At its core, a graphite furnace operates on the principle of electrical resistance. It generates immense heat by passing a large electrical current through graphite heating elements. This process takes place inside a sealed chamber where the atmosphere is tightly controlled—either a vacuum is pulled or the chamber is filled with an inert gas—to prevent the graphite from combusting and to ensure the purity of the material being processed.
A graphite furnace is not just a high-temperature oven; it is a precisely controlled environment. Its defining feature is the use of graphite for both the heating elements and insulation, allowing it to achieve extreme temperatures (up to 3000°C) while maintaining a pure, oxygen-free atmosphere essential for processing advanced materials.

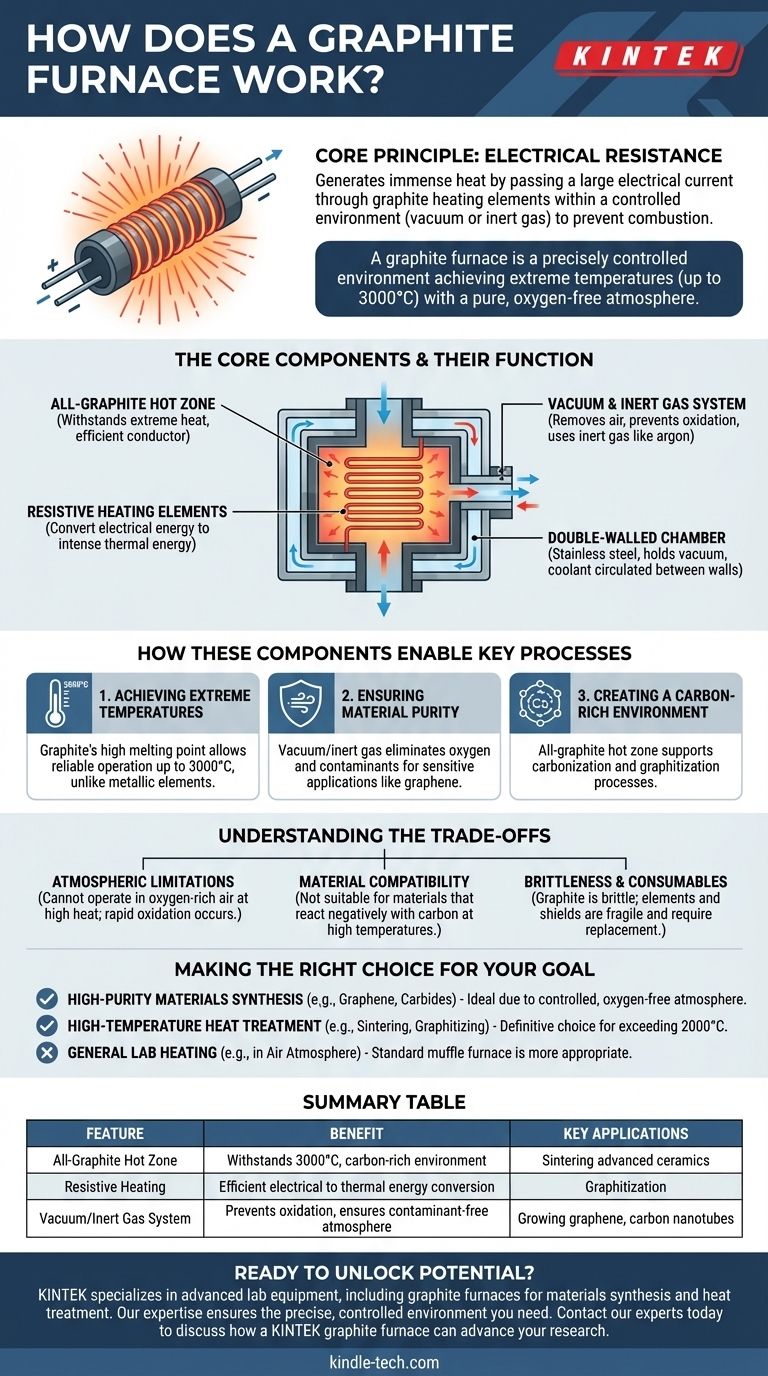
The Core Components and Their Function
To understand how a graphite furnace works, it's essential to look at its key components. Each part plays a critical role in creating the unique high-temperature, low-contaminant environment.
The All-Graphite Hot Zone
The "hot zone" is the heart of the furnace. In this design, it is constructed entirely from graphite, including the heating elements and the surrounding insulation shields.
Graphite is chosen for its remarkable ability to withstand extreme heat without melting and its efficiency as an electrical conductor.
