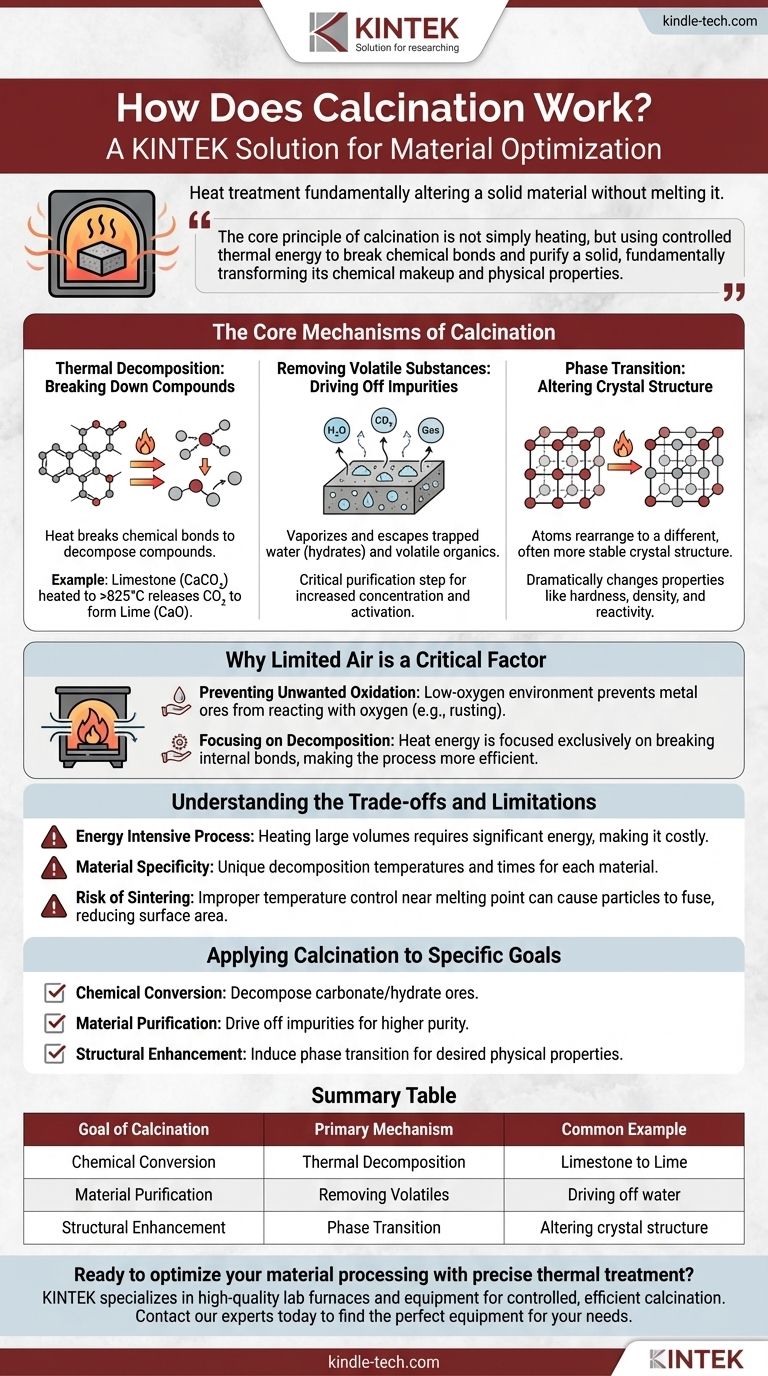
In essence, calcination is a heat treatment process that fundamentally alters a solid material without melting it. By heating a substance to a high temperature in a low-oxygen environment, it forces thermal decomposition, drives off volatile impurities like water and carbon dioxide, or changes the material's internal crystal structure.
The core principle of calcination is not simply heating, but using controlled thermal energy to break chemical bonds and purify a solid, fundamentally transforming its chemical makeup and physical properties.
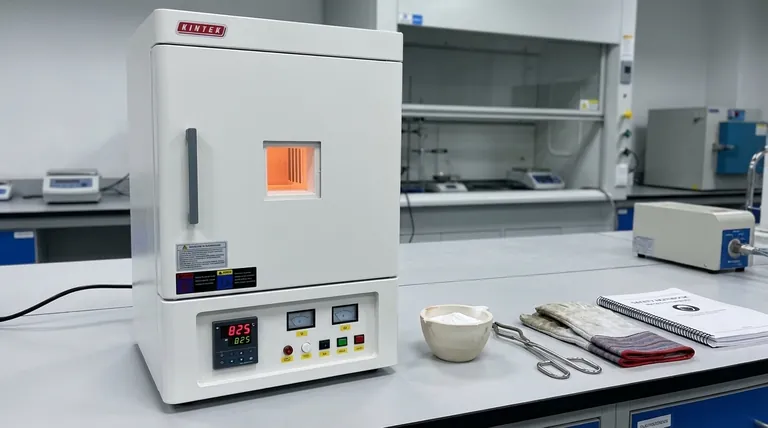

The Core Mechanisms of Calcination
To understand how calcination works, you must look at the three primary changes it can induce in a material when subjected to high heat.
