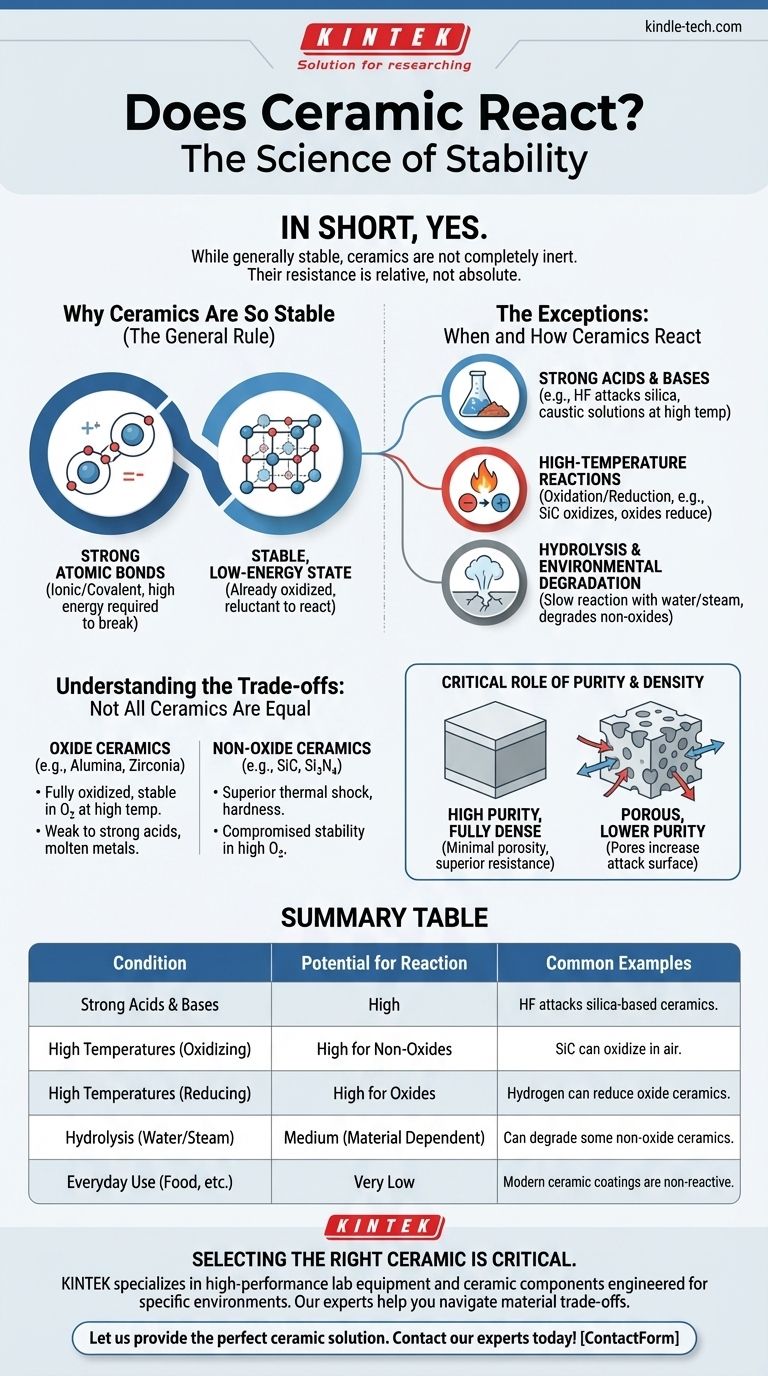
In short, yes. While ceramics are famous for their chemical stability, they are not completely inert. Under specific conditions involving aggressive chemicals, high temperatures, or prolonged environmental exposure, ceramics can and do react.
The core principle to understand is that ceramic inertness is relative, not absolute. Their resistance comes from incredibly strong atomic bonds, but potent chemicals or extreme energy (like high heat) can break those bonds, often through the same types of reactions used to create the ceramic in the first place.

Why Ceramics Are So Stable (The General Rule)
Strong Atomic Bonds
The defining characteristic of a ceramic material is its powerful atomic bonds. These are typically ionic (electrons are transferred) or covalent (electrons are shared).
These bonds require a significant amount of energy to break, which is why ceramics generally exhibit high hardness, high melting points, and excellent chemical resistance compared to metals or polymers.
A Stable, Low-Energy State
Most common ceramics, like aluminum oxide or silicon dioxide, are already in a highly stable, oxidized state. They have already reacted with oxygen and settled into a low-energy configuration, making them reluctant to react further under normal conditions.
The Exceptions: When and How Ceramics React
The stability of a ceramic can be overcome. The conditions that cause a reaction are often specific and aggressive, directly targeting the atomic bonds that give the material its strength.
