Getting a lab-grown diamond appraised follows the same fundamental process as a natural diamond appraisal, but with a critical difference in focus. The process begins with securing a grading report from a reputable gemological laboratory like the GIA or IGI to confirm the diamond's identity and quality. You then take this report and the diamond to a qualified appraiser, who will use it to determine the stone's market value based on its specific characteristics within the lab-grown market.
A successful appraisal for a lab-grown diamond is less about proving it's a "real" diamond and more about establishing its value within its own distinct market. The key is combining a certified lab report with an appraiser who understands the specific pricing and dynamics of lab-grown gems.
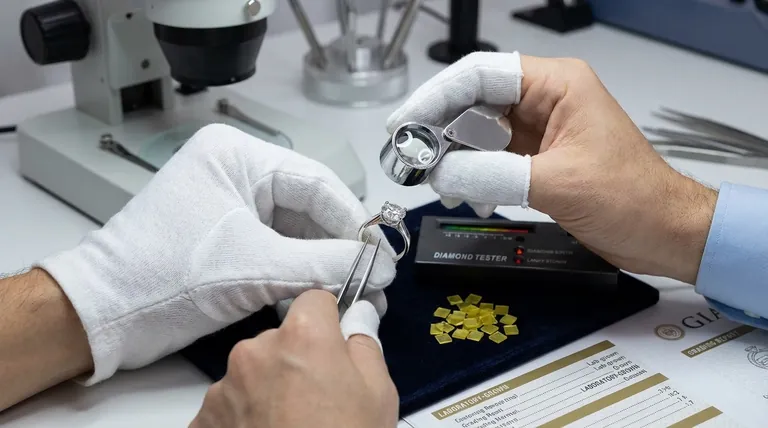

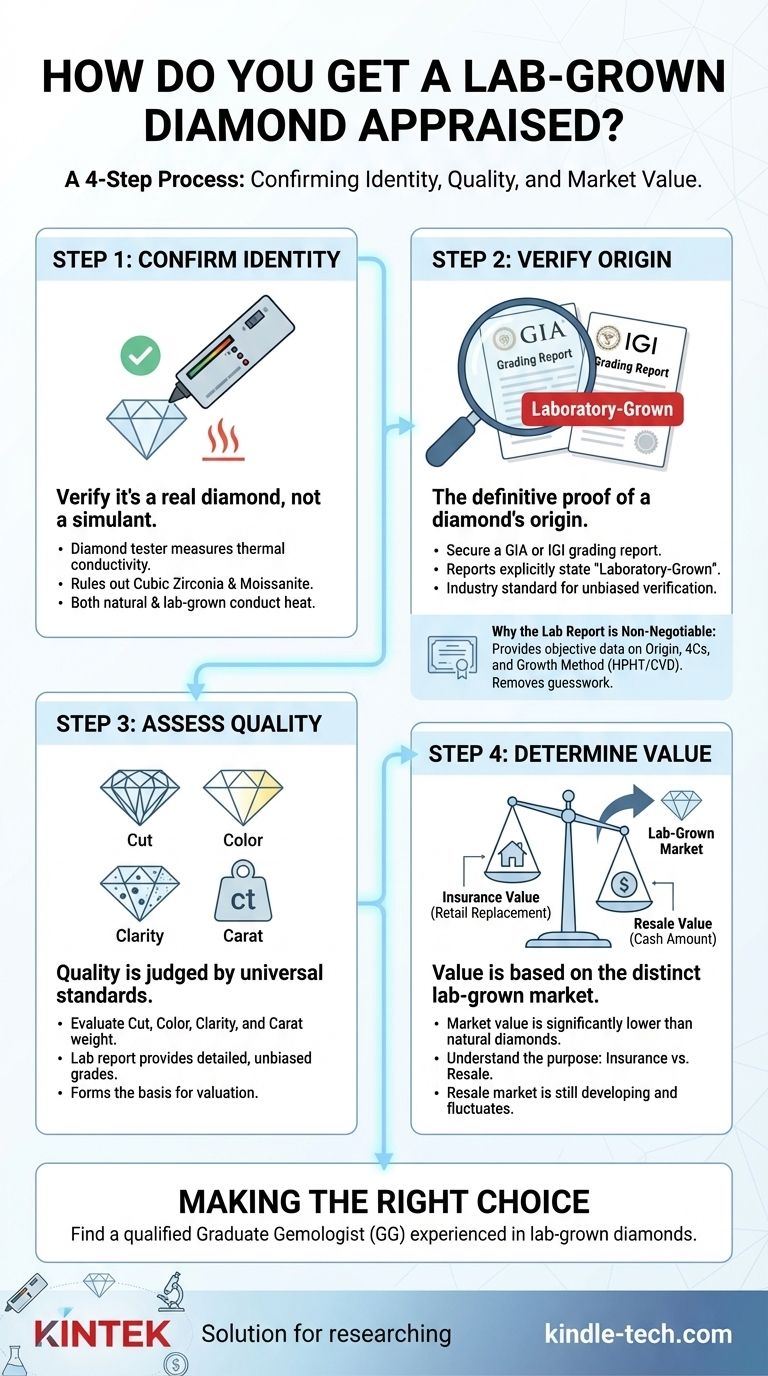
The Foundation of a Diamond Appraisal
Before any value can be assigned, an appraiser must confirm two things: the material's identity and its quality. This process is standardized for all diamonds, whether mined or lab-grown.
