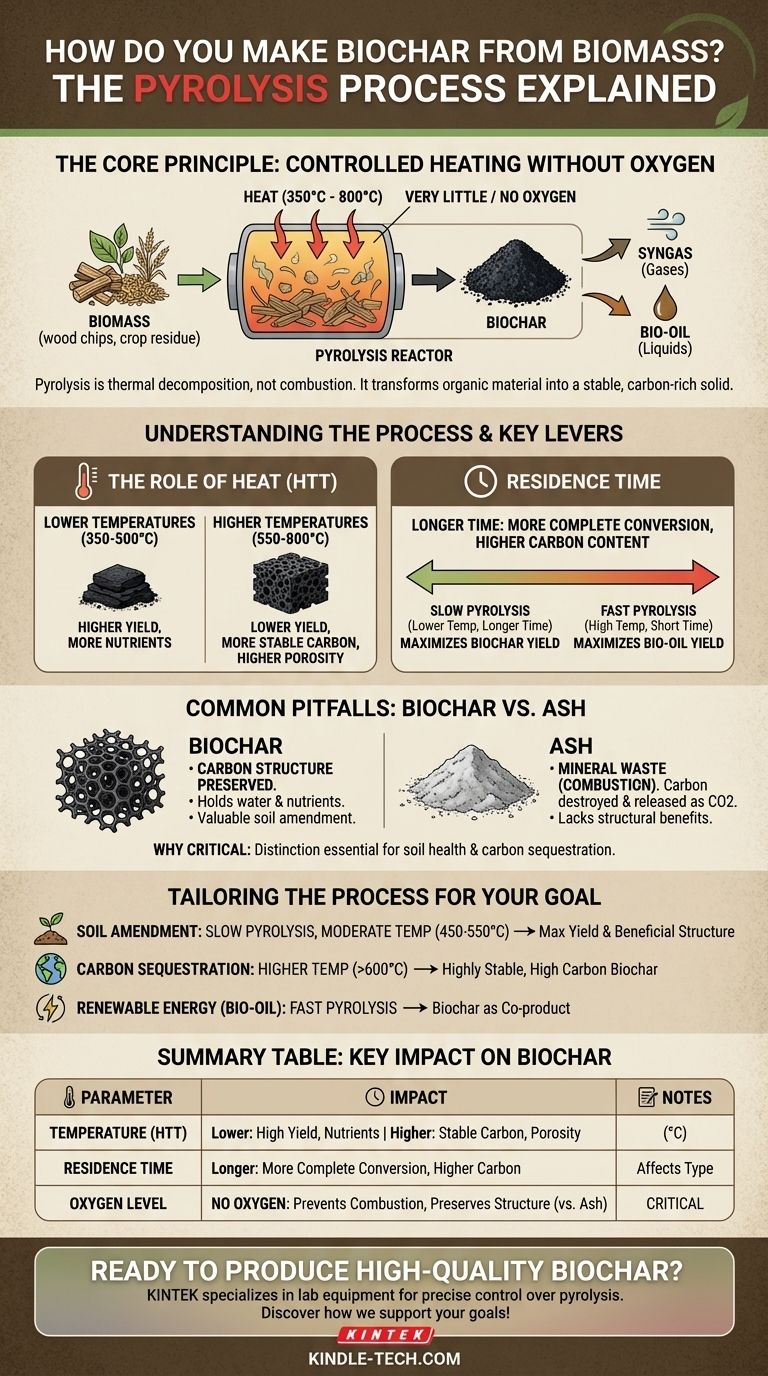
The short answer is you make biochar by heating biomass, such as wood or crop residue, in an environment with very little or no oxygen. This process, known as pyrolysis, is a thermal decomposition, not a combustion. Instead of burning and turning to ash, the organic material transforms into a stable, carbon-rich solid.
The core principle of making biochar is controlled heating without oxygen. Unlike burning, which destroys the carbon structure, this method chemically alters the biomass to lock carbon into a highly stable form.

Understanding the Core Process: Pyrolysis
Pyrolysis is the fundamental process behind biochar creation. It involves applying high heat to an organic material in the absence of oxygen, causing it to break down into new, more stable substances without combusting.
The Role of Heat
Heat provides the energy needed to break the complex chemical bonds within the raw biomass. As these bonds break, volatile compounds are driven off as gases and liquids (syngas and bio-oil), leaving behind the solid carbon skeleton that we call biochar.
