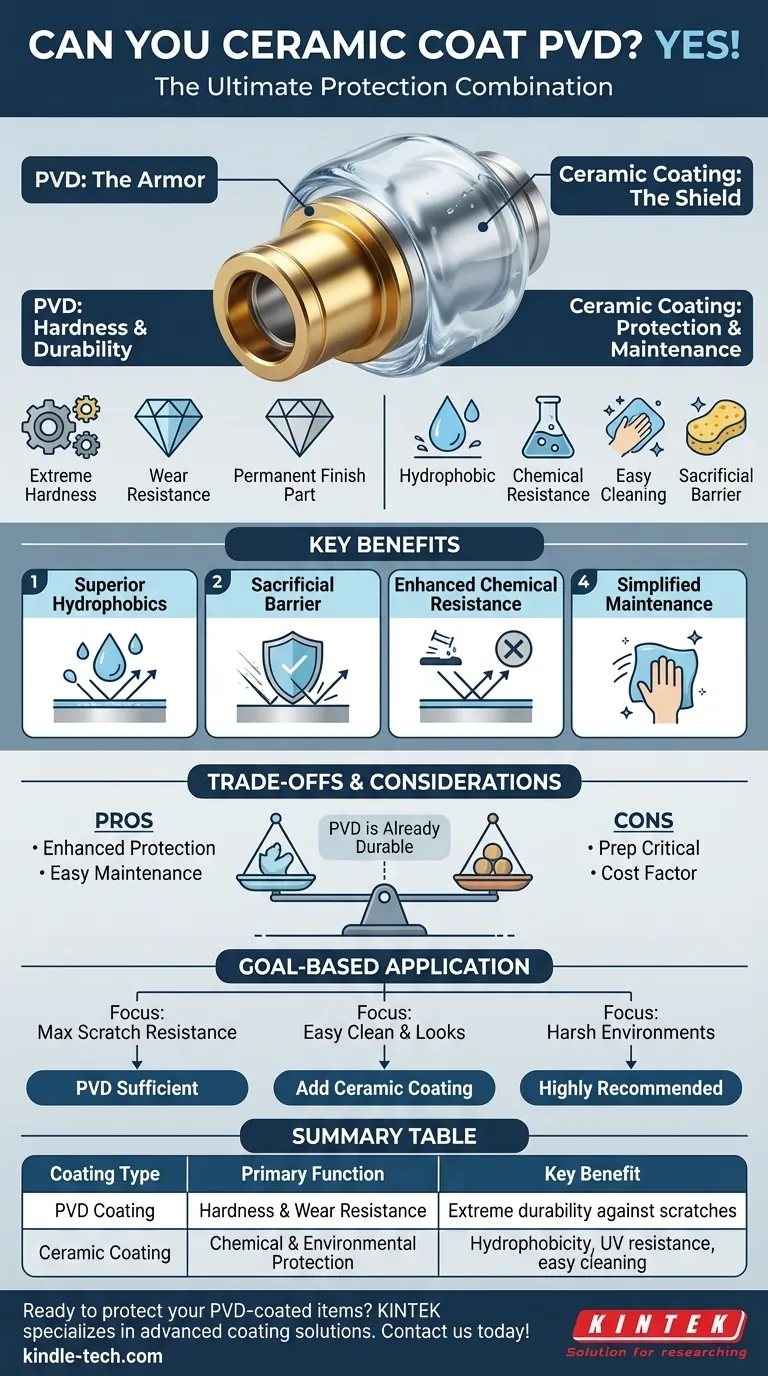
Yes, you can absolutely apply a ceramic coating to a PVD surface. A high-quality ceramic coating will bond effectively to PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition) finishes, providing an additional layer of protection and enhancing its properties. The key to success lies not in whether it's possible, but in meticulous surface preparation before application.
While PVD provides exceptional hardness and abrasion resistance, a ceramic coating adds complementary benefits: superior chemical resistance, hydrophobicity, and a sacrificial barrier. Think of PVD as the armor and the ceramic coating as the invisible, self-cleaning shield that protects the armor.
The Role of Each Coating
To understand why you would combine these two technologies, it's essential to recognize their distinct functions. They are not redundant; they serve different primary purposes.
What PVD Provides: Hardness and Durability
PVD is a process that deposits a very thin, extremely hard layer of metal or ceramic material onto a substrate. Its primary benefits are durability and wear resistance.
The PVD coating is fundamentally part of the item's finish. As the references note, it perfectly conforms to the underlying surface, meaning a polished part will have a polished PVD finish, and a brushed part will have a brushed PVD finish.
