To prepare a pressed pellet sample for XRF analysis, you must convert a raw sample into a fine powder, mix it with a binding agent, and compress it under high pressure. This process creates a sample with a perfectly flat, homogeneous surface, which is essential for obtaining accurate and repeatable analytical results.
The fundamental goal of creating a pressed pellet is to eliminate physical variations between samples. By ensuring every sample presented to the X-ray beam has the same density, surface finish, and particle size, you remove major sources of analytical error.
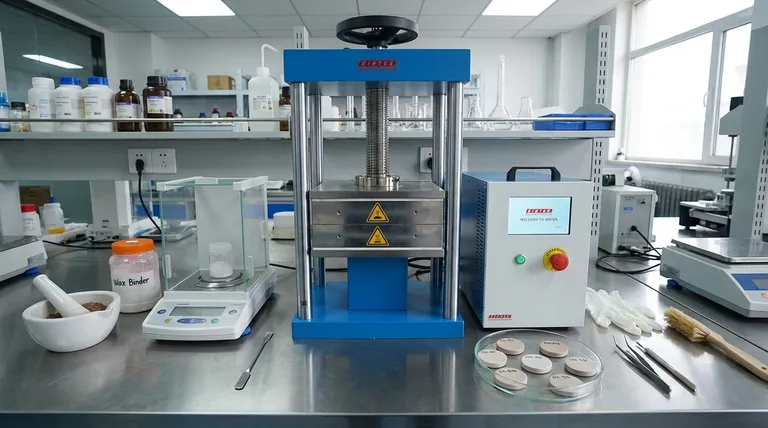

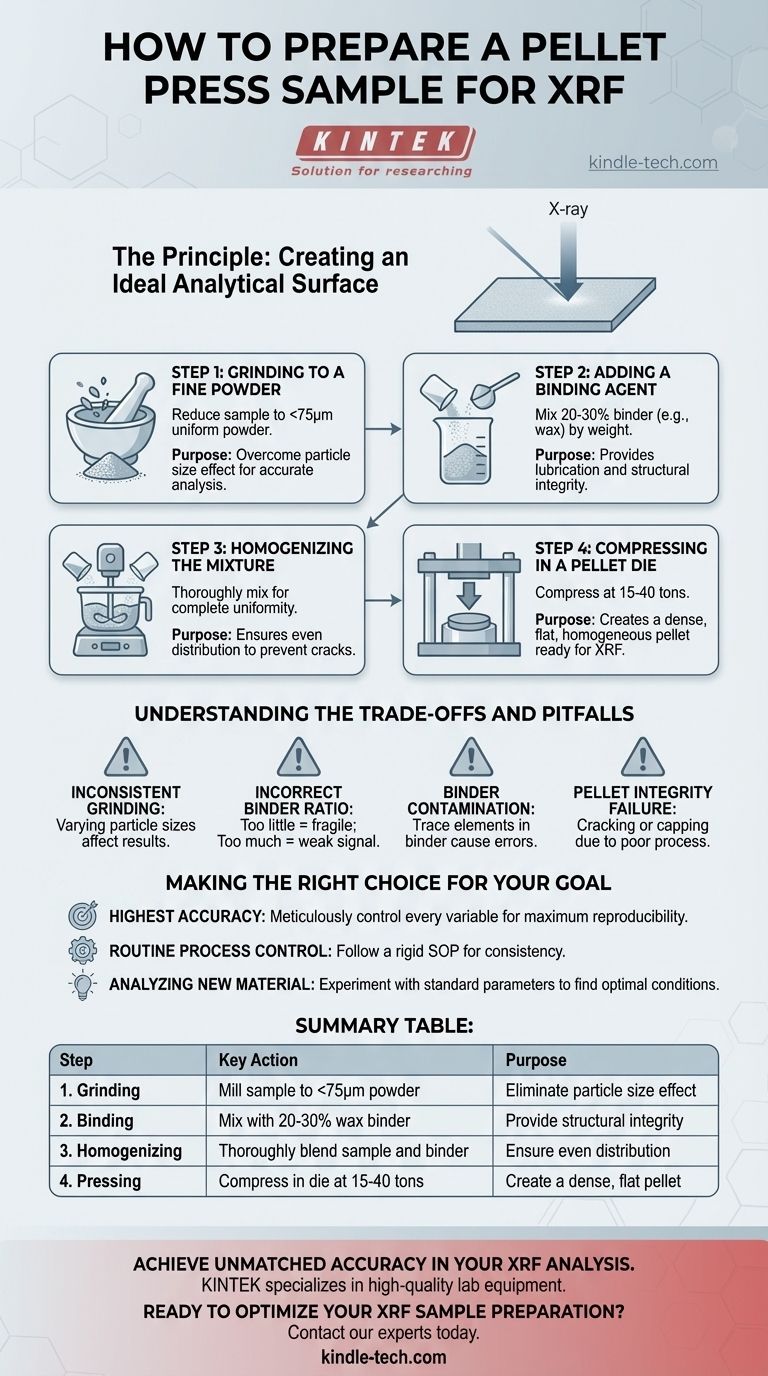
The Principle: Creating an Ideal Analytical Surface
X-Ray Fluorescence (XRF) is a surface analysis technique. The primary X-rays only penetrate a shallow depth into the sample, meaning the quality and consistency of that surface directly control the quality of your data.
