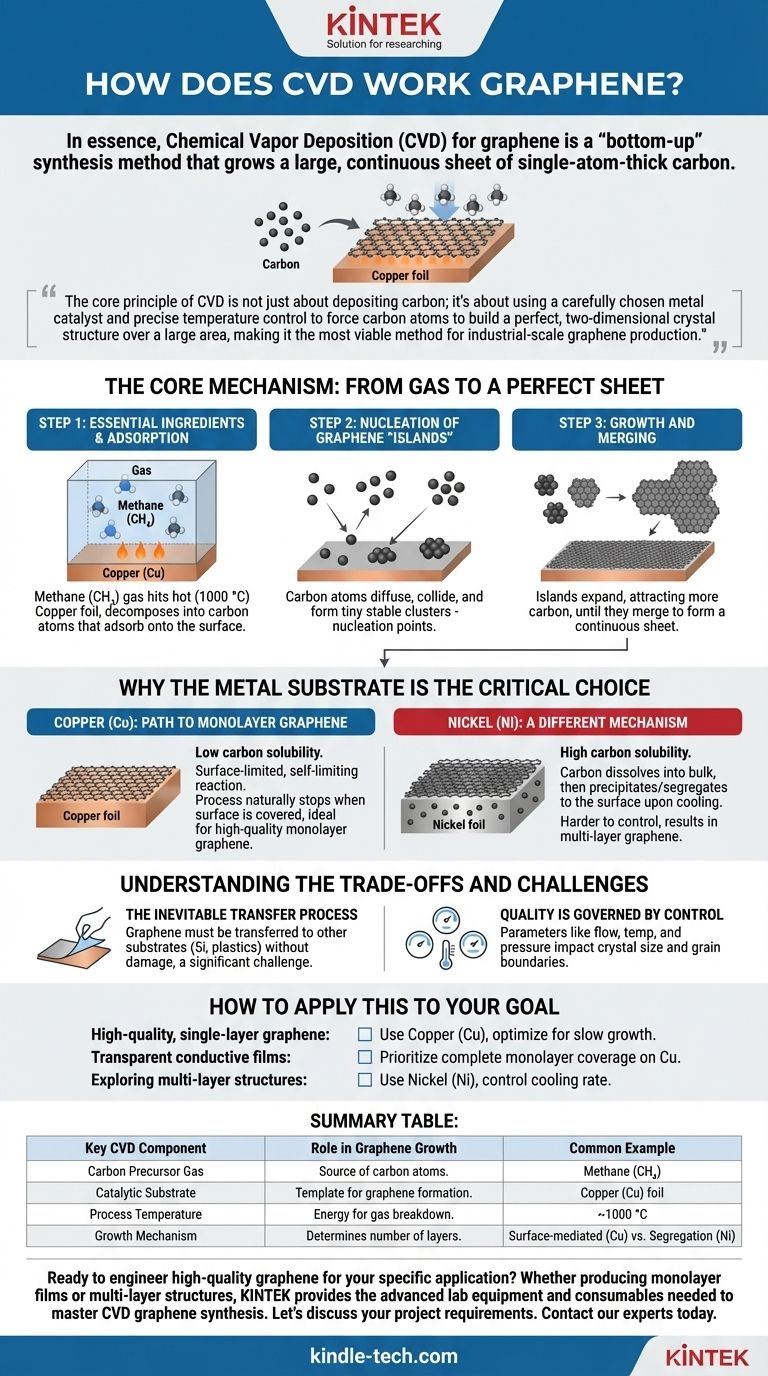
In essence, Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) for graphene is a "bottom-up" synthesis method that grows a large, continuous sheet of single-atom-thick carbon. The process works by heating a carbon-containing gas, such as methane, to a high temperature over a metal catalyst foil, typically copper. The heat breaks the gas down, and the metal surface acts as a template, guiding the liberated carbon atoms to self-assemble into the hexagonal lattice structure of graphene.
The core principle of CVD is not just about depositing carbon; it's about using a carefully chosen metal catalyst and precise temperature control to force carbon atoms to build a perfect, two-dimensional crystal structure over a large area, making it the most viable method for industrial-scale graphene production.

The Core Mechanism: From Gas to a Perfect Sheet
To truly understand how CVD works, it's best to break it down into its fundamental stages. The entire process occurs inside a controlled chamber, usually under vacuum, at temperatures around 1000 °C.
The Essential Ingredients
The process requires two key components: a carbon precursor gas and a catalytic substrate. The most common precursor is methane (CH₄), and the most widely used substrate for high-quality graphene is a thin foil of copper (Cu).
