Yes, you can absolutely melt copper using an induction furnace. This is not just possible but is a common, highly effective, and modern method used across various industries. Induction furnaces are prized for their ability to provide the precise temperature control and low metal loss required for high-quality copper and copper alloy applications.
Induction heating offers a superior method for melting copper, providing exceptional speed, purity, and temperature control. The core advantage is its ability to generate heat directly within the copper itself, bypassing the inefficiencies and contamination risks of traditional fuel-fired furnaces.
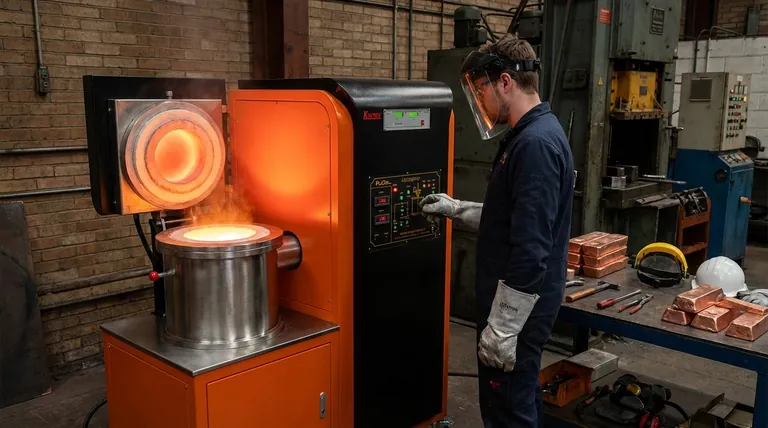

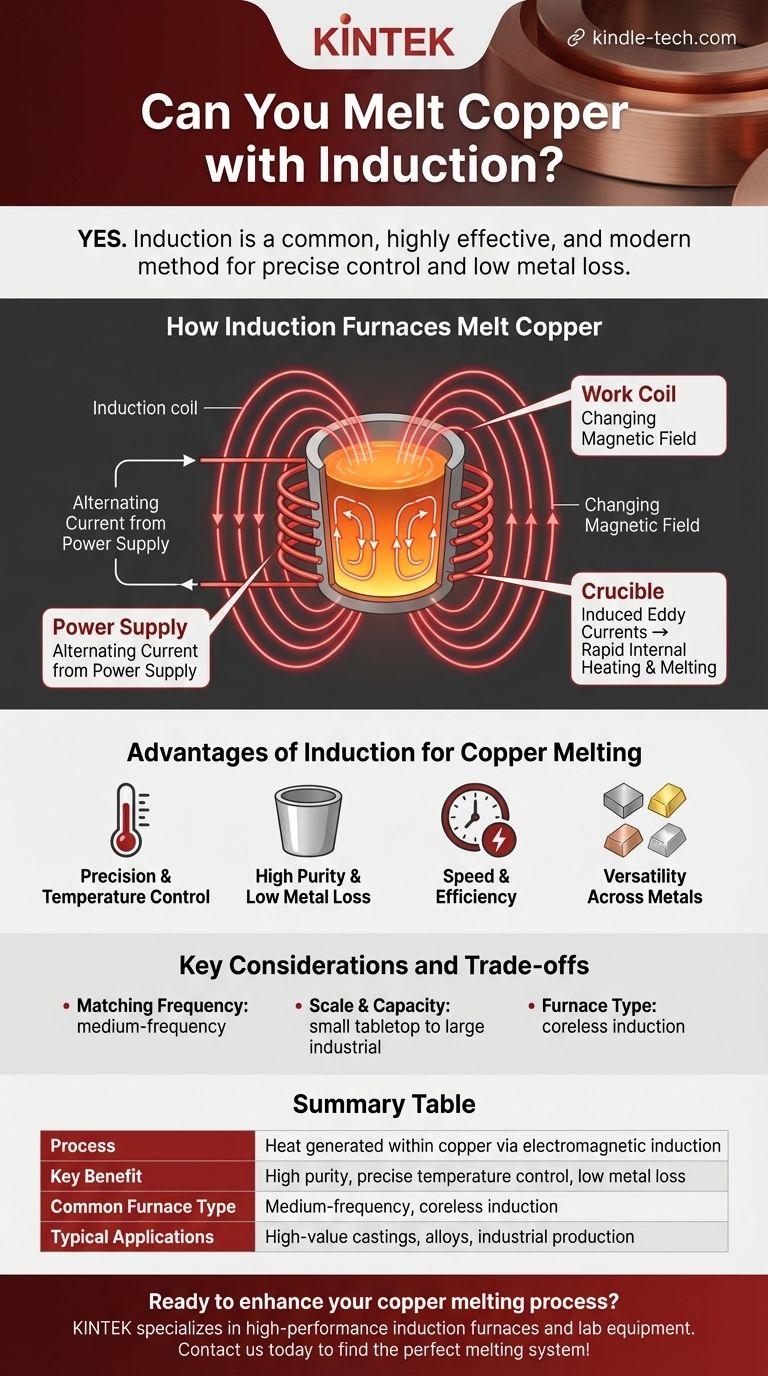
How Induction Furnaces Melt Copper
Induction melting is a clean, contained process that relies on the principles of electromagnetism. It's fundamentally different from using an external flame or heating element.
