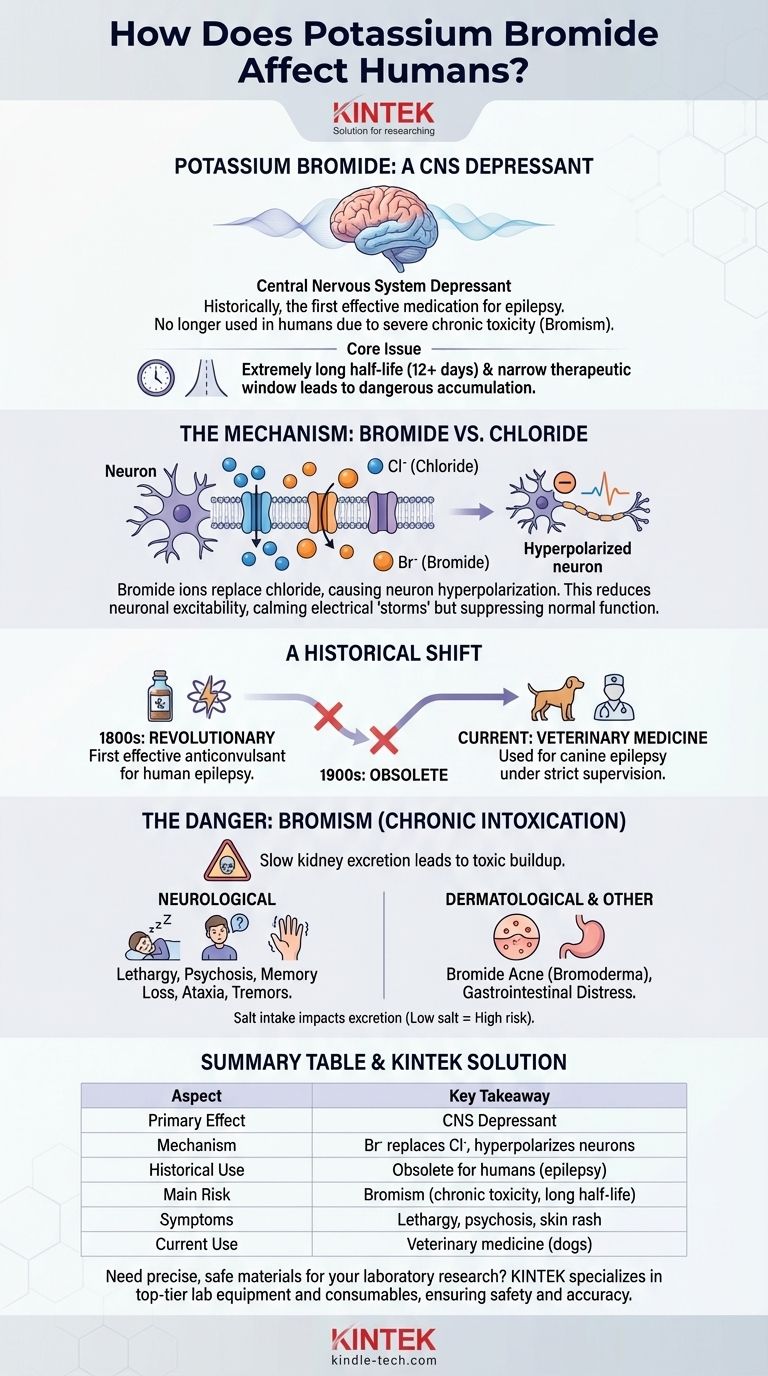
In short, potassium bromide acts as a potent central nervous system depressant. While it was historically the first effective medication for epilepsy, it is no longer used in humans due to a high risk of severe chronic toxicity known as "bromism." Its effects range from sedation and seizure control at therapeutic doses to psychosis, severe lethargy, and skin disorders with long-term accumulation.
The core issue with potassium bromide is its extremely long half-life and narrow therapeutic window. The body struggles to excrete it, leading to a dangerous accumulation that causes neurological and dermatological toxicity, making it unsafe for human use by modern standards.

The Primary Mechanism: How Bromide Affects the Brain
Bromide Ions vs. Chloride Ions
The active component is the bromide ion, not the potassium. In the body, bromide ions compete with and substitute for chloride ions in various tissues, most importantly in the central nervous system.
Depressing Neuronal Activity
Nerve cells (neurons) use chloride channels to regulate their electrical charge. When bromide ions enter neurons instead of chloride, they cause the neuron to become hyperpolarized. In simple terms, this makes the neuron less excitable and less likely to fire an electrical signal.
