At its core, making a quartz tube involves melting extremely pure quartz sand at incredibly high temperatures and then drawing that molten material into a precise tubular shape. The process is a form of high-temperature glassworking, but it requires much higher temperatures and stricter controls than conventional glass due to quartz's unique properties.
The entire manufacturing process is engineered to do one thing: transform high-purity silicon dioxide (quartz sand) into a dimensionally stable tube while preserving its exceptional chemical purity and thermal resistance.

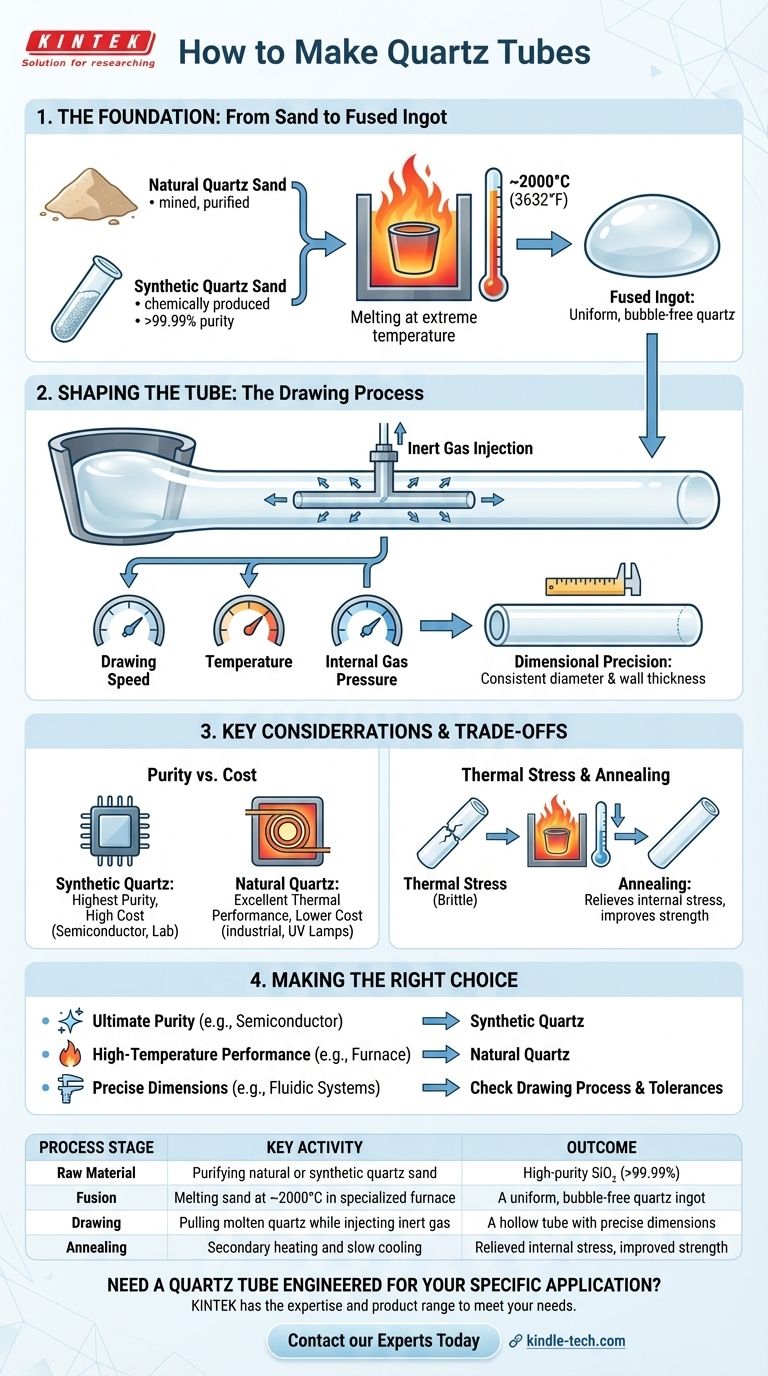
The Foundation: From Sand to Fused Ingot
The quality of the final tube is determined long before it takes shape. The journey begins with the selection and purification of the raw material.