Thermal Decomposition: Breaking Down Compounds
This is the most common goal of calcination. Heat provides the necessary energy to break the chemical bonds within a compound, causing it to decompose into simpler substances.
The classic example is the production of lime (calcium oxide) from limestone (calcium carbonate). When heated to over 825°C (1517°F), the limestone breaks down, releasing carbon dioxide gas and leaving behind the purified lime.
Removing Volatile Substances: Driving Off Impurities
Many raw materials contain trapped water (hydrates) or other volatile organic compounds. Calcination heats the material to a point where these substances vaporize and escape.
This is a critical purification step, leaving a more concentrated or anhydrous (water-free) version of the desired material. This increases the purity and can "activate" the material for subsequent processes.
Phase Transition: Altering Crystal Structure
Sometimes, the goal is not to change the chemical composition but to alter the material's physical form.
Heating can cause the atoms in a solid to rearrange themselves into a different, often more stable or useful, crystal structure. This is known as a phase transition, and it can dramatically change properties like hardness, density, and reactivity.
Why Limited Air is a Critical Factor
The condition of using a limited supply of air (or no air at all) is what distinguishes calcination from other heat treatments like roasting.
Preventing Unwanted Oxidation
Many metal ores, when heated in the presence of oxygen, will react with it to form an oxide. This is the same basic process as rusting.
By performing the heating in a low-oxygen environment, calcination specifically prevents these unwanted oxidation reactions from occurring, ensuring the desired chemical change takes place.
Focusing on Decomposition
With oxygen removed from the equation, the applied heat energy is focused exclusively on one task: breaking the internal bonds of the material itself. This makes the process more efficient and predictable for its intended purpose.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, calcination is a precise industrial process with important considerations.
Energy Intensive Process
Heating large volumes of solid materials to hundreds or even thousands of degrees requires a significant amount of energy. This makes it a costly and resource-intensive step in any production chain.
Material Specificity
There is no universal temperature for calcination. Every material has a unique decomposition temperature and required heating time. What works perfectly for limestone may be completely ineffective or even destructive for another type of ore.
Risk of Sintering
If the temperature is controlled improperly and gets too close to the material's melting point, the particles can begin to fuse. This process, called sintering, can reduce the surface area and reactivity of the final product, which is often undesirable.
Applying Calcination to Specific Goals
The decision to use calcination depends entirely on your desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is chemical conversion: Calcination is the ideal method for decomposing a carbonate or hydrate ore into a more useful oxide form.
- If your primary focus is material purification: Use calcination to drive off volatile impurities like water or residual solvents, creating a more concentrated and pure final product.
- If your primary focus is structural enhancement: Apply calcination to induce a phase transition, changing the material's crystal structure to achieve desired physical properties.
Ultimately, calcination is a fundamental tool for precisely engineering the chemical composition and physical properties of solid materials.
Summary Table:
| Goal of Calcination | Primary Mechanism | Common Example |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Conversion | Thermal Decomposition | Limestone (CaCO₃) to Lime (CaO) |
| Material Purification | Removing Volatiles | Driving off water from a hydrate |
| Structural Enhancement | Phase Transition | Altering a material's crystal structure |
Ready to optimize your material processing with precise thermal treatment? The calcination process is critical for achieving the right chemical and physical properties in your materials. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab furnaces and equipment designed for controlled, efficient calcination. Whether you're in research, development, or production, our solutions help you drive off impurities, induce phase transitions, and achieve superior results. Contact our experts today to find the perfect calcination equipment for your laboratory's specific needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is a muffle furnace used for in pharma? Ensuring Purity and Regulatory Compliance
- What is the design and construction of a muffle furnace? A Guide to Its Isolated Heating Chamber
- How is the sintering temperature related to the melting temperature? A Guide to Solid-State Bonding
- What is the function of a muffle furnace? Achieve Pure, Contamination-Free Heating
- What is the use of muffle furnace in food analysis? Master Ashing for Accurate Mineral Content



















