To be direct, the environmental impact of nanotubes is a complex balance of benefits and risks. While their manufacturing process is often less carbon-intensive than that of alternative materials like carbon black and graphene, significant questions remain about their long-term behavior and potential toxicity once they enter the environment.
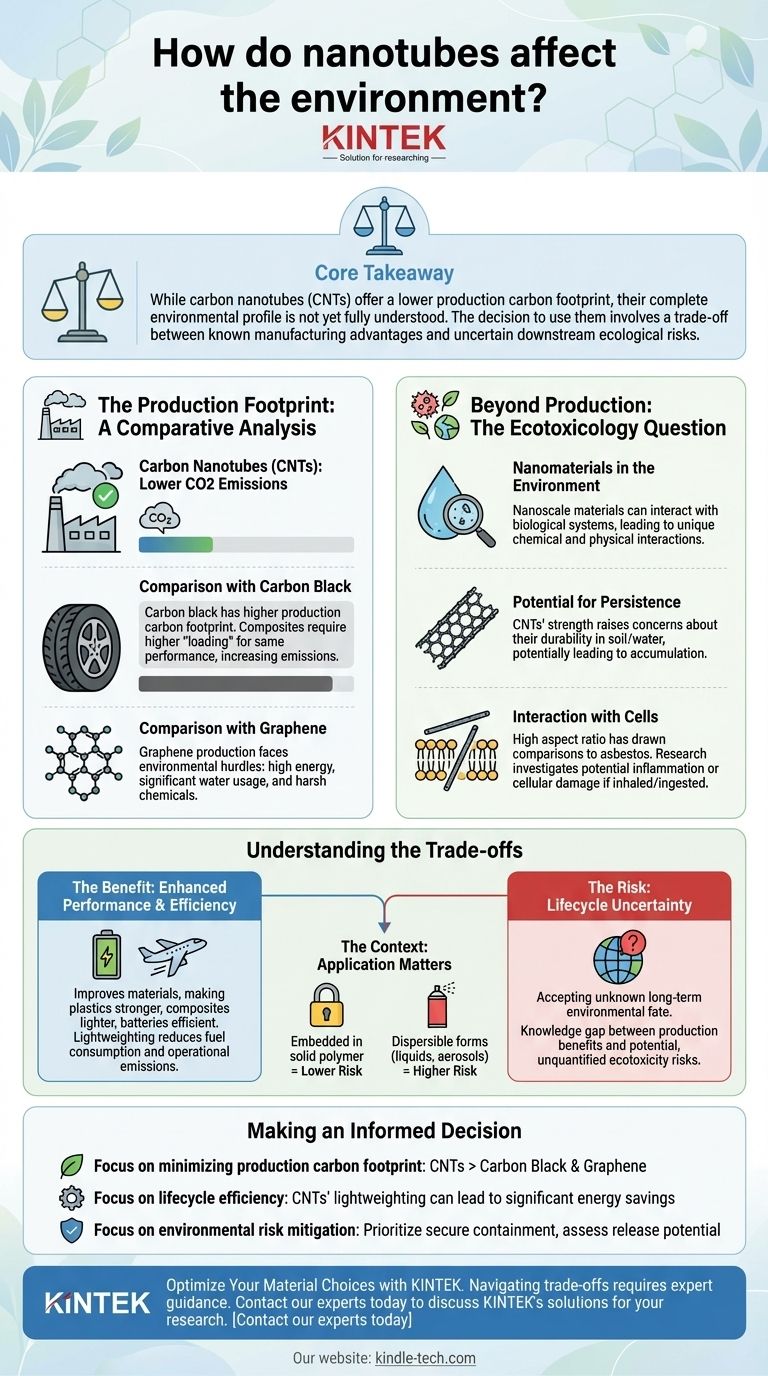
The core takeaway is that while carbon nanotubes (CNTs) offer a lower production carbon footprint, their complete environmental profile is not yet fully understood. The decision to use them involves a trade-off between known manufacturing advantages and uncertain downstream ecological risks.

The Production Footprint: A Comparative Analysis
When evaluating any material, its initial production is a critical starting point for its environmental impact. In this area, nanotubes often have a distinct advantage.
Carbon Nanotubes (CNTs): Lower CO2 Emissions
The synthesis of CNTs, when compared kilogram for kilogram, generally results in lower carbon dioxide emissions than many competing materials. This efficiency makes them an attractive option from a climate perspective.
Comparison with Carbon Black
Carbon black, a common additive for reinforcement, has a significantly higher production carbon footprint. Furthermore, composites often require a much higher "loading" of carbon black to achieve the same performance as a smaller amount of CNTs, compounding its overall emissions impact per application.
