Yes, absolutely. Stainless steel is one of the most common and versatile materials used in the powder metallurgy (PM) process, also known as sintering. This method is widely employed to create complex, net-shape stainless steel parts for industries ranging from automotive and aerospace to medical and consumer goods.
The question is not whether stainless steel can be sintered, but when it is the right manufacturing choice. Sintering excels at producing intricate parts in high volumes at a lower cost, but this comes with specific trade-offs in mechanical properties compared to traditional wrought or machined steel.
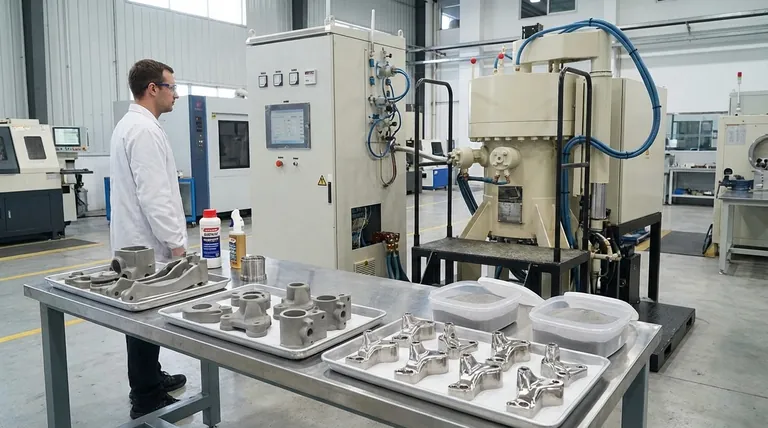

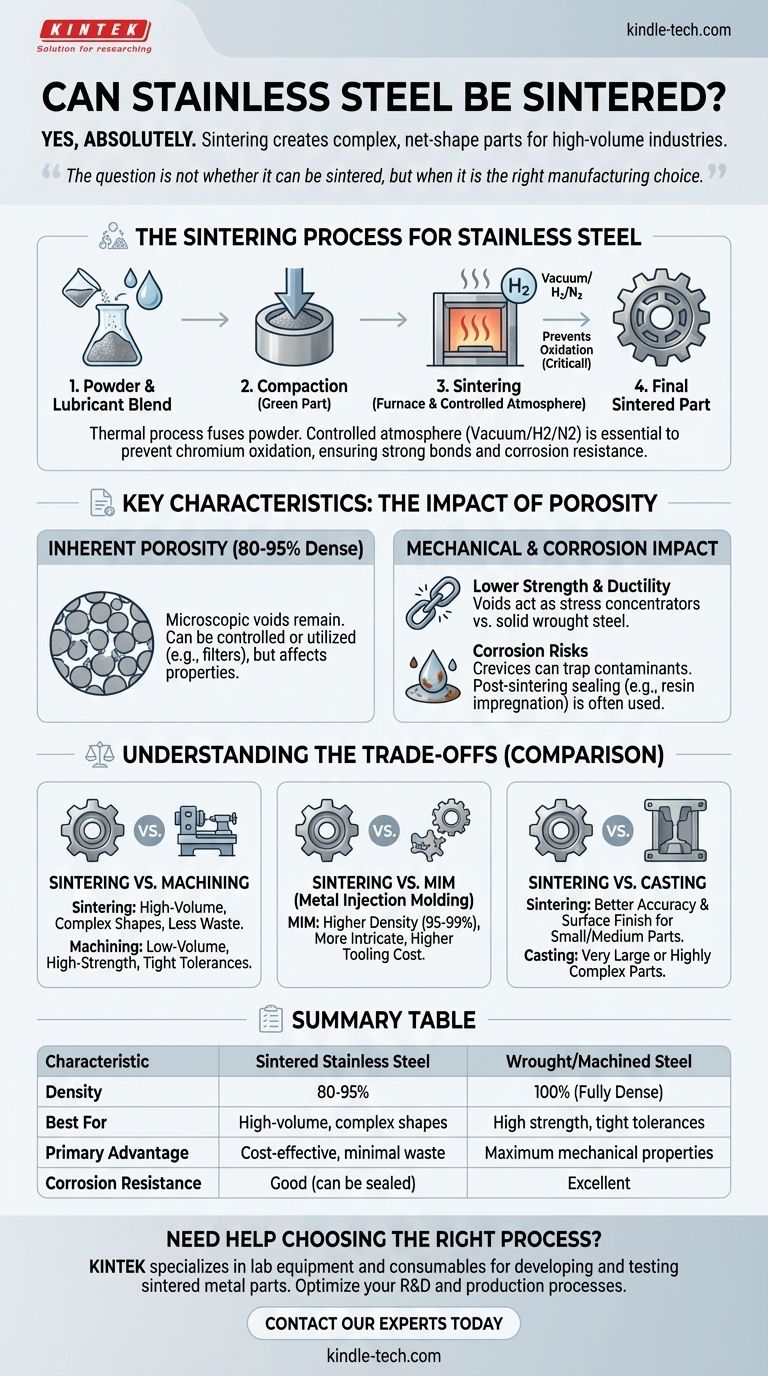
What Sintering Means for Stainless Steel
Sintering is a thermal process that fuses metal powder particles together, transforming a compacted powder shape into a solid, functional component. For stainless steel, this process has unique considerations.
