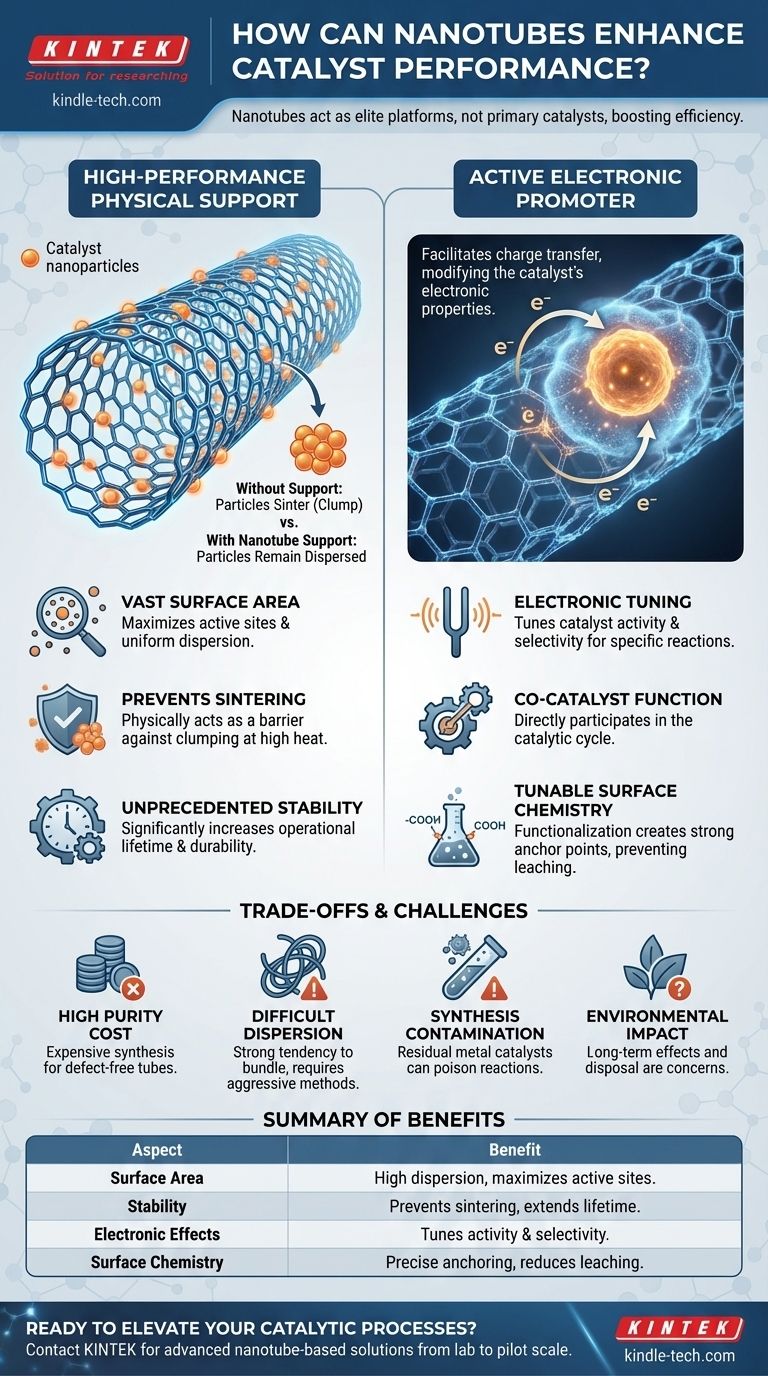
In practice, nanotubes are rarely the primary catalyst themselves. Instead, their extraordinary properties make them elite platforms, or catalyst supports, that significantly enhance the performance of traditional catalytic materials, such as metal nanoparticles. They achieve this by providing vast surface area and creating unique electronic interactions that boost reaction efficiency and stability.
The true value of nanotubes in catalysis is not in replacing conventional catalysts, but in making them dramatically better. By acting as a structured, high-surface-area scaffold, nanotubes prevent catalyst deactivation and can actively tune reactions for higher performance.

The Dual Role of Nanotubes in Catalysis
To understand their function, it's crucial to see nanotubes not as a single-purpose tool, but as a multifunctional platform. They primarily serve in one of two roles: as a superior physical support or as an active electronic promoter.
Nanotubes as High-Performance Supports
The most common application is using a carbon nanotube (CNT) as a structural foundation to anchor active catalytic particles.
The nanotube's hollow, cylindrical structure provides an immense surface-area-to-volume ratio. This allows for a very high and uniform dispersion of catalyst nanoparticles, maximizing the number of active sites exposed to the reactants.
Furthermore, the robust structure of the nanotube acts as a physical barrier. It prevents the small catalyst particles from clumping together (sintering) at high reaction temperatures—a primary cause of catalyst deactivation and failure.
Nanotubes as Electronic Promoters
Beyond being a passive scaffold, nanotubes can actively influence the catalyst's behavior.
Due to their unique electronic structure, carbon nanotubes can donate or accept electrons from the metal nanoparticles they support. This charge transfer modifies the electronic properties of the catalyst itself.