Selecting the Raw Material
The primary ingredient is silicon dioxide (SiO₂), which comes in two main forms. Natural quartz sand is mined and then purified to remove mineral contaminants.
Synthetic quartz sand is produced chemically to achieve even higher purity levels, often exceeding 99.99%. This is critical for applications that cannot tolerate even trace amounts of metallic impurities.
The Fusion Process
The purified sand is loaded into a refractory crucible, often made of tungsten or molybdenum, inside a specialized furnace. It is then heated to its melting point, approximately 2000°C (3632°F).
This extreme heat fuses the individual grains of sand into a single, viscous, transparent mass. This molten blob, often called a boule or ingot, must be free of bubbles and impurities to ensure the optical clarity and structural integrity of the final product.
Shaping the Tube: The Drawing Process
Once a uniform molten ingot is formed, it must be carefully shaped into a tube with consistent diameter and wall thickness.
Continuous Drawing
In the most common method, the molten quartz is continuously drawn from the bottom of the crucible. As it is pulled downward, a precise amount of inert gas is injected into its center.
This internal gas pressure prevents the molten cylinder from collapsing on itself, creating the hollow center of the tube.
Achieving Dimensional Precision
The final dimensions are controlled by a delicate balance of three factors: the drawing speed, the temperature of the molten quartz, and the internal gas pressure.
Slight adjustments to these variables allow manufacturers to produce tubes with the tight tolerances on diameter and wall thickness required for high-tech industrial applications.
Key Considerations and Trade-offs
The choice of material and process involves balancing performance requirements with practical limitations. Understanding these trade-offs is key to selecting the right component.
Purity vs. Cost
Tubes made from synthetic quartz offer the highest purity, making them essential for semiconductor manufacturing and high-end laboratory equipment. This purity comes at a significantly higher cost.
Tubes made from natural quartz provide excellent thermal performance at a lower price point, making them ideal for industrial heating elements, furnace liners, and UV lamps.
Thermal Stress and Annealing
The rapid transition from molten to solid can lock thermal stress into the material, making it brittle.
To counteract this, many quartz tubes undergo a secondary heating and slow-cooling process called annealing. This relieves internal stresses, dramatically improving the tube's strength and resistance to thermal shock.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final selection depends entirely on the specific demands of your project.
- If your primary focus is ultimate purity (e.g., semiconductor processing): You must specify tubes made from high-purity synthetic quartz to avoid contamination.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature performance (e.g., furnace liners): Tubes made from natural quartz provide an excellent balance of thermal stability and cost-effectiveness.
- If your primary focus is precise dimensions (e.g., fluidic or optical systems): Inquire about the manufacturer's drawing process and dimensional tolerances to ensure a proper fit.
Understanding the journey from sand to a finished tube empowers you to select the precise material engineered for your critical application.
Summary Table:
| Process Stage | Key Activity | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Raw Material | Purifying natural or synthetic quartz sand | High-purity SiO₂ (>99.99%) |
| Fusion | Melting sand at ~2000°C in a specialized furnace | A uniform, bubble-free quartz ingot |
| Drawing | Pulling molten quartz while injecting inert gas | A hollow tube with precise dimensions |
| Annealing | Secondary heating and slow cooling | Relieved internal stress, improved strength |
Need a Quartz Tube Engineered for Your Specific Application?
Whether your project demands the ultimate purity of synthetic quartz for semiconductor processing or the robust thermal performance of natural quartz for industrial furnaces, KINTEK has the expertise and product range to meet your needs. Our lab equipment and consumables are designed for precision and reliability.
Contact our experts today via our Contact Form to discuss your requirements and discover how our quartz solutions can enhance your laboratory's capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- Why use quartz tubes and vacuum sealing for sulfide solid-state electrolytes? Ensure Purity & Stoichiometry
- What happens when quartz is heated? A Guide to Its Critical Phase Transitions and Uses
- What is the primary function of quartz tubes in halide electrolyte synthesis? Ensure Purity & Precise Stoichiometry
- What is the technical value of using a quartz tube reaction chamber for static corrosion testing? Achieve Precision.
- What is the function of quartz tubes and vacuum sealing systems? Secure Your High-Purity Solid Solution Synthesis



















