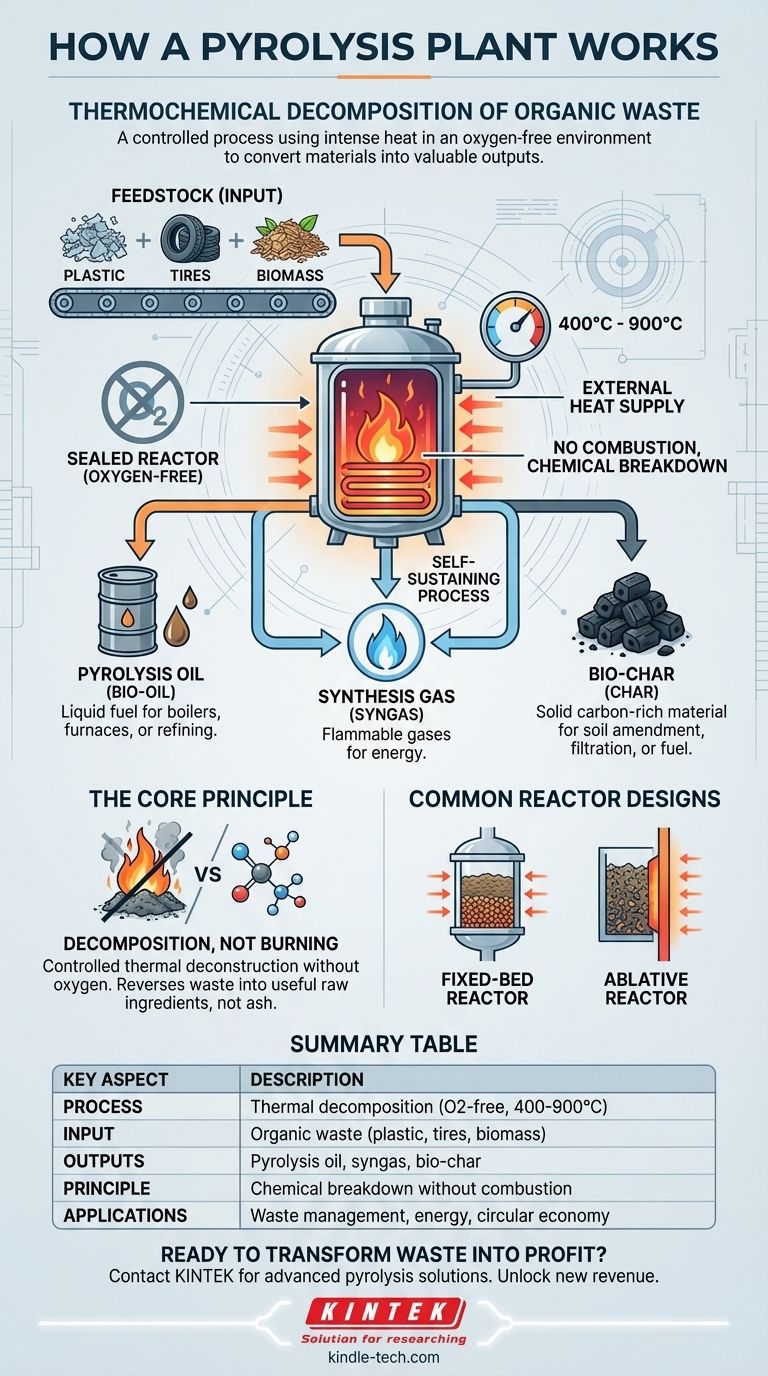
A pyrolysis plant works by using intense heat in an oxygen-free environment to chemically decompose organic materials like plastic, tires, or biomass. This process, known as thermochemical decomposition, breaks down large, complex molecules into smaller, simpler ones, effectively converting waste into valuable outputs like synthetic oil, gas, and a solid residue called bio-char.
At its core, pyrolysis is not burning; it is a controlled thermal deconstruction. By removing oxygen from the equation, a pyrolysis plant chemically dismantles waste materials, reversing them back into useful raw ingredients instead of simply incinerating them into ash and emissions.

The Core Principle: Decomposition Without Oxygen
To truly understand how a pyrolysis plant operates, it's essential to grasp the fundamental science that drives it. The entire process is built around controlling heat and preventing combustion.
What "Pyrolysis" Actually Means
The term comes from the Greek words pyro (fire) and lysis (separating). It literally means "separating by fire."
However, this is distinct from burning (incineration). Burning requires oxygen to create a flame and release energy rapidly. Pyrolysis intentionally starves the reaction of oxygen, forcing a different chemical pathway.
The Transformation: Breaking Molecular Bonds
The process begins by feeding organic materials, known as feedstock, into a sealed reactor vessel.