Resistive Heating Elements
The furnace generates heat using the simple principle of electrical resistance. A high electrical current is passed through the graphite heating elements.
As the electricity struggles to move through the graphite, this electrical energy is converted directly into thermal energy, causing the elements to glow and radiate intense heat.
The Vacuum and Inert Gas System
This system is fundamental to the furnace's operation. Before heating, a vacuum pump removes nearly all the air from the chamber.
This is critical because at high temperatures, the oxygen in the air would rapidly burn and destroy the graphite components. Once the vacuum is established, the chamber can be backfilled with an inert gas like argon to create a stable, non-reactive processing environment.
The Double-Walled Chamber
The entire system is housed within a double-walled stainless steel chamber. This chamber provides the structural integrity to hold a vacuum.
Often, water or another coolant is circulated between the walls to keep the exterior of the furnace at a safe temperature despite the thousands of degrees inside.
How These Components Enable Key Processes
The unique combination of these components allows the furnace to perform specialized tasks that are impossible for conventional furnaces.
Achieving Extreme Temperatures
Standard metallic heating elements typically fail or melt well below 2000°C. Graphite's high melting point allows the furnace to reliably operate at temperatures up to 3000°C.
This capability is essential for processes like sintering advanced ceramics, graphitization, and growing synthetic carbides.
Ensuring Material Purity
The vacuum and inert gas system eliminates oxygen and other potential atmospheric contaminants.
This purity is non-negotiable for sensitive applications like growing graphene films or preparing carbon nanotubes, where even trace amounts of other elements can ruin the final product.
Creating a Carbon-Rich Environment
By its very nature, an all-graphite hot zone creates a carbon-rich atmosphere.
This is highly beneficial for processes like carbonization (converting organic substances into carbon) or graphitization (converting amorphous carbon into crystalline graphite), as the environment itself supports the desired chemical transformation.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, graphite furnaces have specific limitations that make them unsuitable for certain applications. Understanding these trade-offs is key to using the technology correctly.
Atmospheric Limitations
A graphite furnace cannot operate in an oxygen-rich or ambient air atmosphere at high temperatures. The presence of oxygen would cause the graphite elements and insulation to rapidly oxidize and fail.
Material Compatibility
The carbon-rich environment means this furnace is not suitable for processing materials that react negatively with carbon at high temperatures.
Brittleness and Consumables
Graphite is a brittle material. The heating elements and shields can be fragile and require careful handling. Over time, they are considered consumables that will eventually need to be replaced.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Deciding if a graphite furnace is the correct tool depends entirely on your process requirements for temperature and atmospheric purity.
- If your primary focus is high-purity materials synthesis (graphene, carbides): The controlled, oxygen-free atmosphere is its most critical advantage, making it the ideal choice.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature heat treatment (sintering, graphitizing): Its ability to exceed 2000°C, where conventional metal furnaces fail, is the definitive reason to use it.
- If your primary focus is general lab heating in an air atmosphere: A standard muffle furnace or convection oven is a far more appropriate and cost-effective tool for your needs.
Ultimately, choosing a graphite furnace is a decision to prioritize an extremely high-temperature and pure environment above all else.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| All-Graphite Hot Zone | Withstands extreme heat (up to 3000°C) and creates a carbon-rich environment. |
| Resistive Heating | Efficiently converts electrical energy into intense, radiant thermal energy. |
| Vacuum/Inert Gas System | Prevents graphite oxidation and ensures a pure, contaminant-free atmosphere. |
| Key Applications | Ideal for sintering advanced ceramics, graphitization, and growing graphene or carbon nanotubes. |
Ready to unlock the potential of high-temperature, high-purity processing in your lab?
KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment, including graphite furnaces designed for demanding applications like materials synthesis and heat treatment. Our expertise ensures you get the precise, controlled environment you need for your most critical work.
Contact our experts today to discuss how a KINTEK graphite furnace can advance your research and development.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- Vertical High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace IGBT Experimental Graphitization Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between graphite furnace and flame AAS? Choose the Right Technique for Your Lab
- What gas is used in graphite furnace? Maximize Accuracy with the Right Inert Gas
- What is the temperature of graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry? Mastering the Multi-Stage Heating Program
- What happens to graphite when heated? Unlock Its High-Temperature Potential or Risk Oxidation
- What is the disadvantage of graphite furnace? Managing Reactivity and Contamination Risks
- What are the stages of graphite furnace? A Guide to Precise Multi-Stage Temperature Programming
- What does graphite furnace measure? A Key Tool for Trace Analysis & High-Temp Processing
- What is the temperature of a graphite furnace? Achieve Extreme Heat Up to 3000°C



