The Powder Metallurgy Steps
First, a fine stainless steel powder (such as 316L or 410) is blended with a lubricant. This mix is then poured into a die and compacted under high pressure to form a "green part," which is solid but fragile.
The final and most critical step is sintering. The green part is placed in a tightly controlled atmosphere furnace and heated to a temperature just below the material's melting point, causing the individual powder particles to bond and densify.
Why the Furnace Atmosphere is Critical
Stainless steel gets its corrosion resistance from chromium, which readily oxidizes when heated. If sintered in a standard air atmosphere, the chromium on the surface of each powder particle would form an oxide layer, preventing the particles from fusing properly.
To prevent this, stainless steel must be sintered in a controlled atmosphere, typically a vacuum or a dry hydrogen/nitrogen mix. This protective atmosphere prevents oxidation and allows for strong metallurgical bonds to form, ensuring the final part has the desired strength and corrosion resistance.
The Primary Benefit: Complex Shapes, Less Waste
The main advantage of sintering stainless steel is its ability to produce complex, three-dimensional parts to their final (or "net") shape with minimal waste. This is a sharp contrast to subtractive manufacturing like machining, where you start with a solid block and cut away material.
For high-volume production runs, this translates to significant cost savings on both material and secondary machining operations.
Key Characteristics of Sintered Stainless Steel
Understanding sintered stainless steel requires acknowledging its fundamental difference from steel bar stock: inherent, controlled porosity.
Inherent Porosity
Even after sintering, microscopic voids remain between the original powder particles. This means sintered parts are typically 80-95% as dense as their solid, wrought counterparts.
This porosity is not necessarily a defect; it can be controlled and even utilized for applications like self-lubricating bearings or filters. However, it directly impacts the part's physical properties.
Mechanical Properties
Due to this porosity, a sintered stainless steel part will generally exhibit lower tensile strength and ductility than an identical part machined from solid bar stock. The voids act as stress concentrators, making the material slightly less tough.
Corrosion Resistance
Porosity can create crevices where moisture or contaminants can become trapped, potentially compromising the corrosion resistance for which stainless steel is known. For demanding applications, post-sintering processes like resin impregnation can be used to seal this surface porosity.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing sintering is a strategic decision based on cost, volume, and performance requirements.
Sintering vs. Machining
Sintering is ideal for high-volume (thousands to millions of parts) production of complex shapes where the ultimate strength of wrought material is not required. Machining is superior for low-volume production, high-strength applications, and achieving the tightest possible tolerances.
Sintering vs. Metal Injection Molding (MIM)
MIM is a related powder metallurgy process that can achieve much higher densities (95-99%) and create even more intricate geometries than conventional sintering. It is an excellent choice for smaller, highly complex parts but comes with significantly higher tooling costs.
Sintering vs. Casting
Casting is well-suited for very large or highly complex parts that would be impossible to compact in a die. Sintering generally offers superior dimensional accuracy and a better surface finish for small to medium-sized components.
Making the Right Choice for Your Project
Selecting the correct manufacturing process requires aligning the method's strengths with your primary goal.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective, high-volume production of a complex part: Sintering is a leading candidate that minimizes material waste and machining time.
- If your primary focus is maximum strength, impact toughness, or fatigue life: Machining from solid wrought stainless steel bar is the superior and more reliable choice.
- If your primary focus is the absolute best corrosion resistance in a critical environment: A fully dense, machined part is generally preferred, though properly processed sintered 316L can be highly effective.
- If your primary focus is an extremely intricate, small part with high performance needs: Metal Injection Molding (MIM) should be strongly considered as a more capable alternative.
Ultimately, choosing to sinter stainless steel is an engineering decision that balances the unique design freedom and economic benefits of the process against its inherent material properties.
Summary Table:
| Characteristic | Sintered Stainless Steel | Wrought/Machined Steel |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 80-95% of theoretical | 100% (Fully Dense) |
| Best For | High-volume, complex shapes | High strength, tight tolerances |
| Primary Advantage | Cost-effective, minimal waste | Maximum mechanical properties |
| Corrosion Resistance | Good (can be sealed) | Excellent |
Need help choosing the right manufacturing process for your stainless steel components?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the lab equipment and consumables essential for developing and testing sintered metal parts. Whether you're in R&D or production, our expertise can help you optimize your sintering process for superior results.
Contact our experts today to discuss how KINTEK's solutions can support your laboratory and manufacturing goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the impact factor of powder metallurgy progress? A 2022 Analysis & Context
- What technical functions does a vacuum hot pressing sintering furnace provide? Optimize CoCrFeNi Alloy Coatings
- How does a vacuum environment system contribute to the hot pressing sintering of B4C-CeB6? Unlock Peak Ceramic Density
- What is the function of a VHPS system in CoCrFeNiMn alloys? Achieve Near-Theoretical Density and High Purity
- What are the primary advantages of using a vacuum hot pressing sintering furnace? Maximize Density in B4C-CeB6 Ceramics



















