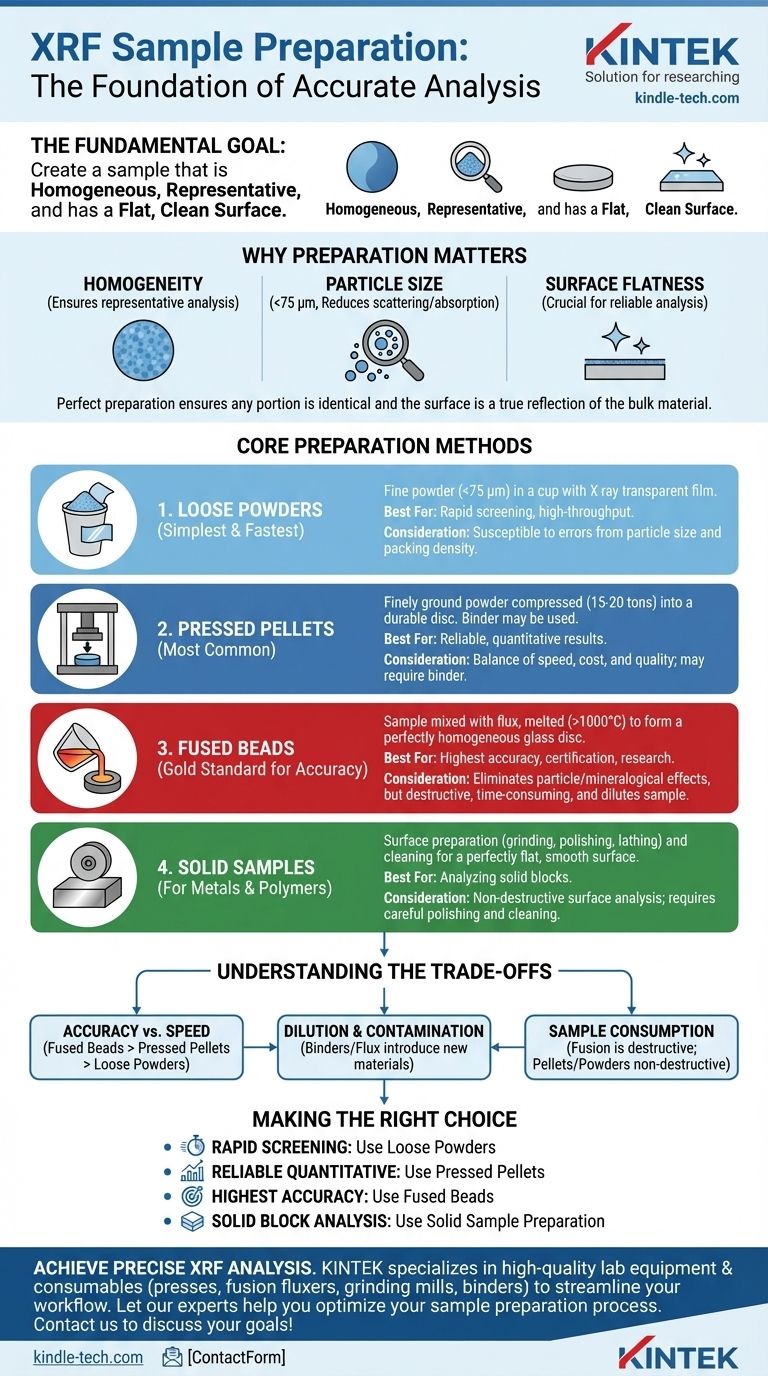
The fundamental goal of XRF sample preparation is to create a sample that is homogeneous, representative, and has a flat, clean surface for analysis. The most common methods involve processing the material into a fine powder which can be analyzed directly, pressed into a solid pellet, or melted with a flux to form a glass-like fused bead. Solid samples, like metals, are typically prepared by polishing their surface.
The method you choose is a critical decision that balances analytical accuracy against preparation time and cost. While simple powder analysis is fast, creating fused beads offers the highest precision by completely eliminating physical effects like particle size variation.

The Foundation of Accurate XRF: Why Preparation Matters
The quality of your XRF data is directly determined by the quality of your sample preparation. Because XRF analyzes a relatively small surface area, that surface must be a perfect representation of the entire bulk material to yield accurate results.
Why Homogeneity is Non-Negotiable
X-rays penetrate only a shallow depth into the sample. If the sample is not perfectly homogeneous, the analysis will only reflect the composition of the small area being measured, leading to significant and unpredictable errors. Grinding and mixing are performed to ensure any portion of the sample is identical to any other.
The Critical Role of Particle Size
For powdered samples, the goal is to grind the material to a fine, uniform grain size, typically less than 75 micrometers (µm). Large or inconsistent particle sizes can scatter X-rays and cause absorption effects, which distort the measured elemental intensities and compromise the accuracy of your results.
