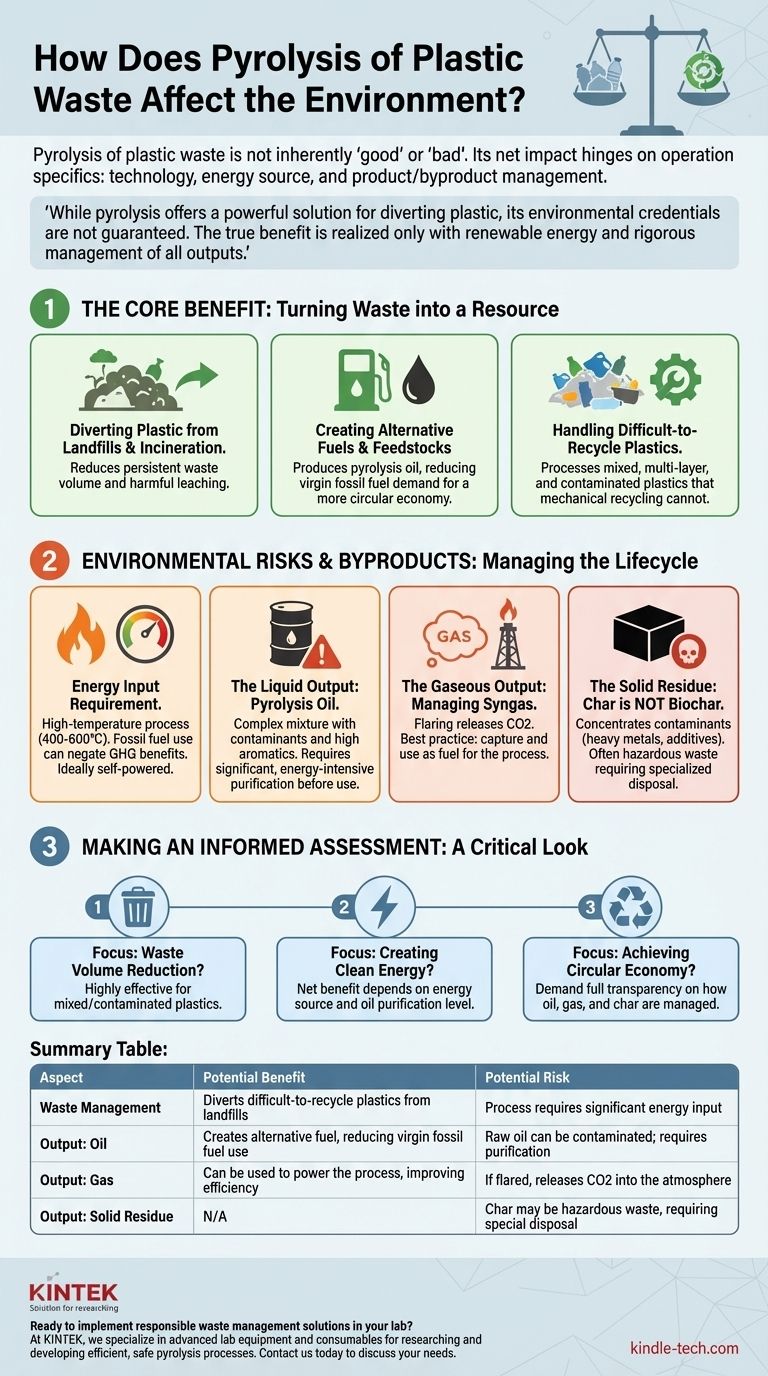
Pyrolysis of plastic waste is not inherently "good" or "bad" for the environment. It is a complex chemical conversion process with significant potential benefits but also critical environmental risks. Its net impact hinges entirely on the specifics of the operation, including the technology used, the source of energy, and how the resulting products and byproducts are managed.
While pyrolysis offers a powerful solution for diverting plastic from landfills, its environmental credentials are not guaranteed. The true benefit is only realized when the process is powered renewably and all outputs—oil, gas, and solid char—are handled with a rigorous focus on preventing secondary pollution.

The Core Benefit: Turning Waste into a Resource
The primary environmental advantage of pyrolysis is its ability to reframe "waste" as a valuable feedstock. It breaks down long-chain plastic polymers into smaller, useful molecules.
Diverting Plastic from Landfills and Incineration
Pyrolysis provides an alternative destination for plastics that are difficult or impossible to recycle mechanically. This includes mixed plastics, multi-layer packaging, and contaminated materials.
By converting this waste, pyrolysis directly reduces the volume of plastic sent to landfills, where it can persist for centuries and leach harmful substances into the soil and water.
Creating Alternative Fuels and Feedstocks
The main product of plastic pyrolysis is a synthetic crude oil, often called pyrolysis oil. This oil can be refined and upgraded for use as fuel.
Using this recycled fuel can reduce the demand for virgin fossil fuels, thereby decreasing the environmental damage associated with oil and gas extraction. The oil can also serve as a chemical feedstock to create new plastics, creating a more circular economic loop.
Handling Difficult-to-Recycle Plastics
Mechanical recycling requires clean, sorted streams of specific plastic types. Pyrolysis is far more tolerant of contamination and mixed plastic types.
This makes it a crucial complementary technology, capable of processing the vast quantities of plastic waste that the traditional recycling infrastructure cannot handle.
