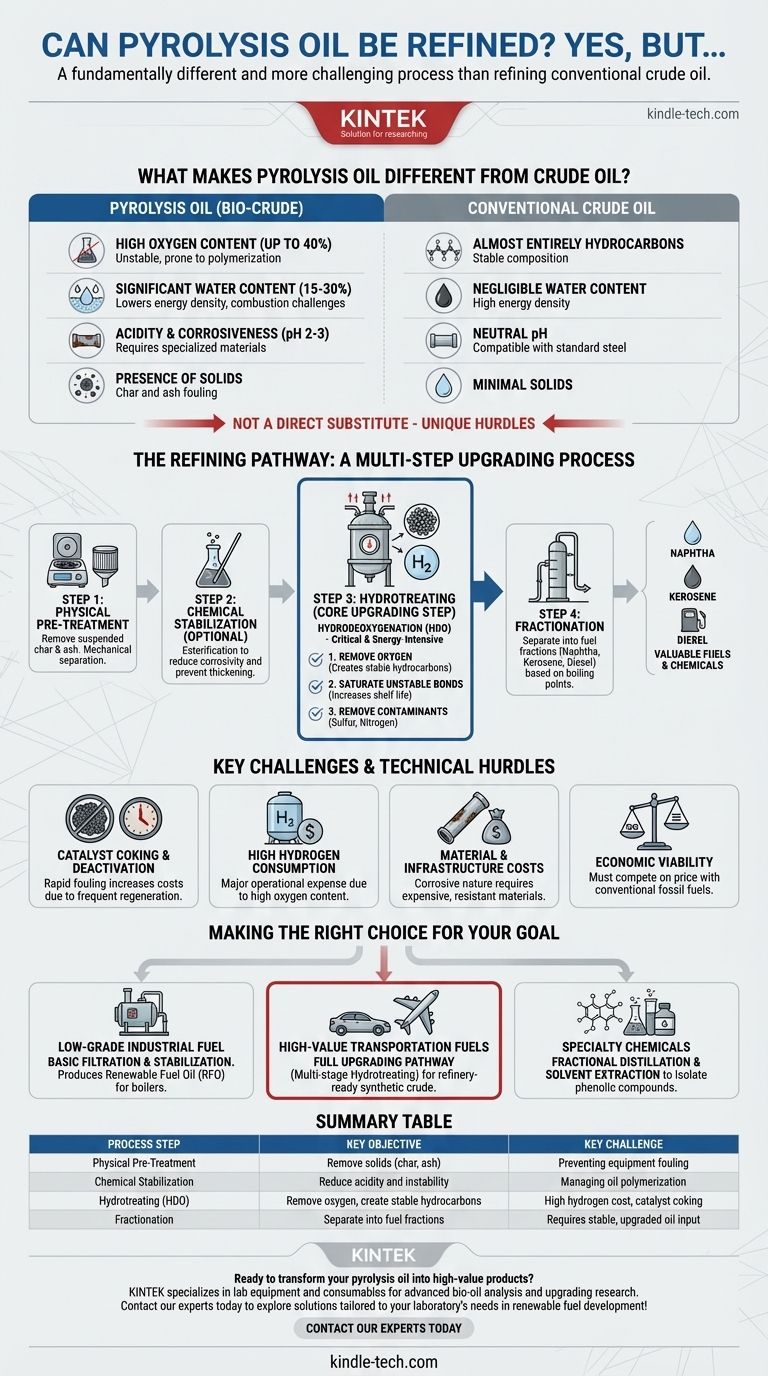
Yes, pyrolysis oil can be refined, but it is a fundamentally different and more challenging process than refining conventional crude oil. It requires specialized pre-treatment and chemical upgrading to manage its inherent instability, high oxygen content, and corrosiveness before it can yield valuable fuels or chemicals.
The core challenge of refining pyrolysis oil is not simple separation, but rather a process of decontamination and stabilization. Its value is unlocked by first removing aggressive contaminants like oxygen and acids through a critical upgrading step, most commonly hydrotreating, which makes it suitable for further processing.

What Makes Pyrolysis Oil Different from Crude Oil?
Before discussing refining, it is critical to understand that pyrolysis oil, often called bio-crude, is not a direct substitute for fossil crude oil. Its unique chemical composition presents several major hurdles.
High Oxygen Content
Unlike crude oil, which is almost entirely hydrocarbons (hydrogen and carbon), pyrolysis oil can contain up to 40% oxygen by weight. This oxygen is bound in molecules like acids, aldehydes, and phenols, which makes the oil unstable and prone to polymerization (thickening into sludge) over time.
Significant Water Content
Pyrolysis oil often contains a significant amount of water, typically between 15-30%. This water is finely emulsified within the oil, lowering its energy density and creating challenges for processing and combustion.
Acidity and Corrosiveness
The presence of organic acids, particularly acetic and formic acid, makes pyrolysis oil highly acidic (with a pH of 2-3). This makes it extremely corrosive to standard steel pipes, pumps, and storage tanks, requiring specialized and more expensive materials.