This electronic modification can "tune" the catalyst, making it more selective or more active for a specific chemical transformation. In this capacity, the nanotube acts as a co-catalyst or promoter, directly participating in the catalytic cycle.
Key Advantages of Nanotube-Based Catalysts
Using nanotubes as a support material unlocks several key advantages over conventional supports like activated carbon or silica.
Enhanced Catalyst Dispersion
The exceptionally high surface area ensures that catalytic nanoparticles can be spread out thinly and evenly. This prevents the particles from being "buried" and inaccessible, ensuring maximum efficiency.
Unprecedented Stability and Lifetime
By anchoring catalyst particles and preventing sintering, nanotubes dramatically increase the operational lifetime and durability of the catalyst. This is critical for industrial processes where catalyst replacement is costly and disruptive.
Tunable Surface Chemistry
The surface of a carbon nanotube can be chemically modified through a process called functionalization. Specific chemical groups (like carboxyl or hydroxyl groups) can be attached to the nanotube walls.
These functional groups act as "anchor points" for better adhesion of metal nanoparticles, preventing them from detaching (leaching) into the reaction mixture. They can also alter the local chemical environment to favor desired reaction pathways.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
Despite the clear advantages, the widespread adoption of nanotube-based catalysts faces significant hurdles that must be considered.
The High Cost of Purity
Synthesizing high-purity, defect-free carbon nanotubes remains an expensive process. This high material cost is a major barrier to scaling up their use from the laboratory to large-volume industrial applications.
Difficulties in Dispersion
Nanotubes have a strong tendency to bundle together due to intermolecular forces. If they are not properly dispersed in a solvent or matrix, their high surface area is lost, negating their primary benefit. Achieving stable dispersion often requires aggressive methods that can damage the nanotubes.
Contamination from Synthesis
The most common methods for producing CNTs rely on metal catalysts (e.g., iron, cobalt, nickel). Residual metal impurities can remain in the final nanotube product, potentially poisoning the intended catalytic reaction or causing unwanted side reactions.
End-of-Life and Environmental Concerns
The robustness that makes nanotubes excellent supports also makes them difficult to break down. The long-term environmental impact of nanomaterials and the challenges associated with recycling or safely disposing of spent nanotube-based catalysts are areas of active research and concern.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Your choice of a nanotube-based catalyst strategy should be dictated by your primary technical or economic goal.
- If your primary focus is maximizing catalytic activity: Prioritize using high-purity, single-walled nanotubes (SWCNTs) for their superior electronic properties and ensure your process includes a robust method for achieving uniform dispersion.
- If your primary focus is enhancing durability and lifetime: Concentrate on the functionalization of the nanotube surface to create strong anchoring sites that prevent both sintering and nanoparticle leaching over long operational cycles.
- If your primary focus is industrial scalability and cost-effectiveness: Consider using more affordable multi-walled nanotubes (MWCNTs) or exploring hybrid materials, as the cost of high-purity SWCNTs is likely prohibitive for bulk applications.
Ultimately, integrating nanotubes into a catalytic system is a powerful strategy for pushing the boundaries of performance and efficiency.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Benefit of Nanotube Support |
|---|---|
| Surface Area | Provides vast area for high dispersion of catalyst nanoparticles, maximizing active sites. |
| Stability | Prevents sintering and deactivation of catalysts at high temperatures, extending lifetime. |
| Electronic Effects | Tunes catalyst activity and selectivity via charge transfer with supported metals. |
| Surface Chemistry | Functionalization allows precise anchoring of nanoparticles, reducing leaching. |
Ready to elevate your catalytic processes with advanced nanotube-based solutions? KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables tailored for nanotechnology and materials science research. Whether you're developing next-generation catalysts or optimizing reaction efficiency, our products support your innovation from lab to pilot scale. Contact us today to discuss how we can help you achieve superior performance and durability in your catalytic applications!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Conductive Carbon Cloth Carbon Paper Carbon Felt for Electrodes and Batteries
- Conductive Boron Nitride BN Ceramics Composite for Advanced Applications
- Custom-Made Alumina Zirconia Special-Shaped Ceramic Plates for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Processing
- Laboratory CVD Boron Doped Diamond Materials
- Electrode Polishing Material for Electrochemical Experiments
People Also Ask
- How were the first gem-quality synthetic diamonds produced? Discover the 1970 GE Breakthrough
- What is thin film technology examples? From Microchips to Solar Panels and Beyond
- What is the substrate for thin film deposition? A Guide to Choosing Your Foundation
- What is the arcing of sputtering targets? Prevent Film Defects and Process Instability
- Which parameters affect sputter yield using an ion beam? Master Ion Energy, Mass, Angle & Material Properties
- What are the properties of diamond coating? Unlock Extreme Performance for Your Components
- What is the structure of single-wall carbon nanotubes? Understanding Chirality for Metallic or Semiconducting Properties
- What is deposition process in chemistry? A Guide to Thin-Film Engineering



















