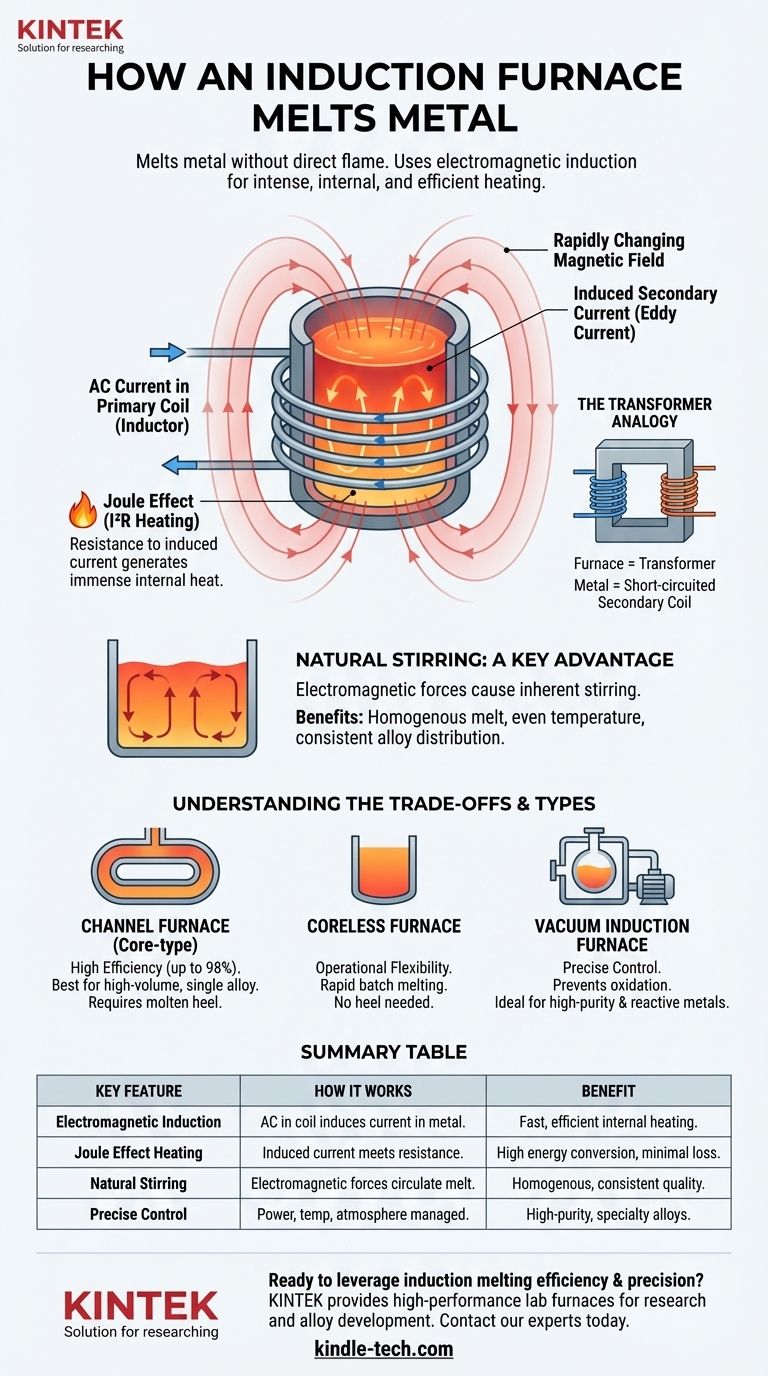
At its core, an induction furnace melts metal without any direct flame or external heating element. It uses the principle of electromagnetic induction to generate intense heat directly within the metal charge itself. An alternating electric current flows through a primary coil, creating a powerful, rapidly changing magnetic field that induces a secondary electrical current within the metal, melting it efficiently from the inside out.
An induction furnace functions like a powerful transformer where the metal to be melted acts as a short-circuited secondary coil. This method provides highly efficient and controllable melting, combined with a natural stirring action that is critical for producing high-quality, homogenous alloys.
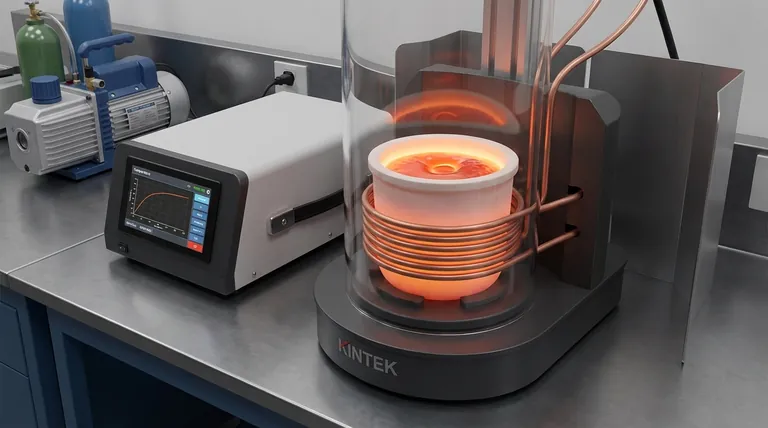

The Core Principle: Electromagnetic Heating
The technology behind an induction furnace is a direct application of Faraday's Law of Induction and the Joule effect. It converts electrical energy into thermal energy with remarkable efficiency.
