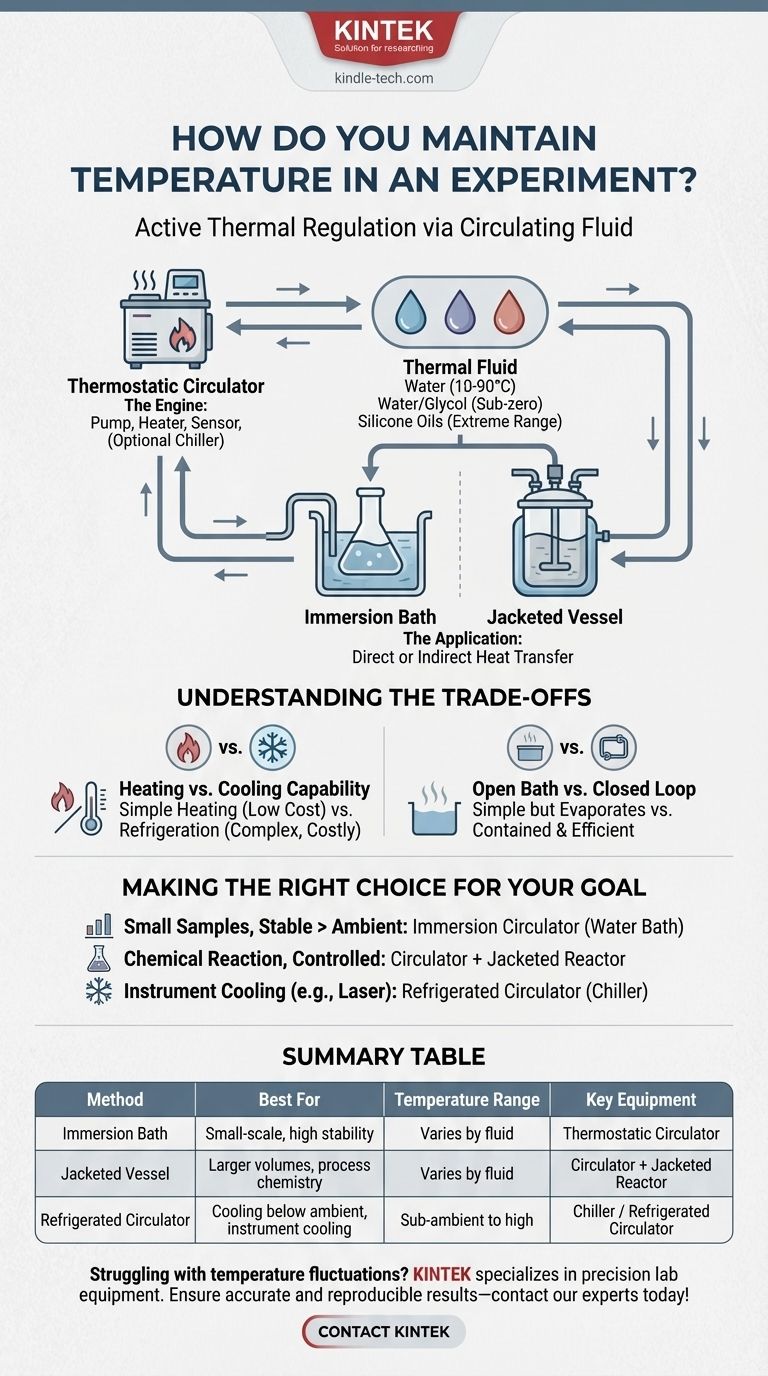
To maintain temperature in an experiment, you use a system that actively adds or removes heat from your setup via a circulating fluid. The most common and versatile tool for this is a thermostatic circulator, which can act as a heater, a chiller, or both. This device pumps a temperature-controlled liquid, such as water or an ethylene glycol mixture, either through a jacket surrounding your vessel or within a bath where your experiment is directly immersed.
The core challenge of experimental temperature control is not just heating or cooling, but achieving and holding a stable temperature. The most reliable solution is to use an active thermal regulation system—a circulator—that continuously monitors and adjusts the temperature of a fluid to create a consistent thermal environment.

The Core Principle: Active Thermal Regulation
Controlling temperature is an active process of balancing heat flow. Your experiment will naturally lose heat to or gain heat from its surroundings. A control system works against this by constantly adding or removing the precise amount of thermal energy needed to hold a setpoint.
The Heart of the System: The Circulator
A thermostatic circulator is the engine of temperature control. This single unit typically contains a pump, a heating element, and a temperature sensor.
