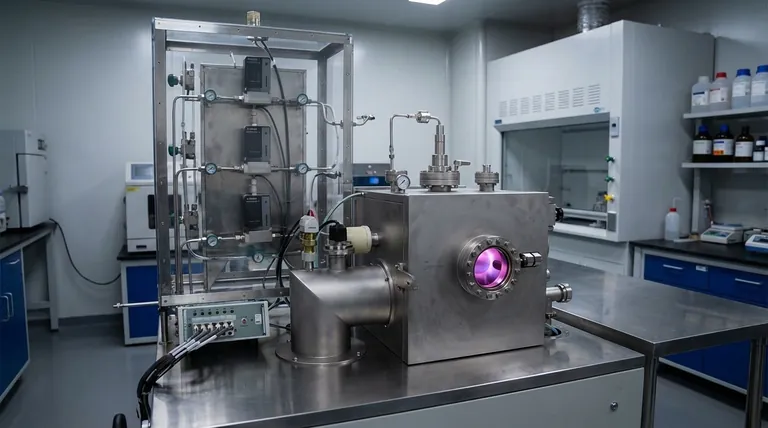
At its core, Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition (PECVD) is a process that builds ultra-thin films by using an energized gas, known as a plasma, instead of high heat. This fundamental shift allows for the deposition of coatings at significantly lower temperatures than traditional methods. The process involves introducing a precursor gas into a vacuum chamber, using an energy source like a radio frequency (RF) or microwave field to excite that gas into a plasma, which then decomposes and deposits onto a substrate as a solid thin film.
The central advantage of PECVD is its ability to substitute the brute-force energy of high temperature with the precise energy of a plasma. This enables the creation of high-quality coatings on materials, like plastics or certain semiconductors, that would be damaged or destroyed by the heat required for conventional Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD).
The Core Principle: Replacing Heat with Plasma
To understand PECVD, it's essential to first grasp the method it enhances: traditional Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD).
How Traditional CVD Works
In a standard thermal CVD process, a substrate is placed in a reaction chamber and heated to very high temperatures, often several hundred degrees Celsius.
A volatile precursor gas, containing the atoms for the desired film, is then introduced into the chamber.
The intense heat provides the energy needed to break the chemical bonds in the gas, causing it to decompose and react on the hot substrate surface, gradually building the coating layer by layer.
How PECVD Changes the Equation
PECVD fundamentally alters the energy source for the reaction. Instead of relying solely on thermal energy, it generates a plasma.
A plasma is often called the fourth state of matter. It is a gas that has been energized to the point where its atoms are broken apart into a mixture of positive ions, free electrons, and highly reactive neutral radicals.
This energized plasma provides the necessary energy to break down the precursor gas molecules, initiating the chemical reactions required for deposition without needing extreme heat.
A Look Inside the PECVD Process
The PECVD process unfolds in a carefully controlled sequence within a vacuum chamber.
Step 1: Creating a Vacuum
First, the chamber is pumped down to a vacuum. This removes air and other contaminants that could interfere with the chemical reaction and compromise the purity of the final film.
Step 2: Introducing Precursor Gases
The precursor gases—the chemical building blocks of the film—are then carefully metered into the chamber.
Step 3: Igniting the Plasma
An electrical field, typically from a radio frequency (RF), direct current (DC), or microwave source, is applied to the chamber.
This field energizes the gas, stripping electrons from atoms and creating the highly reactive plasma. Techniques like Microwave Electron Cyclotron Resonance (MWECR) use a combination of microwaves and magnetic fields to create particularly dense and active plasmas.
Step 4: Deposition on the Substrate
The reactive ions and radicals within the plasma bombard the substrate surface. The substrate is kept at a much lower temperature than in thermal CVD.
These reactive species condense and react on the cooler surface, forming a stable, solid, and uniform thin film. This process continues until the desired film thickness is achieved.
Understanding the Key Advantages
The shift from thermal to plasma energy provides several significant benefits that have made PECVD a critical technology in industries like microelectronics and optics.
Low-Temperature Deposition
This is the primary advantage of PECVD. It allows for coating on temperature-sensitive substrates, such as polymers, plastics, and fully fabricated semiconductor devices, without causing thermal damage.
Enhanced Material Versatility
The unique, high-energy environment of the plasma enables the deposition of materials that are difficult or impossible to create with thermal CVD. This includes materials like silicon carbide (SiC) films and vertically aligned carbon nanotubes.
High-Quality and Dense Films
The energetic bombardment of the substrate surface during PECVD can result in films that are very dense and have excellent adhesion and uniformity. The process parameters can be tuned to precisely control the film's final structure and properties.
Inherent Trade-offs and Considerations
While powerful, PECVD is not without its complexities and potential downsides.
Increased System Complexity
PECVD reactors are more complex and expensive than their thermal CVD counterparts. They require sophisticated power supplies (RF or microwave generators), impedance matching networks, and advanced control systems to maintain a stable plasma.
Potential for Substrate Damage
Although the process is low-temperature, the energetic ions in the plasma can physically damage the substrate or the growing film if the energy is not carefully controlled. This can introduce defects that affect performance.
Film Impurities
The chemical reactions in a plasma are incredibly complex. Sometimes, precursor molecules do not fully decompose, leading to the incorporation of impurities (such as hydrogen) into the film, which can alter its electrical or optical properties.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting between PECVD and other deposition techniques depends entirely on your material, substrate, and desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is coating heat-sensitive substrates: PECVD is the definitive choice, as its low-temperature nature prevents thermal damage.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest possible film purity and crystallinity: Traditional high-temperature CVD may be superior, as the thermal energy can provide a cleaner reaction pathway with fewer incorporated impurities for certain materials.
- If your primary focus is depositing novel or complex materials: PECVD offers unmatched flexibility to create unique film compositions and structures that are not achievable with thermal methods alone.
Ultimately, PECVD empowers engineers and scientists to build advanced materials by fundamentally changing how energy is delivered to a chemical system.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Plasma Enhanced CVD (PECVD) | Traditional Thermal CVD |
|---|---|---|
| Process Temperature | Low (substrate-friendly) | High (hundreds of °C) |
| Energy Source | Plasma (RF, DC, microwave) | Thermal heat only |
| Key Advantage | Coats temperature-sensitive materials | High purity & crystallinity for certain materials |
| Ideal For | Polymers, plastics, prefabricated devices | High-temperature stable substrates |
Need to deposit high-quality thin films on temperature-sensitive materials? KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment, including PECVD systems, to help you achieve precise, low-temperature coatings for your research or production needs. Our expertise ensures you get the right solution for polymers, semiconductors, and other delicate substrates. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can enhance your laboratory capabilities!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
People Also Ask
- How are thin films deposited? A Guide to PVD vs. CVD Methods for Your Application
- Can plasma enhanced CVD deposit metals? Why PECVD is rarely used for metal deposition
- What are the process capabilities of ICPCVD systems? Achieve Low-Damage Film Deposition at Ultra-Low Temperatures
- What is the difference between plasma CVD and thermal CVD? Choose the Right Method for Your Substrate
- What is the difference between PECVD and APCVD? Choose the Right CVD Method for Your Application



