Understanding the Environmental Risks and Byproducts
The potential benefits of pyrolysis can be undermined if the process and its outputs are not managed responsibly. A complete environmental assessment must analyze the entire lifecycle.
The Energy Input Requirement
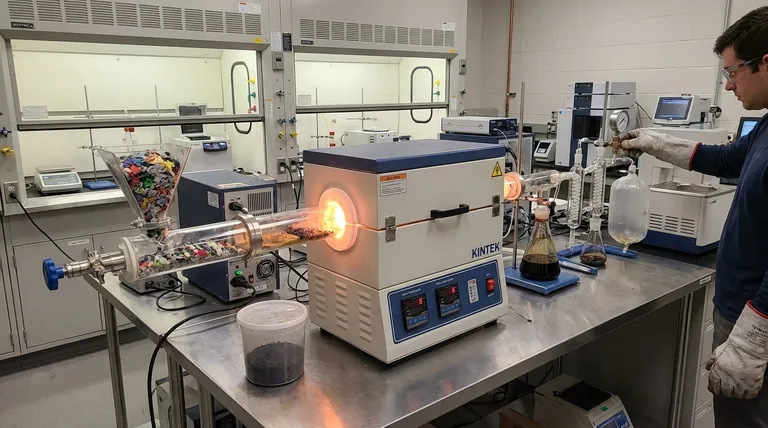
Pyrolysis is an energy-intensive process that requires heating plastic waste to very high temperatures (typically 400-600°C) in an oxygen-free environment.
If the energy for this heating comes from burning fossil fuels, it can offset or even negate the greenhouse gas benefits of producing recycled fuel. Truly "green" pyrolysis operations often use a portion of the gas they produce to power the system, creating a more self-sustaining process.
The Liquid Output: The Reality of Pyrolysis Oil
Pyrolysis oil is not a drop-in replacement for conventional fuel. It is a complex mixture of hydrocarbons, often with a high aromatic content and contaminants like chlorine or sulfur derived from the original plastic.
This raw oil requires significant, energy-intensive purification before it can be used as a fuel or chemical feedstock. Without proper upgrading, burning it can release harmful pollutants.
The Gaseous Output: Managing Syngas
The process also creates non-condensable gases, known as syngas. If this gas is simply flared (burned off), it releases CO2 into the atmosphere.
Best-practice facilities capture this syngas and use it as fuel to power the pyrolysis reactor, improving overall energy efficiency and reducing the facility's carbon footprint.
The Solid Residue: A Critical Distinction from Biochar
While biomass pyrolysis creates a beneficial soil amendment called biochar, the solid residue from plastic pyrolysis is fundamentally different.
This char is a carbonaceous solid that concentrates contaminants from the original plastic waste, such as heavy metals, flame retardants, and other additives. This material often must be treated as hazardous waste and disposed of in a specialized, controlled landfill to prevent environmental contamination.
Making an Informed Assessment
To determine if a pyrolysis project is environmentally sound, you must look beyond the simple conversion of waste to fuel and ask critical questions about the entire operation.
- If your primary focus is waste volume reduction: Pyrolysis is highly effective, especially for the mixed and contaminated plastics that would otherwise go to a landfill.
- If your primary focus is creating clean energy: The net benefit depends on the facility's energy source and the level of purification applied to the final pyrolysis oil.
- If your primary focus is achieving a circular economy: Demand full transparency on how all three outputs—oil, gas, and char—are managed to ensure one environmental problem is not being traded for another.
Ultimately, the environmental merit of plastic pyrolysis is determined not by the promise of the technology itself, but by the rigor and responsibility with which it is implemented.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Potential Benefit | Potential Risk |
|---|---|---|
| Waste Management | Diverts difficult-to-recycle plastics from landfills | Process requires significant energy input |
| Output: Oil | Creates alternative fuel, reducing virgin fossil fuel use | Raw oil can be contaminated; requires purification |
| Output: Gas | Can be used to power the process, improving efficiency | If flared, releases CO2 into the atmosphere |
| Output: Solid Residue | N/A | Char may be hazardous waste, requiring special disposal |
Ready to implement responsible waste management solutions in your lab?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the advanced lab equipment and consumables necessary for researching and developing efficient, safe pyrolysis processes. Whether you're analyzing pyrolysis outputs or optimizing reaction conditions, our reliable tools help you achieve accurate and safe results.
Contact us today via our [#ContactForm] to discuss how KINTEK can support your laboratory's specific needs in sustainability and material science.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace IGBT Experimental Graphitization Furnace
- Vacuum Dental Porcelain Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What happens inside a rotary kiln? Unlock the Secrets of Industrial Thermal Processing
- Where does pyrolysis occur? Unlocking the Power of Controlled Thermal Decomposition
- How does a continuous furnace work? Unlock High-Volume, Consistent Thermal Processing
- What are the materials suitable for pyrolysis? Unlocking Value from Waste Streams
- What is the purpose of a calciner? Boost Efficiency in High-Temperature Processing
- What is the feedstock for biomass gasification? Unlock the Potential of Diverse Organic Materials
- What are the advantages of bio oil pyrolysis? Turn Waste into Renewable Energy & Carbon Sinks
- What is bio-oil production from biomass by using pyrolysis method? Turn Waste into Liquid Fuel



