Ensuring a Flat, Even Surface
Any surface irregularities, such as bumps or voids, can alter the distance between the sample and the spectrometer's detector. This changes the intensity of the measured X-rays and introduces errors. A perfectly flat and smooth surface is essential for repeatable and reliable analysis.
Core Preparation Methods Explained
Your choice of method depends on your sample type (solid, powder, liquid), the elements of interest, and the required level of accuracy.
Method 1: Loose Powders
This is the simplest and fastest method. The sample is ground to a fine powder (<75 µm), placed into a sample cup, and covered with a thin X-ray transparent film. The surface is then tapped or pressed lightly to ensure it is flat.
This approach is excellent for quick screenings but is the most susceptible to errors from particle size and packing density variations.
Method 2: Pressed Pellets
This is the most common method, offering a great balance of speed, cost, and quality. The finely ground powder is poured into a die and compressed under high pressure (typically 15-20 tons) to form a solid, durable disc.
For powders that do not bind well on their own, a small amount of wax binder can be mixed in before pressing. This improves the pellet's mechanical stability.
Method 3: Fused Beads
This is the gold standard for accuracy and precision. The sample is mixed with a flux, typically a lithium borate salt, and heated in a crucible to over 1000°C. The molten mixture dissolves the sample completely, creating a perfectly homogeneous glass disc upon cooling.
This method eliminates all particle size and mineralogical effects, but it is more complex, time-consuming, and dilutes the sample, which can be a drawback for analyzing trace elements.
Method 4: Solid Samples
For solid materials like metals, alloys, or polymers, the primary task is surface preparation. The sample is cut to fit the spectrometer, and the analysis surface is prepared by grinding, polishing, or lathing to make it perfectly flat and smooth.
It is critical to then clean the surface, often with a solvent, to remove any contaminants from the preparation process.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No single method is perfect for every situation. You must understand the compromises inherent in each choice to select the right one.
Accuracy vs. Speed
Fused beads provide the highest accuracy but are the slowest to prepare. Direct analysis of loose powder is the fastest but the least precise. Pressed pellets sit comfortably in the middle.
Dilution and Contamination
Using a binder for pellets or a flux for beads introduces another material into your sample. While necessary, this dilutes the concentration of your elements of interest, making it harder to detect trace amounts. It also risks introducing contaminant elements present in the binder or flux itself.
Sample Consumption
Fusion is a destructive technique that permanently alters the sample. If your sample material is limited or precious, a non-destructive method like creating a pressed pellet (which can be broken up again) or analyzing a loose powder may be preferable.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Select your preparation method based on your specific analytical requirements.
- If your primary focus is rapid screening or high-throughput analysis: Use the direct measurement of loose powders for its unmatched speed.
- If your primary focus is reliable, quantitative results for general use: Choose pressed pellets as the best overall balance of accuracy, cost, and effort.
- If your primary focus is the highest possible accuracy for certification or research: Use the fused bead method, as it eliminates physical effects and produces the most precise data.
- If your primary focus is analyzing a solid block of metal or polymer: Prepare the sample through careful surface polishing and cleaning to ensure a flat, representative surface.
Ultimately, mastering sample preparation is the key to unlocking trustworthy and actionable data from your XRF instrument.
Summary Table:
| Method | Best For | Key Advantage | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Loose Powders | Rapid screening, high-throughput | Fastest preparation | Lower accuracy due to particle effects |
| Pressed Pellets | Reliable quantitative analysis | Best balance of speed, cost, and quality | May require a binder |
| Fused Beads | Highest accuracy, certification | Eliminates particle size/mineralogy effects | Destructive, dilutes sample, slower |
| Solid Samples | Metals, alloys, polymers | Non-destructive surface analysis | Requires careful polishing and cleaning |
Achieve precise and reliable XRF analysis every time. The right sample preparation is the foundation of accurate results. KINTEK specializes in providing the high-quality lab equipment and consumables—including presses, fusion fluxers, grinding mills, and binders—you need to streamline your XRF workflow.
Let our experts help you select the ideal preparation method and supplies for your specific materials and accuracy requirements.
Contact our team today to discuss your XRF analysis goals and optimize your sample preparation process!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Automatic Laboratory Hydraulic Press for XRF & KBR Pellet Press
- Customizable XRD Sample Holders for Diverse Research Applications
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press for Button Battery
- Laboratory Manual Hydraulic Pellet Press for Lab Use
- Laboratory Disc Rotary Mixer for Efficient Sample Mixing and Homogenization
People Also Ask
- Why is a laboratory hydraulic press utilized for electrolyte pelletizing? Unlock High Ionic Conductivity
- How do laboratory hydraulic presses facilitate biomass pelletization? Optimize Biofuel Density and Prevent Slagging
- How is a laboratory hydraulic press used for LLZTO pellets? Achieve 93% Density in Solid-State Battery Research
- What is KBr disc method? A Complete Guide to IR Spectroscopy Sample Prep
- How does a laboratory manual hydraulic press facilitate the FT-IR characterization of catalysts? Master Sample Prep.



















