, destructive to the underlying material, and not comparable to stripping a conventional coating like paint. The methods required involve physically grinding or polishing away the coating, which also removes the surface of the object itself.
The core issue is that Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) is not a layer on the surface; it is a molecular bond with the surface. Therefore, to remove the PVD coating, you must remove the original material it has bonded to.

Why PVD is So Difficult to Remove
The permanence of PVD is a direct result of its application process and fundamental properties. Understanding this is key to appreciating why it cannot be simply "stripped."
It's a Molecular Bond, Not a Layer of Paint
A traditional coating, like paint or powder coat, sits on top of the substrate. PVD is different.
During the PVD process, a material is vaporized in a vacuum and deposits onto the substrate atom by atom. This creates an extremely thin film that intermingles with and bonds to the surface molecules of the base material itself.
It's less like a coat of paint on wood and more like a dye that has soaked into the wood fibers.
Exceptional Hardness and Durability
PVD coatings are valued for their extreme hardness, often approaching that of a diamond. This makes them incredibly resistant to scratches, wear, and abrasion.
This inherent toughness means that simple mechanical friction that would wear away other coatings has little to no effect on PVD.
There is No Simple Chemical "Stripper"
Because the PVD coating is atomically bonded to the metal, there is no chemical solvent that can selectively dissolve the coating without also attacking and damaging the underlying substrate.
Any acid or chemical agent aggressive enough to break down the PVD film would almost certainly cause pitting, corrosion, or dimensional changes to the part itself.
Methods for PVD Removal (And Their Consequences)
Attempting to remove a PVD coating is a specialized and aggressive process that should be seen as a last resort. It fundamentally alters the part.
Abrasive Blasting or Grinding
The most common method is physically abrading the surface until the coating is gone. This can be done with aggressive media blasting, grinding, or heavy polishing.
The critical consequence is that you are not just removing the coating; you are removing the top layer of the substrate material. This will change the part's dimensions and its original surface finish.
Resurfacing the Entire Part
For a uniform result, the entire part must be aggressively polished or machined down past the depth of the PVD bond.
This is a remanufacturing process, not a simple removal. It requires precision and is often more costly and complex than the original coating process.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The "permanence" of PVD is one of its greatest strengths, but it becomes a significant challenge if modification is ever needed.
Loss of Original Material
Any successful PVD removal guarantees a loss of the original base material. For precision components where tolerances are critical, this can render the part unusable.
Damage to Surface Finish
The original surface finish, whether polished, brushed, or matte, will be destroyed during the removal process. The part will need to be completely refinished from a raw state.
Cost and Complexity
PVD removal is not a DIY task. It requires specialized industrial equipment and expertise. In almost all scenarios, it is far more practical and cost-effective to replace the part than to attempt to strip and refinish it.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your approach should be dictated by your goal. The permanence of PVD is either a primary feature or a critical limitation, depending on your needs.
- If your primary focus is maximum durability: See PVD's permanence as a key advantage and design with the understanding that the finish is for the lifetime of the part.
- If you need to refinish or repair a PVD-coated item: Accept that removal is a destructive remanufacturing process and that creating a new part or re-coating over the old one is often the better path.
- If you are choosing a finish and anticipate future changes: You should consider PVD to be a final, irreversible step and explore other coating options if you require the ability to strip and re-coat easily.
Ultimately, you should treat a PVD coating as an integral and permanent modification of the material itself.
Summary Table:
| Method | Process | Consequence |
|---|---|---|
| Abrasive Blasting/Grinding | Physically abrades the surface | Removes the top layer of the substrate, altering dimensions |
| Resurfacing/Polishing | Aggressive polishing or machining | Destroys original surface finish; a costly remanufacturing process |
Need a Durable, Permanent Coating Solution for Your Components?
PVD's permanence is its greatest strength for applications requiring extreme hardness and wear resistance. At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced lab equipment and consumables, including PVD coating systems designed for precision and longevity. Our solutions are tailored to meet the rigorous demands of laboratory and industrial environments.
Let us help you achieve a finish that lasts the lifetime of your part. Contact our experts today to discuss how our PVD technology can benefit your specific application.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- VHP Sterilization Equipment Hydrogen Peroxide H2O2 Space Sterilizer
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Special Shape Evaporation Boat
People Also Ask
- What is an example of PECVD? RF-PECVD for High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- Why does PECVD commonly use RF power input? For Precise Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What is plasma activated chemical vapour deposition method? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings
- What are the applications of PECVD? Essential for Semiconductors, MEMS, and Solar Cells
- What are the advantages of PECVD? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin-Film Deposition



















