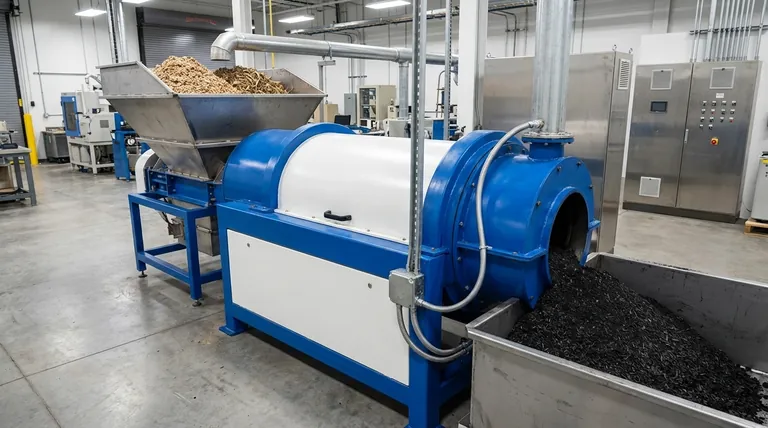
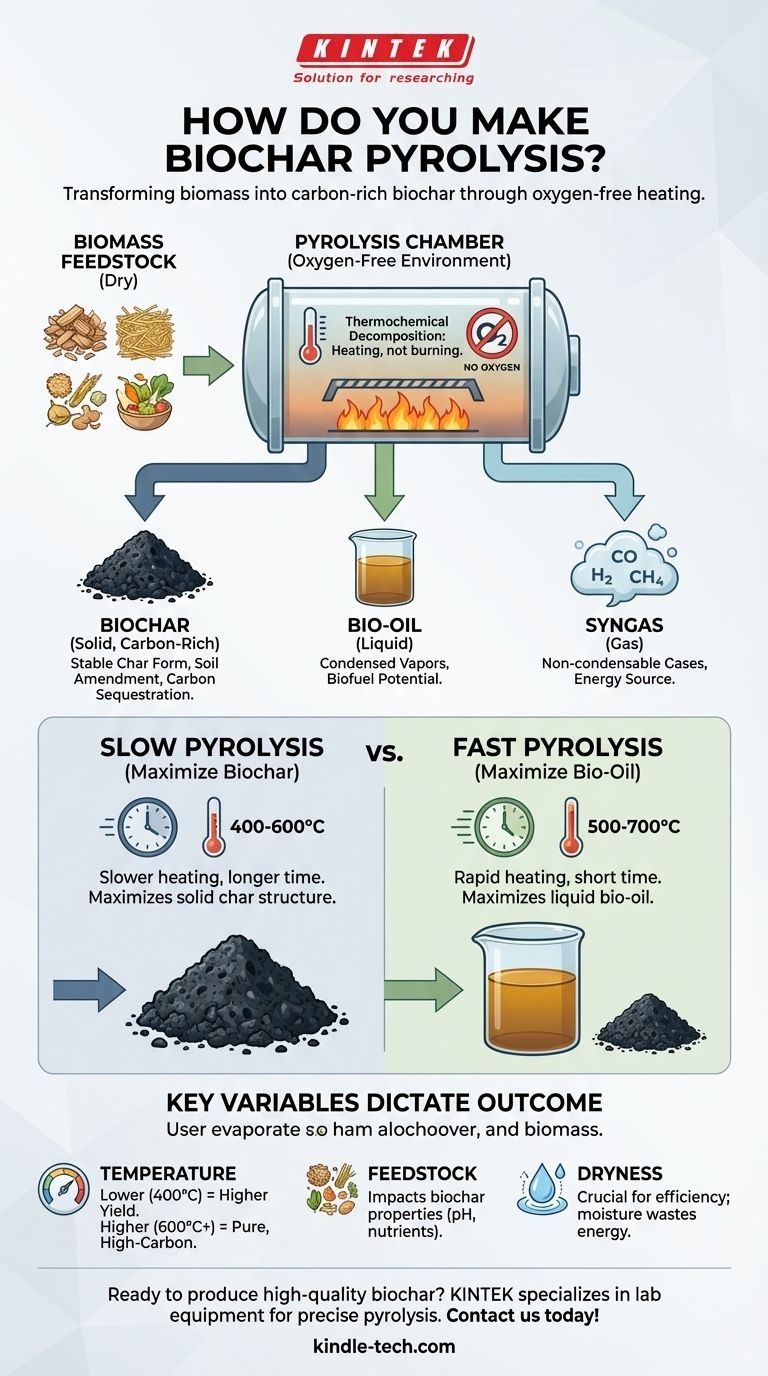
Making biochar through pyrolysis involves heating organic material, known as biomass, to high temperatures in an environment with little to no oxygen. This process, called thermochemical decomposition, prevents the material from burning. Instead, it transforms the biomass into a stable, carbon-rich solid (biochar), along with vapor and gas byproducts.
Pyrolysis is not burning; it's a controlled thermal decomposition. By eliminating oxygen, you prevent combustion and instead chemically transform the biomass, locking its carbon into a stable char form.