Step 1: Confirming It's a Diamond
An appraiser's first step is to verify that the stone is, in fact, a diamond and not a simulant like cubic zirconia or moissanite.
They use tools like a diamond tester, which measures thermal conductivity. Both natural and lab-grown diamonds are excellent heat conductors, while most simulants are not.
Step 2: Verifying the Origin (Lab-Grown vs. Natural)
This is the most crucial step for valuation. The definitive proof of a diamond's origin is its grading report or certificate from a major lab.
The Gemological Institute of America (GIA) and the International Gemological Institute (IGI) are the industry standards. Their reports explicitly state if a diamond is laboratory-grown and are considered the final word on origin. An appraiser will always ask for this document first.
Step 3: Assessing the 4Cs
Once identified as a lab-grown diamond, its quality is judged by the same universal standard as natural diamonds: the 4Cs (Cut, Color, Clarity, and Carat weight).
The lab report provides a detailed, unbiased grade for each of these characteristics, which forms the basis for the appraiser's valuation.
Why the Lab Report is Non-Negotiable
The grading report is the central document in any appraisal. Without it, you are relying solely on one person's opinion.
The Role of GIA and IGI
These institutions provide unbiased, third-party verification. Their name on a report ensures the diamond's characteristics have been accurately and professionally assessed according to strict global standards. This removes guesswork and provides a foundation of trust.
What the Report Tells an Appraiser
The report provides all the objective data needed to determine value:
- Origin: Clearly states "Laboratory-Grown."
- 4Cs: Provides precise grades for cut, color, clarity, and carat weight.
- Growth Method: May indicate the manufacturing process (HPHT or CVD).
- Report Number: A unique number often inscribed on the diamond's girdle, allowing the appraiser to verify the stone matches the document.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Value vs. Price
An appraisal for a lab-grown diamond is where the similarities with a natural diamond evaluation end. The value assigned is based on a completely different market.
The Purpose of an Appraisal: Insurance vs. Resale
It is critical to know what the appraisal is for. Most appraisals determine Retail Replacement Value, which is the cost to buy a new, similar diamond from a retailer. This figure is used for insurance purposes.
This replacement value is almost always higher than the Resale Value, which is the cash amount you could get by selling the diamond today.
Market Value is Different
Lab-grown diamonds share the identical physical and chemical properties of natural diamonds, but their market value is significantly lower—often 60-70% less for comparable quality.
This difference is due to supply and manufacturing efficiency. An appraiser who specializes in lab-grown diamonds will base their valuation on this separate market, not on the price of natural diamonds.
The Evolving Resale Market
The resale market for lab-grown diamonds is still developing and is not as established as the century-old market for natural diamonds. As manufacturing technology improves and costs decrease, resale values can fluctuate more. Be prepared for the resale value to be considerably lower than your original purchase price.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To get a meaningful appraisal, you must find a qualified professional and be clear about your objective. Always seek a Graduate Gemologist (GG) and ask them specifically about their experience appraising lab-grown diamonds.
- If your primary focus is insurance coverage: Your goal is to get a "Retail Replacement Value" that accurately reflects the current cost of a new lab-grown diamond with the same specifications.
- If your primary focus is understanding resale value: You must have a direct conversation with the appraiser about the realistic, secondary market cash value, which will be significantly lower than the insurance value.
- If your primary focus is simply verifying a purchase: The GIA or IGI report is your best tool, but an independent appraiser can confirm that the diamond in your possession matches the report's details.
Ultimately, a proper appraisal provides an objective, expert-validated understanding of your lab-grown diamond's quality and current market position.
Summary Table:
| Appraisal Step | Key Action | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Confirm Identity | Use a diamond tester to verify it's a real diamond. | Rules out simulants like cubic zirconia. |
| 2. Verify Origin | Obtain a GIA or IGI grading report stating "Laboratory-Grown." | Essential for accurate valuation in the lab-grown market. |
| 3. Assess Quality | Evaluate the 4Cs (Cut, Color, Clarity, Carat) from the lab report. | Forms the basis for determining market value. |
| 4. Determine Value | Appraiser assigns value based on the lab-grown diamond market. | Insurance value differs significantly from resale value. |
Need precise, reliable equipment for gemological analysis? KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including diamond testers and tools used by Graduate Gemologists for accurate appraisals. Whether you're a jeweler, appraiser, or lab technician, our products ensure you can verify diamond identity and quality with confidence. Contact our experts today to find the right tools for your laboratory's needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- CVD Diamond for Thermal Management Applications
- Laboratory CVD Boron Doped Diamond Materials
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition and Lab Diamond Growth
- CVD Diamond Domes for Industrial and Scientific Applications
- CVD Diamond Optical Windows for Lab Applications
People Also Ask
- Which is better lab grown or natural diamond? A Clear Guide to Choosing Your Perfect Stone
- Are lab-grown diamonds comparable to natural diamonds? Discover the Science Behind the Sparkle
- What is the hardness of a lab grown diamond? It's as Hard as a Natural Diamond
- What pressure is needed for chemical vapor deposition of diamonds? Master the Low-Pressure 'Sweet Spot'
- How do scientists grow diamonds? Replicating Nature's Process in a Lab
- Can I buy lab diamonds? Your Guide to Modern, Ethical, and Affordable Diamonds
- What is the frequency of MPCVD? A Guide to Choosing 2.45 GHz vs. 915 MHz for Your Application
- Can a jeweler distinguish a lab grown diamond? The Truth About Identifying Diamond Origin