The Principle of Induction
An induction furnace uses a powerful alternating current passed through a copper coil. This coil generates a rapidly changing magnetic field around the crucible holding the copper to be melted.
Generating Heat Directly
This magnetic field induces powerful electrical currents, known as eddy currents, directly within the copper. The copper's natural electrical resistance causes it to heat up rapidly and intensely as these currents flow, leading it to melt from the inside out.
Key Components
The system consists of three main parts: the power supply (which provides the high-frequency electricity), the work coil (which creates the magnetic field), and the crucible (a container that holds the copper but is unaffected by the magnetic field).
The Advantages of Induction for Copper Melting
Professionals choose induction for copper for several distinct and compelling reasons that directly impact the quality of the final product.
Precision and Temperature Control
Induction offers unparalleled control over the melting temperature. This is critical when working with copper alloys like brass or bronze, where precise temperatures are needed to achieve specific material properties and avoid damaging the metal.
High Purity and Low Metal Loss
Because there is no combustion, no gases or impurities are introduced into the molten copper. The references highlight low metal loss as a key benefit, as the metal is not being burned away or reacting with byproducts from a flame.
Speed and Efficiency
Heat is generated instantly and directly within the copper, making the melting process significantly faster and more energy-efficient than many alternative methods. This translates to higher productivity and lower operational costs.
Versatility Across Metals
The same medium-frequency induction furnace used for copper can also effectively melt a wide range of other materials. This includes steel, aluminum, iron, and even precious metals like gold and silver.
Key Considerations and Trade-offs
While highly effective, choosing the right induction setup requires understanding a few technical factors. This isn't a one-size-fits-all technology.
Matching Frequency to the Job
The references specifically mention medium-frequency furnaces. The frequency of the electrical current is a critical parameter that influences heating efficiency and is selected based on the type of metal and the size of the melt.
Scale and Capacity
Induction furnaces are highly scalable. They can range from small tabletop units melting as little as 3KG for custom castings or jewelry, up to industrial furnaces capable of melting 500KG or more for large-scale production.
Furnace Type
Coreless induction furnaces are a common design used for melting copper and other non-ferrous alloys. In this design, the crucible is placed directly within the coil, allowing for efficient energy transfer and a strong stirring action that ensures a homogenous melt.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right melting process depends entirely on the goal of your work.
- If your primary focus is high-value custom castings or alloys: Induction is the ideal choice due to its precise temperature control and minimal metal loss.
- If your primary focus is consistent industrial production: The scalability and efficiency of induction furnaces make them a reliable solution for casting large bronze structures or other copper-based products.
- If your primary focus is workshop versatility: A medium-frequency induction furnace provides the flexibility to work with a wide variety of metals beyond just copper.
Ultimately, using induction is about embracing a controlled, clean, and highly efficient method for transforming solid copper into a liquid state.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Induction Melting for Copper |
|---|---|
| Process | Heat generated directly within the copper via electromagnetic induction |
| Key Benefit | High purity, precise temperature control, and low metal loss |
| Common Furnace Type | Medium-frequency, coreless induction furnace |
| Typical Applications | High-value castings, copper alloys (brass, bronze), industrial production |
Ready to enhance your copper melting process? KINTEK specializes in high-performance induction furnaces and lab equipment, delivering the precise temperature control and purity your laboratory or production facility requires. Whether you're working with copper, its alloys, or other metals, our solutions ensure efficiency and superior results. Contact us today to find the perfect melting system for your needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Non Consumable Vacuum Arc Induction Melting Furnace
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Induction Melting Spinning System Arc Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between VAR and VIM? Legacy Vimscript Variables vs. Modern Neovim API
- How does vacuum arc melting equipment facilitate Ti-Cr-Al-Nb alloy prep? Precision High-Temp Melting Explained
- Does higher heat capacity mean higher melting point? Unraveling the Critical Difference
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of brazing? A Guide to Strong, Clean Metal Joining
- What is the role of a laboratory vacuum arc remelting furnace? Mastering High-Entropy Alloy Synthesis



