This feedstock—be it shredded plastic, old tires, or agricultural waste—is heated to very high temperatures, typically between 400°C and 900°C (750°F to 1650°F).
This intense heat provides the energy needed to break the strong chemical bonds holding the large polymer molecules together. The material effectively vaporizes and breaks down into simpler, smaller molecules.
The Outputs: A Trio of Useful Products
Once the feedstock is decomposed, the resulting smaller molecules are collected and separated. This yields three primary products:
- Pyrolysis Oil (Bio-oil): A liquid fuel similar to industrial diesel that can be used in boilers, furnaces, or upgraded into higher-grade fuels.
- Synthesis Gas (Syngas): A mixture of flammable gases (like hydrogen and methane) that is often redirected to power the pyrolysis plant itself, making the process more self-sustaining.
- Bio-char (Char): A solid, carbon-rich material similar to charcoal. It can be used as a soil amendment to improve fertility, as a filtration medium (activated carbon), or as a solid fuel.
A Look Inside the Pyrolysis Reactor
The reactor is the heart of the plant where the thermochemical conversion takes place. While designs vary, they all share the goal of efficiently transferring heat to the feedstock in a closed, oxygen-deprived system.
The Central Heating System
A pyrolysis reactor is a closed vessel that relies on an external heat supply. Heat is applied to the outside of the reactor walls, and this thermal energy diffuses inward to decompose the material inside.
This ensures no direct contact between the heating flame and the feedstock, which is critical for preventing combustion.
Common Reactor Designs
While many configurations exist, a common and straightforward design is the fixed-bed reactor.
In this setup, the feedstock is loaded into the reactor and sits in a stationary "bed." Heat from the reactor walls slowly penetrates the pile of material, causing it to break down. The resulting gases and vapors rise and are piped out for collection and condensation.
Another approach is the ablative reactor, which uses pressure to press the feedstock against a very hot surface. This causes the material to "melt" and decompose almost instantly, a process useful for certain types of biomass like wood.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While powerful, pyrolysis technology is not a magic bullet. Its successful implementation depends on managing several key factors.
Feedstock Quality is Critical
The purity of the input material directly impacts the quality of the output products. Contaminants like metals, dirt, or certain types of plastics can reduce the efficiency of the process and degrade the value of the resulting oil and char.
The Energy Balance Equation
Pyrolysis is an energy-intensive process that requires a significant initial heat input to reach and maintain its high operating temperatures. A successful plant must be designed so that the energy recovered from the syngas is sufficient to sustain the reaction and, ideally, create a net energy surplus.
Managing the Final Products
The outputs of pyrolysis are raw materials, not finished goods. The oil may require further refining before it can be used in certain engines, and the char may need processing to be sold as a soil product. These downstream steps are a crucial part of the overall economic model.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Pyrolysis technology can be applied to solve several different problems, from waste reduction to energy generation.
- If your primary focus is waste management: Pyrolysis offers a powerful method to divert large volumes of non-recyclable plastics and tires from landfills, converting them into a much smaller volume of useful products.
- If your primary focus is energy production: The process effectively converts low-value or negative-value waste streams into usable energy in the form of liquid and gaseous fuels.
- If your primary focus is creating a circular economy: Pyrolysis is a key technology for "chemical recycling," breaking down plastics into a raw oil that can be used to create new plastics, closing the loop on material use.
Ultimately, pyrolysis redefines waste not as an endpoint, but as a valuable chemical resource waiting to be unlocked.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Process | Thermal decomposition in an oxygen-free environment (400-900°C) |
| Input (Feedstock) | Organic materials (plastic, tires, biomass) |
| Primary Outputs | Pyrolysis oil, syngas, bio-char |
| Core Principle | Chemical breakdown without combustion |
| Common Reactor Types | Fixed-bed, ablative |
| Main Applications | Waste management, energy production, circular economy |
Ready to transform your waste streams into profit?
KINTEK specializes in advanced pyrolysis solutions for converting plastic, tire, and biomass waste into valuable oil, gas, and char. Our expertise in lab equipment and thermal processing ensures efficient, scalable systems tailored to your needs—whether for waste reduction, energy recovery, or circular economy goals.
Contact KINTEK today to explore how our pyrolysis technology can unlock new revenue from your waste!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- CVD Diamond for Thermal Management Applications
- Non Consumable Vacuum Arc Induction Melting Furnace
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
People Also Ask
- What are the different types of pyrolysis machines? Choose the Right System for Your Output
- What are the reactions involved in pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock the Chemistry for Tailored Bio-Products
- What are the components of biomass pyrolysis? A Complete Guide to the System, Products, and Process
- What are the products of pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock Bio-Char, Bio-Oil, and Syngas
- What are the conditions for biomass pyrolysis? Optimize Temperature, Heating Rate & Time



