The Core Principle: Heating Without Oxygen
What is Pyrolysis?
Pyrolysis is a chemical change brought about by heat. Think of it as cooking in a sealed container rather than grilling over an open flame.
When you burn wood in a campfire (combustion), oxygen reacts with the biomass, releasing energy as heat and light, leaving behind only a small amount of ash.
In pyrolysis, sealing the biomass from oxygen prevents this reaction. The heat breaks down the complex organic polymers in the material, fundamentally altering its chemical structure.
The Critical Role of an Oxygen-Free Environment
The absence of oxygen is the single most important factor in pyrolysis. It is the defining difference between turning biomass into ash versus turning it into biochar.
Without oxygen to fuel a fire, the carbon in the biomass reorganizes itself into the stable, solid structure of biochar.
The Three Key Outputs
The pyrolysis process typically yields three distinct products:
- Biochar (Solid): The primary solid product, rich in carbon.
- Bio-oil (Liquid): Vapors that are condensed into a liquid, sometimes called pyrolysis oil or bio-crude.
- Syngas (Gas): A mix of non-condensable gases, including hydrogen, carbon monoxide, and methane.
For biochar production, the process is optimized to maximize the solid char output.
Slow vs. Fast Pyrolysis: Two Paths for Different Goals
The speed and temperature of the process dramatically change the final products. For making biochar, one method is clearly superior.
Slow Pyrolysis: Maximizing Biochar
This is the standard method for producing biochar. It involves heating biomass at a slower rate to lower temperatures (typically 400-600°C).
The longer processing time allows for more of the carbon to stabilize into the solid char structure, maximizing its yield.
Fast Pyrolysis: Prioritizing Bio-Oil
Fast pyrolysis uses higher temperatures (500-700°C) and heats the biomass very rapidly.
This process is designed to break down the biomass into vapors that can be condensed into liquid bio-oil, which can be used as a biofuel. In this system, biochar is often considered a secondary co-product.
What Can You Use as Feedstock?
A wide range of organic materials can be converted into biochar, and the source material is known as feedstock.
Woody Biomass
Materials like pine wood chips, sawdust, and forest debris are common feedstocks. They produce a durable, high-carbon biochar ideal for soil amendment.
Agricultural Residues
Crop waste such as wheat straw, corn stover, and rice husks are excellent feedstocks. This turns agricultural byproducts from waste into a valuable resource.
Organic and Green Waste
Materials like yard trimmings, food waste, and even dried algae can be used. This provides a powerful method for recycling nutrients and diverting organic waste from landfills.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Key Variables
Creating a specific type of biochar is not a one-size-fits-all process. The outcome is dictated by a few key variables.
Temperature Dictates the Outcome
Lower temperatures (around 400°C) tend to produce a higher yield of biochar, but it may contain more residual organic compounds.
Higher temperatures (600°C+) produce a lower yield but result in a more pure, higher-carbon biochar with a greater surface area.
Feedstock Determines Quality
The type of biomass used directly impacts the final biochar's characteristics. A biochar made from wood will have different properties (e.g., pH, nutrient content) than one made from animal manure or straw.
The Importance of Dryness
Feedstock must be as dry as possible. Any moisture in the biomass must be boiled off before pyrolysis can begin, which wastes significant energy and makes the process inefficient.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The ideal pyrolysis method depends entirely on what you want to achieve.
- If your primary focus is maximizing soil amendment and carbon sequestration: Prioritize slow pyrolysis at moderate temperatures (450-550°C) to get the highest possible biochar yield from your chosen feedstock.
- If your primary focus is creating liquid biofuels: You would shift to fast pyrolysis, which uses higher temperatures and rapid heating to maximize the production of bio-oil.
- If your primary focus is waste management: Your feedstock is the starting point, and the pyrolysis conditions should be optimized to efficiently convert that specific material, such as turning green waste into a nutrient-rich biochar.
Understanding these core principles empowers you to see biochar production not as a simple recipe, but as a versatile tool for sustainable resource management.
Summary Table:
| Pyrolysis Type | Temperature | Primary Goal | Biochar Yield |
|---|---|---|---|
| Slow Pyrolysis | 400-600°C | Maximize Biochar | High |
| Fast Pyrolysis | 500-700°C | Maximize Bio-Oil | Low (Co-product) |
Ready to produce high-quality biochar for your agricultural or environmental project? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables for precise pyrolysis processes. Our reliable solutions help you efficiently convert biomass into stable biochar, enhancing soil health and supporting carbon sequestration efforts. Contact us today to discuss your specific needs and discover the right equipment for your laboratory!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Reactor for Hydrothermal Synthesis
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of pyrolysis technology? Turn Waste into Profit and Reduce Emissions
- Is pyrolysis viable? A Guide to Economic, Technological, and Environmental Success
- What are the components of biomass pyrolysis? A Complete Guide to the System, Products, and Process
- What are the different types of pyrolysis machines? Choose the Right System for Your Output
- What is the process of biomass fast pyrolysis? Turn Biomass into Bio-Oil in Seconds



