Comparison with Graphene
While also a nanomaterial with incredible properties, graphene production currently faces its own environmental hurdles. Many common methods are plagued by high energy consumption, significant water usage, and the need for harsh, difficult-to-manage chemical reagents.
Beyond Production: The Ecotoxicology Question
A material's impact does not end once it is made. The central uncertainty for nanotubes lies in how they behave over their full lifecycle, especially if released into the ecosystem.
Nanomaterials in the Environment
Materials at the nanoscale can interact with biological systems in ways their larger counterparts cannot. Their minute size and high surface area can lead to unique chemical and physical interactions with cells and tissues.
Potential for Persistence
CNTs are prized for their incredible strength and stability. While a benefit in applications, this durability raises concerns that they may not break down easily in soil or water, leading to their persistence and potential accumulation over time.
Interaction with Cells
The high aspect ratio (long and thin shape) of some nanotubes has drawn comparisons to asbestos fibers. This has spurred a significant amount of research into their potential to cause inflammation or other cellular damage if inhaled or ingested by organisms. This remains the most critical area of ongoing scientific investigation.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing to use nanotubes requires weighing their proven performance benefits against their potential lifecycle risks. Neither side of this equation should be ignored.
The Benefit: Enhanced Performance and Efficiency
The primary reason to use CNTs is their ability to dramatically improve materials. Adding a small amount can make plastics stronger, composites lighter, and batteries more efficient. This lightweighting of vehicles and aircraft, for example, directly reduces fuel consumption and emissions over the product's entire operational life.
The Risk: Lifecycle Uncertainty
The fundamental trade-off is accepting the unknown long-term environmental fate of CNTs. We have a knowledge gap between the clear, measurable benefits in production and performance versus the potential, but not fully quantified, risks of ecotoxicity.
The Context: Application Matters
The risk profile changes drastically based on the application. Nanotubes that are permanently locked within a solid polymer composite pose a much lower risk of release than those used in a liquid, coating, or aerosol, where environmental exposure is more likely.
Making an Informed Decision
Your choice to use nanotubes should be guided by your project's specific priorities and tolerance for risk.
- If your primary focus is minimizing production carbon footprint: CNTs present a compelling advantage over traditional fillers like carbon black and current graphene production methods.
- If your primary focus is lifecycle efficiency: The lightweighting and strengthening properties of CNTs can lead to significant energy savings in the final application, potentially offsetting other environmental concerns.
- If your primary focus is environmental risk mitigation: You must prioritize applications where the nanotubes are securely contained and assess the potential for material release during use, abrasion, or end-of-life disposal.
Ultimately, evaluating nanotubes requires balancing their clear production and performance benefits against the unresolved questions of their long-term ecological behavior.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Advantage | Risk/Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Production Footprint | Lower CO2 emissions than carbon black & graphene | Harsh chemicals may be used in some synthesis methods |
| Material Efficiency | High performance with low loading reduces overall material use | Potential for persistence in the environment |
| Lifecycle Impact | Lightweighting applications can reduce operational emissions | Long-term ecotoxicology and cellular interactions are not fully understood |
| Application Context | Low risk when securely embedded in composites | Higher risk if used in dispersible forms (e.g., liquids, aerosols) |
Optimize Your Material Choices with KINTEK
Navigating the trade-offs of advanced materials like carbon nanotubes requires expert guidance and reliable equipment. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables tailored to your research and production needs. Whether you're developing safer nanomaterials, conducting ecotoxicity studies, or optimizing synthesis for lower emissions, our products support precise, reproducible results.
Let us help you make informed, sustainable decisions.
Contact our experts today to discuss how KINTEK's solutions can enhance your laboratory's efficiency and safety while addressing the complex environmental challenges of nanotechnology.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- Multi-zone Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- Why is a magnetic stirrer considered essential during PdLa/ATO catalyst preparation? Ensure Uniform Particle Dispersion
- What are the safety precautions for heat experiment? Essential Steps to Prevent Lab Burns and Accidents
- Can all plastics be used in pyrolysis? Choose the Right Feedstock for Optimal Results
- What are the advantages of using a Hot Isostatic Press (HIP)? Achieve 99.54% Density for Cu/Ti3SiC2/C Composites
- What is the role of a laboratory ultra-low temperature freezer in stainless steel corrosion studies? Ensure Data Integrity
- Does heat treatment increase strength? Unlock Maximum Metal Performance for Your Components
- What is gold coating SEM for? Prevent Charging & Get Clearer SEM Images
- What are the hazards of heating in a laboratory? Essential Safety Protocols to Prevent Burns, Fires, and Explosions



