Reaction with Strong Acids and Bases
Certain powerful acids and bases can chemically attack ceramics. The most well-known example is hydrofluoric acid (HF), which is one of the few substances that can dissolve silica-based ceramics like glass and quartz.
Strong alkaline or caustic solutions can also slowly corrode some oxide ceramics, such as aluminum oxide, especially at elevated temperatures.
High-Temperature Reactions (Redox Chemistry)
The processes mentioned in ceramic synthesis—oxidation and reduction—can also be a source of degradation.
At very high temperatures, a non-oxide ceramic like silicon carbide (SiC) can be forced to react with oxygen, converting it into silicon dioxide (SiO₂) and carbon monoxide. Conversely, an oxide ceramic can be "reduced" if heated in the presence of a strong reducing agent like hydrogen or carbon, stripping oxygen atoms away from the ceramic.
Hydrolysis and Environmental Degradation
Some ceramic types, particularly non-oxide ceramics or those with certain grain boundary compositions, can be susceptible to hydrolysis.
This is a slow reaction with water or steam, often at high temperatures, that can degrade the material's mechanical properties over time. This is a critical consideration for components used in turbines or geothermal energy systems.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Not All Ceramics Are Equal
The term "ceramic" covers a vast family of materials. Their reactivity depends heavily on their specific chemistry and structure.
Oxide vs. Non-Oxide Ceramics
Oxide ceramics (e.g., Alumina, Zirconia) are already fully oxidized. This makes them exceptionally stable in oxygen-rich environments, even at high temperatures. Their weakness tends to be very strong acids or molten metals.
Non-oxide ceramics (e.g., Silicon Carbide, Silicon Nitride, Boron Nitride) offer superior properties in other areas, like thermal shock resistance or hardness. However, their stability is compromised in highly oxidizing atmospheres at extreme temperatures, as they can react with oxygen.
The Critical Role of Purity and Density
Chemical attack often begins at weak points. In ceramics, these weak points are impurities and the boundaries between crystalline grains.
A high-purity, fully dense ceramic with minimal porosity will have vastly superior chemical resistance compared to a porous, lower-purity version of the same material. Pores increase surface area, giving chemicals more opportunity to attack the material.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Choosing the right ceramic requires matching the material's specific resistances to the demands of your environment.
- If your primary focus is maximum chemical inertness for labware or medical use: Select a high-purity, fully dense oxide ceramic like alumina (Al₂O₃) or yttria-stabilized zirconia (YSZ), but always verify its resistance to your specific chemical agents.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature performance in air: An oxide ceramic is almost always the superior choice due to its inherent stability in oxidizing atmospheres.
- If your primary focus is performance in an inert or reducing high-temperature environment: A non-oxide ceramic like silicon carbide (SiC) or silicon nitride (Si₃N₄) may provide better mechanical performance and stability.
- If your primary focus is everyday use like cookware: Modern ceramic coatings are engineered to be non-reactive with all common food acids and bases and are exceptionally safe for their intended purpose.
By understanding that ceramic stability is conditional, you can select the precise material to ensure performance, safety, and longevity in your specific application.
Summary Table:
| Condition | Potential for Reaction | Common Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Strong Acids & Bases | High | Hydrofluoric acid (HF) attacks silica-based ceramics. |
| High Temperatures (Oxidizing) | High for Non-Oxides | Silicon carbide (SiC) can oxidize in air. |
| High Temperatures (Reducing) | High for Oxides | Hydrogen can reduce oxide ceramics. |
| Hydrolysis (Water/Steam) | Medium (Material Dependent) | Can degrade some non-oxide ceramics over time. |
| Everyday Use (Food, etc.) | Very Low | Modern ceramic coatings are engineered to be non-reactive. |
Selecting the right ceramic is critical for your application's performance and safety. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including ceramic components engineered for specific chemical and thermal environments. Our experts can help you navigate material trade-offs between oxide and non-oxide ceramics to ensure longevity and reliability.
Let us provide the perfect ceramic solution for your laboratory needs. Contact our experts today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide (SIC) Ceramic Sheet Wear-Resistant Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Engineering Advanced Fine Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Rod Insulated for Industrial Applications
- Zirconia Ceramic Gasket Insulating Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Precision Machined Zirconia Ceramic Ball for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Hexagonal Boron Nitride HBN Ceramic Ring
People Also Ask
- What are the properties of SiC? Unlock High-Temperature, High-Frequency Performance
- What is the resistivity of silicon carbide? It's a tunable property from <0.1 ohm-cm to highly resistive.
- What is the strongest ceramics? Silicon Carbide Leads in Hardness & Thermal Strength
- What are the properties and applications of silicon carbide ceramics? Solve Extreme Engineering Challenges
- Which is harder silicon carbide or tungsten carbide? Discover the Key to Material Selection



















