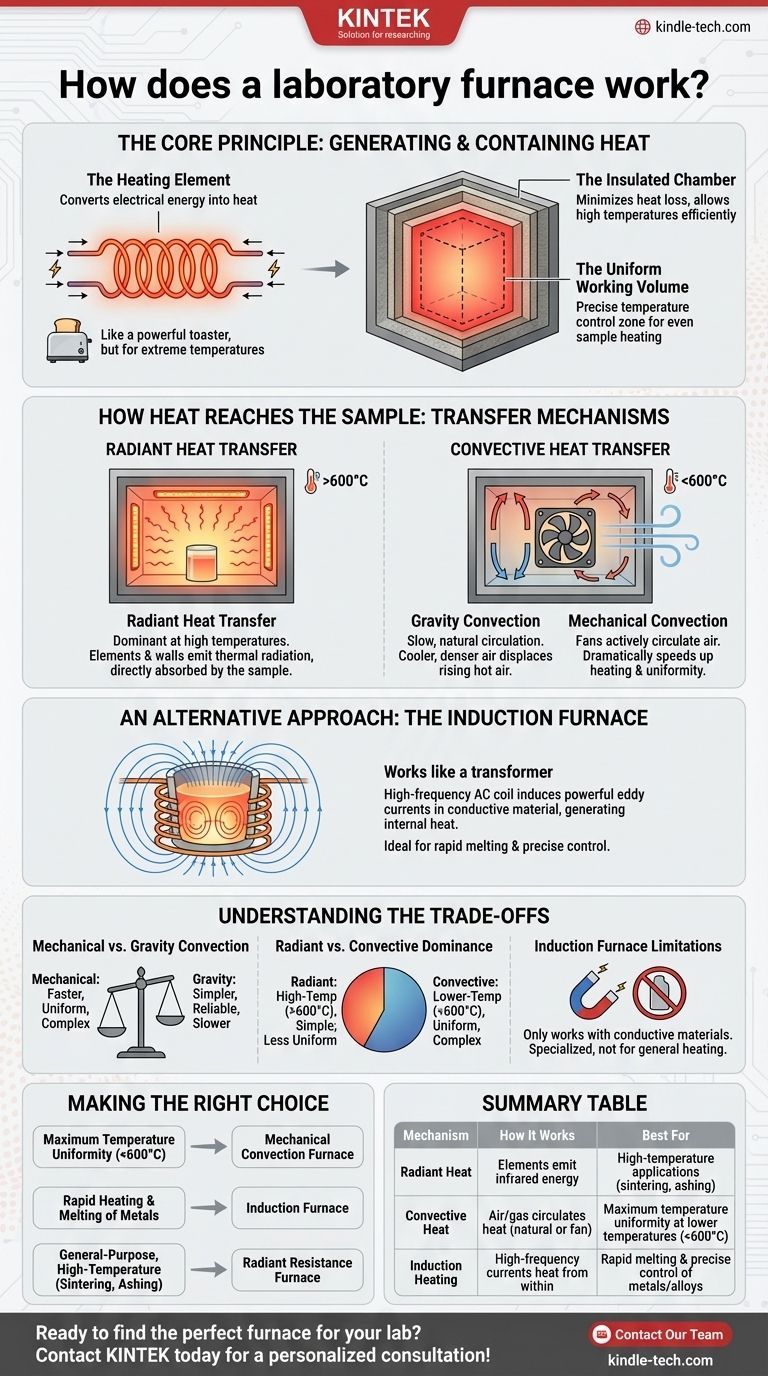
At its core, a laboratory furnace is a device that generates and contains high temperatures within an insulated chamber. It works by converting electrical energy into heat and then transferring that heat to a sample using a combination of thermal radiation and convection to achieve a precise, uniform temperature.
The fundamental goal of any laboratory furnace is to create a highly controlled and uniform thermal environment. The specific mechanisms it uses—primarily radiation at high temperatures and convection for enhanced uniformity—are chosen based on the intended application, such as melting, sintering, or chemical analysis.

The Core Principle: Generating and Containing Heat
A furnace's operation can be broken down into two primary functions: producing heat and keeping it where it's needed.
The Heating Element
Most common laboratory furnaces are electric resistance furnaces. They use heating elements, often made of specialized alloys or ceramics, which heat up significantly when an electric current passes through them.
This is the same principle used in a simple toaster, but engineered for much higher temperatures and greater control.
The Insulated Chamber
The heating elements are housed within a highly insulated chamber. This chamber minimizes heat loss to the surrounding environment, allowing the furnace to reach and maintain high temperatures efficiently and safely.