Presence of Solids
Raw pyrolysis oil contains fine particles of char and ash carried over from the pyrolysis reactor. These solids must be removed through filtration to prevent downstream equipment fouling and catalyst poisoning.
The Refining Pathway: A Multi-Step Upgrading Process
Refining pyrolysis oil is less about simple distillation and more about a chemical transformation called upgrading. The goal is to create a stable, energy-dense, and non-corrosive synthetic crude oil that can be co-processed in a traditional refinery.
Step 1: Physical Pre-Treatment
The first step is always mechanical. This involves filtering or using centrifuges to remove the suspended char and ash particles from the raw oil.
Step 2: Chemical Stabilization (Optional but Recommended)
To manage the oil's inherent instability, a mild upgrading step like esterification (reacting the acids with an alcohol) can be used. This reduces corrosivity and prevents the oil from thickening during storage or heating.
Step 3: Hydrotreating (The Core Upgrading Step)
This is the most critical and energy-intensive stage. The oil is heated under high pressure in the presence of a catalyst and large quantities of hydrogen. This process, known as hydrodeoxygenation (HDO), achieves three vital goals:
- It removes oxygen atoms, converting organic compounds into stable hydrocarbons.
- It saturates unstable chemical bonds, increasing the oil's shelf life.
- It removes other contaminants like sulfur and nitrogen.
The output of this stage is a stable, deoxygenated synthetic crude oil with properties much closer to fossil crude.
Step 4: Fractionation
Once the oil has been upgraded, it can be distilled (fractionated) in a manner similar to conventional crude oil. This process separates the synthetic crude into different cuts based on their boiling points, such as naphtha (for gasoline blending), kerosene (for jet fuel), and diesel.
Key Challenges and Technical Hurdles
While technically feasible, upgrading pyrolysis oil faces significant economic and technical obstacles that are crucial to understand.
Catalyst Coking and Deactivation
The reactive compounds in raw pyrolysis oil can quickly foul and deactivate the expensive catalysts used in hydrotreating. This rapid "coking" increases operational costs due to the need for frequent catalyst regeneration or replacement.
High Hydrogen Consumption
Hydrotreating is an expensive process primarily because hydrogen is a costly industrial commodity. The high oxygen content of pyrolysis oil means a very large amount of hydrogen is consumed during upgrading, representing a major operational expense.
Material and Infrastructure Costs
The corrosive nature of raw bio-crude and the high pressures required for hydrotreating demand the use of expensive, corrosion-resistant materials like stainless steel, increasing the capital cost of the entire facility.
Economic Viability
Ultimately, the high cost of upgrading—driven by hydrogen consumption, catalyst replacement, and capital expenditure—is the largest barrier. The final product must be able to compete on price with conventional fossil fuels, which remains a significant challenge.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The optimal strategy for treating pyrolysis oil depends entirely on your end-market and economic constraints.
- If your primary focus is creating a low-grade industrial fuel: Consider only basic filtration and stabilization. This produces a renewable fuel oil (RFO) suitable for use in industrial boilers and furnaces where crude combustion is acceptable.
- If your primary focus is producing high-value transportation fuels: You must invest in a full upgrading pathway centered on robust, multi-stage hydrotreating to create a refinery-ready synthetic crude oil.
- If your primary focus is extracting specialty chemicals: Your strategy should involve fractional distillation and solvent extraction before major upgrading to isolate valuable phenolic compounds for use in resins, adhesives, and flavorings.
Successfully refining pyrolysis oil is about transforming a challenging, waste-derived intermediate into a stable and valuable commodity by systematically addressing its inherent chemical complexities.
Summary Table:
| Process Step | Key Objective | Key Challenge |
|---|---|---|
| Physical Pre-Treatment | Remove solids (char, ash) | Preventing equipment fouling |
| Chemical Stabilization | Reduce acidity and instability | Managing oil polymerization |
| Hydrotreating (HDO) | Remove oxygen, create stable hydrocarbons | High hydrogen cost, catalyst coking |
| Fractionation | Separate into fuel fractions (e.g., diesel, naphtha) | Requires stable, upgraded oil input |
Ready to transform your pyrolysis oil into high-value products? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables for advanced bio-oil analysis and upgrading research. Whether you're developing stabilization methods or optimizing hydrotreating catalysts, our precision tools help you overcome technical hurdles efficiently. Contact our experts today to explore solutions tailored to your laboratory's needs in renewable fuel development!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Heated Vacuum Press Machine Tube Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a vacuum hot pressing furnace facilitate the densification of Eu:Y2O3 scintillator ceramics?
- How does a vacuum hot press sintering furnace contribute to graphite/copper composites? Key Benefits & Mechanisms
- What is the primary function of a vacuum hot pressing furnace? Mastering SiC Fiber-Reinforced Composite Fabrication
- How does furnace temperature control affect Diamond/Al-Cu composites? Maximize Phase Control and Thermal Performance.
- Why Use a Vacuum Hot Press for SiCp/6061 Composites? Ensure Pure Interface Bonding and Maximum Density



