The Furnace as a Transformer
An induction furnace operates on the same principle as a transformer. A primary coil, wound around a core or the crucible itself, has an alternating current (AC) passed through it.
The metal pieces inside the furnace, or the loop of molten metal in a channel furnace, effectively become the secondary coil. The AC in the primary coil induces a much larger current to flow within the metal.
Generating Heat via the Joule Effect
This large induced current, flowing against the metal's natural electrical resistance, generates immense heat. This phenomenon is known as the Joule effect (or I²R heating).
Because the heat is generated within the metal, the process is extremely fast and efficient, with minimal heat lost to the surrounding environment.
The Critical Role of Alternating Current
A static magnetic field would not induce a current. The process relies on a constantly changing magnetic field, which is why alternating current (AC) at a specific frequency is essential for the furnace to operate.
A Key Advantage: Natural Stirring
One of the most significant benefits of induction melting is the inherent stirring of the molten bath, which is also a result of electromagnetic forces.
How Stirring Occurs
The powerful magnetic field from the coil interacts with the strong electrical currents flowing through the molten metal. This interaction creates forces that cause the liquid metal to move.
Typically, this forces the molten metal to rise in the center and flow downwards along the edges, creating a continuous, self-stirring loop. This is often visible as a raised mound, or meniscus, on the surface of the melt.
Benefits of a Homogenous Melt
This natural stirring action is vital for high-quality metal production. It ensures an even temperature distribution throughout the entire batch.
Furthermore, it guarantees that any added alloys are thoroughly mixed, resulting in a perfectly homogenous final product with consistent chemical composition and properties.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, induction technology is not a universal solution. Understanding its specific characteristics is key to leveraging it properly.
High Efficiency, Specific Applications
Core-type or channel furnaces are extremely efficient, converting up to 98% of electrical energy into heat. However, they are best suited for holding and melting large, continuous volumes of a single type of metal.
These furnaces require a continuous loop of molten metal (a "heel") to operate, making them less flexible for frequent alloy changes or batch operations.
Control vs. Complexity
Modern induction furnaces offer unparalleled control over the melting process. Parameters like power, temperature, and time can be precisely automated.
Systems like vacuum induction furnaces allow for melting under a controlled atmosphere (vacuum or inert gas), which is essential for preventing oxidation when working with reactive metals. This level of control, however, comes with increased equipment complexity and cost.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use a specific type of induction furnace depends entirely on the operational goal.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, continuous melting of one alloy: A channel induction furnace offers the highest possible electrical efficiency for the job.
- If your primary focus is producing high-purity or specialty alloys: A vacuum induction furnace provides the essential atmospheric control to prevent contamination and ensure metallurgical quality.
- If your primary focus is operational flexibility and rapid batch melting: A coreless induction furnace is often the superior choice, as it does not require a molten heel to start.
Ultimately, induction melting provides a unique combination of efficiency, precise control, and metallurgical quality that is unmatched by traditional fuel-fired methods.
Summary Table:
| Key Feature | How It Works | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Electromagnetic Induction | AC current in a coil induces a powerful secondary current within the metal itself. | Heat is generated internally for fast, efficient melting. |
| Joule Effect Heating | The induced current meets the metal's electrical resistance, creating intense heat. | Highly efficient energy conversion with minimal heat loss. |
| Natural Stirring | Electromagnetic forces cause the molten metal to circulate. | Ensures a homogenous melt with even temperature and alloy distribution. |
| Precise Control | Power, temperature, and atmosphere (e.g., vacuum) can be precisely managed. | Ideal for producing high-purity and specialty alloys with consistent quality. |
Ready to leverage the efficiency and precision of induction melting in your lab?
KINTEK specializes in providing high-performance lab equipment, including induction furnaces tailored for research, alloy development, and high-purity metal production. Our solutions deliver the control and homogeneity you need for superior results.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application and find the perfect induction melting system for your laboratory's needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- How to clean a tube furnace? A Step-by-Step Guide for Safe and Effective Maintenance
- What materials are used for the tubes in tube furnaces? A Guide to Selecting the Right Tube for Your Process
- What precautions should be taken when using a tube furnace? Ensure Safe, Effective High-Temperature Processing
- How does a quartz tube vacuum furnace contribute to the crystallization process of Ag-doped Li-argyrodite electrolytes?
- How does a tubular furnace work? A Guide to Controlled High-Temperature Processing



