The Uniform Working Volume
Within this chamber is a specific region known as the uniform working volume. This is the three-dimensional space where the temperature is controlled within very tight tolerances, ensuring that the entire sample is heated evenly.
How Heat Reaches the Sample: The Transfer Mechanisms
Once heat is generated, it must be transferred to the item being processed. This happens through two main physical processes, often working in tandem.
Radiant Heat Transfer
At the high temperatures achieved in many furnaces, radiant heat is the dominant transfer mechanism. The hot heating elements emit thermal radiation (infrared energy), which travels through the space and is absorbed directly by the sample.
The chamber walls also heat up and radiate energy, creating a uniform heating effect from all directions.
Convective Heat Transfer
Convection involves heat transfer through the movement of a fluid, in this case, the air or gas inside the furnace. This method is crucial for ensuring temperature uniformity, especially at lower temperatures.
There are two forms of convection:
- Gravity Convection: As air near the heating element gets hot, it becomes less dense and rises. This displaces cooler, denser air, which sinks toward the element to be heated, creating a slow, natural circulation pattern.
- Mechanical Convection: These furnaces use fans or blowers to actively and forcefully circulate the air. This dramatically speeds up heating and produces a much more uniform temperature throughout the chamber.
An Alternative Approach: The Induction Furnace
A less common but highly effective type is the high-frequency induction furnace, which operates on a completely different principle.
The Transformer Principle
An induction furnace works like a transformer. A primary coil connected to a high-frequency AC supply surrounds the sample (or a conductive crucible holding it). This induces powerful eddy currents directly within the sample, which acts as the secondary coil.
The resistance to these swirling currents generates rapid and intense heat from within the material itself, rather than from an external source.
Key Advantages
This method allows for extremely fast melting times and exceptionally precise temperature control, making it ideal for metallurgical applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The design of a furnace dictates its performance, and each approach comes with inherent compromises.
Mechanical vs. Gravity Convection
A furnace with mechanical convection provides superior temperature uniformity and faster heating. However, the inclusion of blowers adds complexity, cost, and a potential point of mechanical failure. Gravity convection is simpler and more reliable but slower.
Radiant vs. Convective Dominance
Furnaces designed for very high temperatures rely almost entirely on radiation, as fans cannot operate in such extreme heat. While simple and effective, achieving perfect uniformity requires careful design. Convection ovens excel at uniformity below ~600°C.
Induction Furnace Limitations
While fast and precise, induction furnaces only work with conductive materials. They are specialized instruments and are not suited for general-purpose heating of ceramics or other insulators unless a conductive crucible is used.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your specific goal determines which operating principle is most important.
- If your primary focus is maximum temperature uniformity for sensitive processes: Choose a furnace with mechanical convection for applications below 600°C.
- If your primary focus is rapid heating or melting of metals: An induction furnace provides unmatched speed and precision control.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose, high-temperature work like sintering or ashing: A standard radiant resistance furnace offers a reliable and effective solution.
Ultimately, understanding how a furnace generates and transfers heat empowers you to select and operate this critical piece of laboratory equipment correctly and effectively.
Summary Table:
| Mechanism | How It Works | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Radiant Heat | Heating elements emit infrared energy, heating the sample directly. | High-temperature applications (e.g., sintering, ashing). |
| Convective Heat | Air or gas circulates heat (naturally or with a fan) for uniformity. | Maximum temperature uniformity at lower temperatures (<600°C). |
| Induction Heating | High-frequency currents heat conductive materials from within. | Rapid melting and precise control of metals and alloys. |
Ready to find the perfect furnace for your lab's unique needs? Whether you require uniform heating for sensitive processes, rapid melting for metallurgy, or reliable high-temperature performance, KINTEK has the solution. Our experts will help you select from our range of mechanical convection, gravity convection, and high-temperature radiant furnaces to ensure optimal results for your application. Contact our team today for a personalized consultation and see how KINTEK's lab equipment can enhance your efficiency and precision!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why does heating increase temperature? Understanding the Molecular Dance of Energy Transfer
- What is the difference between upflow and horizontal furnace? Find the Perfect Fit for Your Home's Layout
- What is the temperature of a quartz tube furnace? Master the Limits for Safe, High-Temp Operation
- What is the standard thickness of plating? Optimize Durability, Corrosion & Cost
- What is a vertical tube furnace? Leverage Gravity for Superior Uniformity and Process Control



