Step 1: Adsorption and Decomposition
First, the methane gas is introduced into the hot chamber. When the gas molecules hit the hot surface of the copper foil, the thermal energy causes them to break apart, or decompose. This reaction liberates individual carbon atoms, which then stick to the metal surface in a process called adsorption.
Step 2: Nucleation of Graphene "Islands"
These individual carbon atoms are not stationary. They diffuse, or skate, across the copper surface. Eventually, atoms collide and begin to form tiny, stable clusters. These clusters are the initial "seeds" or nucleation points for graphene growth.
Step 3: Growth and Merging
Once a nucleation site is formed, it acts as a magnet for other carbon atoms diffusing on the surface. These atoms attach to the edges of the initial seed, causing it to grow outwards into a hexagonal graphene crystal, often called an "island." These islands continue to expand until they meet and merge, forming a continuous, single-atom-thick sheet of graphene covering the entire copper foil.
Why the Metal Substrate is the Critical Choice
The type of metal used as the catalyst fundamentally changes how the graphene forms and dictates the quality of the final product. The key difference lies in how well the metal dissolves carbon.
Copper (Cu): The Path to Monolayer Graphene
Copper has a very low carbon solubility. This means carbon atoms cannot easily dissolve into the bulk of the copper. Instead, the entire process happens directly on the surface.
This surface-limited reaction is self-limiting. Once the copper surface is completely covered with a single layer of graphene, there is no more exposed catalyst to break down the methane gas. The process naturally stops, making copper the ideal substrate for producing large sheets of high-quality monolayer graphene.
Nickel (Ni): A Different Mechanism
In contrast, nickel has a high carbon solubility. At high temperatures, carbon atoms from the precursor gas dissolve into the bulk of the nickel, much like sugar dissolving in water.
When the system is cooled, the nickel can no longer hold as much dissolved carbon. The carbon then precipitates or "segregates" back out onto the surface, forming graphene. This process is harder to control and often results in multiple, uneven layers of graphene.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
While CVD is a powerful technique, it is not without its complexities. The quality of the final product depends on meticulous control over the process.
The Inevitable Transfer Process
The graphene is grown on a metal foil, but its applications are on other substrates like silicon wafers or flexible plastics. This requires a delicate transfer process to peel the atomic-thin graphene sheet off the copper and move it to its final destination without tearing or contamination. This step remains a significant technical challenge.
Quality is Governed by Control
The final quality of the graphene sheet is highly dependent on process parameters. The rate of gas flow, reaction temperature, and pressure all influence the size of the graphene crystals. Imperfections can arise at the "grain boundaries" where different graphene islands merge.
How to Apply This to Your Goal
Controlling the CVD process allows for the engineering of graphene for specific outcomes. Your choice of parameters should be directly tied to your end goal.
- If your primary focus is high-quality, single-layer graphene: Use a copper (Cu) substrate and optimize for slow, steady growth to form large, uniform crystal islands.
- If your primary focus is use in transparent conductive films: Prioritize a complete and uniform monolayer coverage on copper to achieve the best balance of low sheet resistance and high optical transparency.
- If your primary focus is exploring multi-layer structures: Consider a nickel (Ni) substrate and carefully control the cooling rate to manage the carbon segregation process.
By understanding these core principles, you can move beyond simply making graphene and begin engineering its properties for specific, high-value applications.
Summary Table:
| Key CVD Component | Role in Graphene Growth | Common Example |
|---|---|---|
| Carbon Precursor Gas | Provides the source of carbon atoms. | Methane (CH₄) |
| Catalytic Substrate | Acts as a template for carbon atoms to form graphene. | Copper (Cu) foil |
| Process Temperature | Provides energy to break down the gas. | ~1000 °C |
| Growth Mechanism | Determines the number of graphene layers. | Surface-mediated (Cu) vs. Segregation (Ni) |
Ready to engineer high-quality graphene for your specific application?
Whether your goal is producing uniform monolayer films for electronics or developing multi-layer structures, precise control over the CVD process is critical. KINTEK specializes in providing the advanced lab equipment and consumables—from high-temperature furnaces to catalytic substrates—needed to master graphene synthesis.
Let's discuss your project requirements. Contact our experts today to explore how our solutions can help you achieve consistent, high-yield graphene production.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace IGBT Experimental Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the steps of the CVD process? A Guide to Precision Thin Film Deposition
- What is the vapor phase deposition technique? A Guide to PVD & CVD Thin-Film Coating Methods
- What is the process of vacuum vapor deposition? Mastering CVD and PVD Thin-Film Coating
- What is PECVD in semiconductor? Enable Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition for ICs
- What are the different types of thin films? A Guide to Optical, Electrical, and Functional Coatings


