This generalized dampening of neuronal activity is the source of both its therapeutic and toxic effects. It calms the electrical "storms" that cause seizures but also suppresses normal brain function.
A Historical Medical Tool
The First Effective Anticonvulsant
Introduced in the mid-19th century, potassium bromide was a revolutionary breakthrough. For the first time, physicians had an effective chemical treatment to control the seizures associated with epilepsy.
Obsolescence in Human Medicine
Despite its effectiveness, the line between a therapeutic dose and a toxic one is very thin. Patients often developed chronic poisoning over time. By the early 20th century, safer and more effective drugs like phenobarbital began to replace it. Today, it is considered obsolete for treating humans.
Current Use in Veterinary Medicine
Potassium bromide is still commonly used in veterinary medicine, particularly to control seizures in dogs that do not respond well to more modern drugs. It is administered carefully under veterinary supervision, with regular blood monitoring to prevent toxicity.
Understanding the Trade-offs: The Danger of Bromism
The primary danger of potassium bromide is chronic intoxication, a condition known as bromism. This occurs because the body has a very difficult time telling bromide and chloride apart, and the kidneys excrete bromide very slowly.
A Deceptively Long Half-Life
The half-life of bromide in the human body can be 12 days or longer. This means that even small, regular doses can build up to toxic levels over weeks or months.
Neurological Symptoms of Bromism
The most significant effects of bromide poisoning are neurological. They can be mistaken for various psychiatric or neurological disorders.
- Lethargy and sleepiness
- Depression and emotional flatness
- Loss of coordination (ataxia) and tremors
- Memory loss and confusion
- In severe cases, hallucinations and "bromide psychosis"
Dermatological and Other Symptoms
A classic sign of bromism is a specific type of skin rash called bromide acne or bromoderma, which can be severe. Other symptoms include gastrointestinal distress and nausea.
The Critical Role of Salt
Because bromide and chloride compete, dietary salt (sodium chloride) intake directly impacts bromide levels. Increasing salt intake helps the kidneys excrete bromide more quickly and is a key part of treating an overdose. Conversely, a low-salt diet dramatically increases the risk of toxicity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To understand potassium bromide is to understand the evolution of medicine and toxicology. It represents a class of substances that are effective but carry an unacceptable risk profile by modern safety standards.
- If your primary focus is its medical history: Recognize it as a foundational but now obsolete treatment for epilepsy, replaced due to its high potential for chronic poisoning.
- If your primary focus is safety: Understand that its danger lies in slow accumulation, leading to a serious neurological condition called bromism that requires medical intervention.
- If your primary focus is its use in animals: Acknowledge it as a valid veterinary medicine for canine epilepsy, but one that demands strict professional supervision and blood monitoring.
Ultimately, potassium bromide is a powerful reminder that in medicine, what a substance does is only half the story; its safety and side effects are what truly define its place in treatment.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|
| Primary Effect | Central Nervous System (CNS) Depressant |
| Mechanism | Bromide ions replace chloride, hyperpolarizing neurons to reduce excitability. |
| Historical Use | First effective anti-epileptic drug; now obsolete for humans. |
| Main Risk | Bromism - chronic toxicity from accumulation (half-life ~12 days). |
| Symptoms of Toxicity | Lethargy, psychosis, memory loss, ataxia, severe skin rash (bromoderma). |
| Current Use | Veterinary medicine for canine epilepsy, with careful monitoring. |
Need precise, safe materials for your laboratory research? Potassium bromide's history underscores the critical importance of using reliable, high-purity chemicals and equipment. KINTEK specializes in providing top-tier lab equipment and consumables, ensuring the safety and accuracy of your work. Let us support your laboratory's needs with our trusted products. Contact our experts today to find the right solutions for your specific applications.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Optical Ultra-Clear Glass Sheet for Laboratory K9 B270 BK7
- Evaporation Crucible for Organic Matter
- Optical Window Glass Substrate Wafer Barium Fluoride BaF2 Substrate Window
- kbr pellet press 2t
- High-Energy Omnidirectional Planetary Ball Mill Machine for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What are the five rules of chemical safety? Build a Proactive Culture of Lab Safety
- What are the key characteristics of RVC glassy carbon sheets? Unlock Superior Electrochemical Performance
- What are the barriers to plastic recycling? The Economic, Material, and Technical Hurdles Explained
- What are the factors that affect the filtration of the solution? Master the Key Variables for Optimal Performance
- What is the temperature range of quartz glass? Master Its Thermal Limits for Demanding Applications