Step 1: Grinding to a Fine Powder
The first step is to reduce the sample to a uniform, fine powder, typically to a particle size of less than 75 microns. This is done using milling or grinding equipment.
The purpose of this step is to overcome the particle size effect, where larger particles of a specific mineral or component can disproportionately influence the X-ray signal, skewing the results.
Step 2: Adding a Binding Agent
Once powdered, the sample is mixed with a binder, such as a wax-based powder. The binder acts as a lubricant during compression and provides structural integrity to the finished pellet.
A common mixing ratio is between 20-30% binder to sample by weight, but this can vary depending on the material's properties.
Step 3: Homogenizing the Mixture
The sample and binder must be mixed thoroughly until the blend is completely uniform. Inadequate mixing is a primary cause of pellet failure.
This homogenization ensures that the binder is evenly distributed, which prevents the formation of cracks and weak spots during compression.
Step 4: Compressing in a Pellet Die
The final mixture is poured into a pellet press die set. The die is then placed into a hydraulic press and compressed at high pressure, typically between 15 and 40 tons.
This pressure compacts the powder into a dense, solid disc with a smooth, flawless surface ready for analysis. The pellet is then carefully removed and labeled.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Pitfalls
While effective, the pressed pellet method requires careful attention to detail. Errors in preparation are a common source of poor XRF data.
Inconsistent Grinding
If one sample is ground finer than another, its analytical results may differ even if the chemical composition is identical. Establishing a consistent grinding time and method for all samples is critical.
Incorrect Binder Ratio
Using too little binder can result in a fragile pellet that crumbles or cracks after pressing. Using too much binder can dilute the sample, potentially weakening the signal for trace elements.
Binder Contamination
You must know the elemental composition of your binder. Using a binder that contains trace amounts of an element you are trying to measure will lead to artificially high and incorrect readings.
Pellet Integrity Failure
A pellet that "caps" (the top surface shears off) or cracks during or after pressing is a sign of a flawed process. This can be caused by air trapped during compression, insufficient binder, or non-homogenous mixing.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your specific analytical objective should guide your preparation technique.
- If your primary focus is the highest possible accuracy: Meticulously control every variable—grinding time, sample/binder ratio, and compression pressure—to ensure maximum reproducibility.
- If your primary focus is routine process control: Develop a rigid Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) and ensure all operators follow it exactly to guarantee consistency across shifts and batches.
- If your primary focus is analyzing a new or difficult material: Begin with a standard binder ratio and pressure, and be prepared to experiment to find the optimal parameters that produce a robust, crack-free pellet.
Ultimately, mastering your sample preparation technique is the single most important step toward achieving reliable XRF results.
Summary Table:
| Step | Key Action | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Grinding | Mill sample to <75µm powder | Eliminate particle size effect for uniform analysis |
| 2. Binding | Mix with 20-30% wax binder | Provide structural integrity and lubrication |
| 3. Homogenizing | Thoroughly blend sample and binder | Ensure even distribution to prevent cracks |
| 4. Pressing | Compress in die at 15-40 tons | Create a dense, flat, homogeneous pellet |
Achieve Unmatched Accuracy in Your XRF Analysis
Mastering sample preparation is the foundation of reliable data. KINTEK specializes in providing the high-quality lab equipment and consumables—including reliable pellet presses, dies, and pure binding agents—that your laboratory needs to eliminate preparation errors and ensure consistent, accurate results batch after batch.
Ready to optimize your XRF sample preparation? Contact our experts today to find the perfect solution for your analytical goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
- Laboratory Hydraulic Pellet Press for XRF KBR FTIR Lab Applications
- Automatic Laboratory Hydraulic Press for XRF & KBR Pellet Press
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press for Button Battery
- Automatic Laboratory Hydraulic Pellet Press Machine for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- What is the pellet technique in IR? Master Solid Sample Preparation for Clear Spectroscopy
- How does a laboratory hydraulic press improve XRF accuracy for catalyst samples? Enhance Precision & Signal Stability
- What is the advantage of KBr? Unmatched IR Transparency for Precise Spectroscopy
- Are hydraulic presses powered by water? Discover the critical role of hydraulic oil.
- Why use KBr for IR? Achieve Clear, Unobstructed Spectra for Solid Samples



