The Critical Low-Oxygen Environment
This is the most important factor distinguishing pyrolysis from burning. When you burn a log in a campfire, abundant oxygen allows for combustion, a rapid oxidation process that releases energy and converts the carbon into carbon dioxide gas and mineral ash.
By starving the process of oxygen, you prevent combustion. The material chemically transforms rather than burns away, preserving the majority of its carbon in a solid, recalcitrant form.
The Two Levers That Define Your Biochar
The final properties of your biochar are not accidental. They are the direct result of two key process conditions that you can control. The quality and characteristics of the end product depend entirely on how you manage heat and time.
Highest Treatment Temperature (HTT)
Temperature is arguably the most influential variable.
- Lower Temperatures (350-500°C): This produces a higher yield of biochar but leaves more volatile organic compounds in the final product. This type of biochar can be richer in certain nutrients.
- Higher Temperatures (550-800°C): This results in a lower biochar yield but a higher concentration of stable carbon. The resulting biochar is more porous and has a greater surface area, which can be ideal for certain applications.
Residence Time
This refers to how long the biomass is held at the highest treatment temperature. A longer residence time ensures a more complete conversion process, driving off more volatiles and leading to a more refined, higher-carbon biochar.
The interplay between temperature and time defines the type of pyrolysis. Slow pyrolysis (lower temperatures, longer times) maximizes biochar yield, while fast pyrolysis (high temperatures, very short times) is often used to maximize the yield of liquid bio-oil.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid: Biochar vs. Ash
A frequent point of confusion is the difference between biochar and simple ash. While both originate from biomass, they are fundamentally different products with different purposes.
Pyrolysis Creates a Carbon Structure
The goal of pyrolysis is to preserve and concentrate carbon. The resulting biochar has a complex, porous physical structure that allows it to hold water and nutrients, making it a valuable soil amendment.
Combustion Creates Mineral Waste
Burning wood in the open air (combustion) destroys this carbon structure. The carbon combines with oxygen and is released as CO2. What remains is ash—the inorganic, mineral component of the biomass, which lacks the structural benefits of biochar.
Why This Distinction Is Critical
The value of biochar—for improving soil health and sequestering carbon—is embedded in its stable carbon framework. Ash does not provide these structural benefits and has a very different chemical composition. Confusing the two means losing the primary advantages of the biochar process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
You can tailor the pyrolysis process to produce biochar with specific properties suited to your objective.
- If your primary focus is creating a soil amendment: Use a slow pyrolysis process with moderate temperatures (450-550°C) to maximize biochar yield and retain a beneficial chemical structure.
- If your primary focus is maximizing long-term carbon sequestration: Use higher temperatures (above 600°C) to produce a highly stable, high-carbon biochar that will resist decomposition for centuries.
- If your primary focus is producing renewable energy (bio-oil): Use a fast pyrolysis process, which will yield biochar as a valuable co-product.
By controlling heat and oxygen, you transform simple biomass into a powerful and versatile material.
Summary Table:
| Process Parameter | Key Impact on Biochar |
|---|---|
| Temperature (HTT) | Lower (350-500°C): Higher yield, more nutrients. Higher (550-800°C): More stable carbon, greater porosity. |
| Residence Time | Longer time: More complete conversion, higher carbon content. |
| Oxygen Level | No oxygen: Prevents combustion, preserves carbon structure (vs. ash). |
Ready to produce high-quality biochar for your specific application?
Whether your goal is creating a superior soil amendment or maximizing carbon sequestration, the right lab equipment is crucial for precise control over pyrolysis parameters like temperature and residence time.
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving all your laboratory needs. Our reliable pyrolysis systems help you achieve consistent, high-quality biochar results.
Contact us today to discuss your project and discover how KINTEK can support your biochar production goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does precision temperature control impact TiAl alloy sintering? Master Microstructure Development
- What are the zones in rotary kiln in cement production? Master the Core Process for High-Quality Clinker
- How does a rotary extractor work? Master Continuous High-Volume Solid Processing
- What is the principle of rotary kiln? Mastering Continuous Thermal Processing
- What is the drying zone in a rotary kiln? Boost Efficiency with Modern Drying Solutions



