What a Ceramic Coating Provides: Protection and Maintenance
A ceramic coating is a liquid-polymer that bonds chemically with a surface to create a semi-permanent, transparent layer of protection. Its primary benefits are environmental protection and ease of cleaning.
This nano-coating creates a slick, hydrophobic surface that repels water, dirt, and contaminants, while also offering resistance to UV rays and harsh chemicals.
Key Benefits of Ceramic Coating a PVD Surface
Applying a ceramic coating over PVD isn't about making it harder; it's about making it better protected and easier to live with, especially on items like car wheels or bathroom fixtures.
Adds Superior Hydrophobics
PVD finishes are not inherently hydrophobic. A ceramic coating creates intense water beading and sheeting, which helps the surface "self-clean" during a rainstorm or rinse.
Creates a Sacrificial Barrier
The ceramic coating acts as the first line of defense. Light scratches, acidic bird droppings, or harsh chemical cleaners will damage the replaceable ceramic coating before they can etch or harm the permanent PVD finish underneath.
Enhances Chemical Resistance
Items like wheels are constantly exposed to corrosive brake dust, road salts, and aggressive wheel cleaners. A ceramic coating provides a robust barrier against these chemicals, preventing staining and corrosion of the PVD finish.
Simplifies Maintenance
The slick, non-stick nature of a ceramic coating means that brake dust, grime, and mineral deposits from water have a much harder time bonding to the surface. Cleaning often requires little more than a gentle wash.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While beneficial, adding a ceramic coating is not a magic bullet. Objectivity requires acknowledging the trade-offs.
The PVD is Already Durable
Do not mistake the benefits of a ceramic coating for a weakness in PVD. PVD is an exceptionally tough and long-lasting finish on its own. The ceramic layer is an enhancement for maintenance and chemical protection, not a necessity for durability against physical wear.
Surface Preparation is Critical
A ceramic coating will fail if the PVD surface is not perfectly clean. Any oils, waxes, or residues from manufacturing or handling will prevent a proper chemical bond. The surface must be decontaminated with a panel prep spray or isopropyl alcohol (IPA) immediately before application.
Cost vs. Added Benefit
You must weigh the cost of a quality ceramic coating and the time for application against the benefits. For a show car's wheels or high-end kitchen fixtures, the investment is easily justified. For a less critical item, the inherent durability of PVD may be sufficient.
How to Apply This to Your Goal
Your decision should be based on your specific goal for the PVD-coated item.
- If your primary focus is maximum scratch and wear resistance: The PVD coating itself already provides this core benefit. A ceramic coating is a helpful, but secondary, addition.
- If your primary focus is ease of cleaning and long-term appearance: Applying a ceramic coating is an excellent decision. It will dramatically reduce the time and effort needed to keep the PVD finish looking new.
- If the item is in a harsh environment (like car wheels): A ceramic coating is highly recommended. It provides crucial protection against brake dust and road chemicals that can eventually damage even a tough PVD finish.
By combining the physical hardness of PVD with the chemical protection of a ceramic coating, you are creating a finish that is truly the best of both worlds.

Summary Table:
| Coating Type | Primary Function | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| PVD Coating | Hardness & Wear Resistance | Extreme durability against scratches and abrasion |
| Ceramic Coating | Chemical & Environmental Protection | Hydrophobicity, UV resistance, and easy cleaning |
Ready to protect your PVD-coated items with a professional-grade ceramic coating? KINTEK specializes in advanced coating solutions for laboratory equipment and precision components. Our expertise ensures your surfaces receive the highest level of protection and performance. Contact us today to learn how we can enhance the durability and longevity of your lab equipment!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Lab Plastic PVC Calender Stretch Film Casting Machine for Film Testing
- Touchscreen Automatic Vacuum Heat Press
- Lab Blown Film Extrusion Three Layer Co-Extrusion Film Blowing Machine
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Herbal Powder Sterilization Machine for Plant
People Also Ask
- What are the effects of magnetron sputtering? Achieve High-Quality, Durable Thin Films for Your Lab
- Is sputtering a PVD? Discover the Key Coating Technology for Your Lab
- What is deposition in environmental chemistry? Understanding How Air Pollution Harms Ecosystems
- What is magnetron sputtering machine? Precision Thin-Film Deposition for Advanced Materials
- How many types of vapor phase deposition techniques are present? PVD vs. CVD Explained



