More advanced models, often called refrigerated circulators or chillers, also include a refrigeration system for cooling below the ambient temperature.
The Lifeblood: The Thermal Fluid
The circulator pumps a thermal fluid to transfer heat to or from your experiment. The choice of fluid is critical and depends entirely on your target temperature range.
- Water: Ideal for temperatures from roughly 10°C to 90°C. It has excellent heat capacity and is inexpensive.
- Water/Glycol Mix: For temperatures below freezing (down to -20°C or -40°C), ethylene glycol is added to water to act as an antifreeze, preventing the fluid from freezing and damaging the circulator's pump.
- Silicone Oils: For very high or very low temperature applications, specialized silicone oils are used. They remain liquid over a vast temperature range and are more chemically inert than water.
The Application: Baths and Jacketed Vessels
You connect your experiment to the circulator in one of two primary ways.
- Immersion Bath: The simplest method involves placing your sample container (e.g., a beaker, flask, or test tube rack) directly into the bath of the circulator itself. This is excellent for small-scale work requiring high stability.
- Jacketed Vessel: For larger volumes or more complex setups, you use a jacketed vessel or reactor. The circulator pumps the thermal fluid through the outer jacket, controlling the temperature of the contents inside without direct contact. This is the standard for process chemistry and scale-up.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right method involves balancing precision, temperature range, and cost. There is no single "best" solution for every experiment.
Heating vs. Cooling Capability
A simple heating immersion circulator is relatively inexpensive. However, if you need to hold a temperature near or below the room's ambient temperature, you need a unit with refrigeration. These refrigerated circulators are significantly more complex and costly.
Open Bath vs. Closed Loop
An open bath is simple but can suffer from evaporation, especially when heated. A closed-loop system, where fluid is pumped to a jacketed vessel and back, is more contained and efficient for controlling external equipment.
Fluid Selection Pitfalls
Using the wrong fluid is a common and costly mistake. Using plain water below its freezing point will destroy the pump. Using a fluid that is too viscous at low temperatures will result in poor flow and inadequate control. Always consult the circulator and fluid manufacturer's specifications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Select your equipment based on the specific demands of your experiment.
- If your primary focus is holding small samples at a stable temperature above ambient: A simple heating immersion circulator (a "water bath") is the most direct and cost-effective solution.
- If your primary focus is running a chemical reaction in a controlled manner: A circulator paired with a jacketed glass reactor provides the best combination of precision, safety, and scalability.
- If your primary focus is removing heat from an instrument (like a laser or rotary evaporator): A refrigerated circulator, or "chiller," sized to handle the instrument's heat load is required.
By matching the control method to your specific requirements for precision and scale, you ensure your experimental results are both accurate and reproducible.
Summary Table:
| Method | Best For | Temperature Range | Key Equipment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Immersion Bath | Small-scale work, high stability | Varies by fluid | Thermostatic Circulator |
| Jacketed Vessel | Larger volumes, process chemistry | Varies by fluid | Circulator + Jacketed Reactor |
| Refrigerated Circulator | Cooling below ambient, instrument cooling | Sub-ambient to high | Chiller / Refrigerated Circulator |
Struggling with temperature fluctuations in your experiments? KINTEK specializes in precision lab equipment, including thermostatic circulators, chillers, and jacketed reactors, to deliver the stable thermal control your research demands. Ensure your results are accurate and reproducible—contact our experts today to find the perfect temperature control solution for your laboratory needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 100L Heating Chilling Circulator Cooling Water Bath Circulator for High and Low Temperature Constant Temperature Reaction
- 10L Heating Chilling Circulator Cooling Water Bath Circulator for High and Low Temperature Constant Temperature Reaction
- 20L Heating Chilling Circulator Cooling Water Bath Circulator for High and Low Temperature Constant Temperature Reaction
- 30L Heating Chilling Circulator Cooling Water Bath Circulator for High and Low Temperature Constant Temperature Reaction
- 100L Chilling Circulator Cooling Water Circulator for Low Temperature Constant Temperature Reaction Bath Water Bath Cooling
People Also Ask
- How do circulating cooling systems ensure accuracy in adsorption tests? Stabilize Thermal Variables for Precise Data
- What are the performance advantages of using a recirculating cooling system for EK-181 steel? Maximize Yield Strength
- How do constant temperature circulators impact weight-loss immersion tests? Ensure Precision in Corrosion Analysis
- How does a water bath work? Master Precise and Gentle Heating for Your Lab
- What is the function of a constant temperature water bath in CO2 absorption kinetics? Achieve High-Precision Research



















