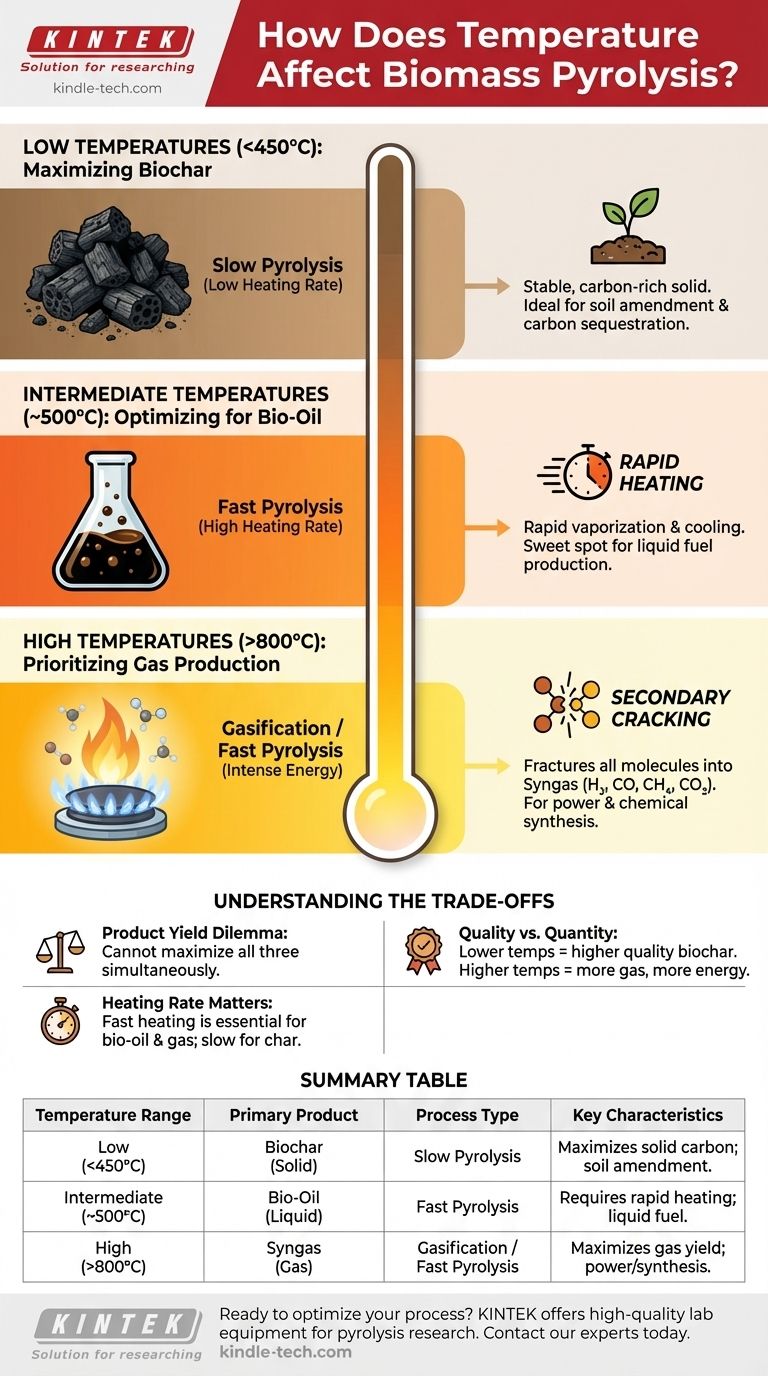
In short, temperature is the primary control lever in biomass pyrolysis, determining whether the process yields a solid (biochar), a liquid (bio-oil), or a gas. Lower temperatures below 450°C favor the production of biochar. Intermediate temperatures with rapid heating rates optimize for bio-oil, while high temperatures above 800°C maximize the output of combustible gases.
The fundamental principle is that increasing pyrolysis temperature provides more energy to break down complex biomass molecules into progressively smaller ones. Your choice of temperature directly shifts the product yield from stable solids at low heat, to complex liquid vapors at medium heat, and finally to simple gases at high heat.

How Temperature Dictates Pyrolysis Products
Temperature directly controls the extent of thermal decomposition. As you increase the thermal energy in the reactor, you systematically break down the large, complex polymers that make up biomass (like cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin) into smaller and smaller molecules.
Low Temperatures (<450°C): Maximizing Biochar
At lower temperatures, the thermal energy is insufficient to completely break down the robust structure of the biomass. This process, often called slow pyrolysis, primarily drives off water and volatile compounds.
The result is a stable, carbon-rich solid known as biochar. The less-intense heat leaves much of the carbon skeleton intact, making this temperature range ideal for producing solid soil amendments or charcoal.
Intermediate Temperatures (~500°C): Optimizing for Bio-Oil
This range represents a critical sweet spot for liquid fuel production. Here, the process requires not just a specific temperature but also a high heating rate, a technique known as fast pyrolysis.
The rapid heat input quickly vaporizes the biomass, breaking it down into a wide range of condensable organic vapors. These vapors are then rapidly cooled and collected as a dark, viscous liquid called bio-oil. The key is to get the vapors out of the hot zone before they can break down further into gas.
High Temperatures (>800°C): Prioritizing Gas Production
At very high temperatures, the energy is so intense that it causes secondary cracking. Not only is the initial biomass broken down, but the intermediate vapors and bio-oil molecules are also fractured into the smallest, most stable gas molecules.
This process maximizes the yield of non-condensable syngas, a mixture of hydrogen (H₂), carbon monoxide (CO), methane (CH₄), and carbon dioxide (CO₂). This gas can be used directly for heat and power generation or as a chemical precursor.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a temperature is not just about choosing a product; it's about navigating a series of interconnected variables and compromises. The ideal temperature depends entirely on your end goal and operational constraints.
The Product Yield Dilemma
You cannot maximize all three products simultaneously. A temperature profile designed to produce the highest yield of biochar will, by definition, produce very little bio-oil and gas. Conversely, optimizing for gas production means sacrificing both biochar and bio-oil yields. This is the central trade-off of pyrolysis.
The Critical Role of Heating Rate
Temperature does not act alone. The rate at which the biomass is heated is equally important.
Slow heating rates, even at higher temperatures, allow time for the biomass to slowly char, favoring biochar production. Rapid heating rates are essential for fast pyrolysis, which is required to maximize the production of bio-oil and gas by quickly vaporizing the material before it can solidify into char.
Quality vs. Quantity
Higher temperatures generally increase the rate of reaction and overall biomass conversion, but this doesn't always mean better quality. For instance, lower-temperature pyrolysis produces a higher yield of high-quality solid biochar. Running a reactor at over 800°C to maximize gas yield requires significantly more energy than running it at 400°C for biochar, impacting the overall energy balance and economic viability.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your target product should dictate your choice of pyrolysis conditions. A clear understanding of your goal is the first step toward successful implementation.
- If your primary focus is soil amendment or carbon sequestration: Use slow pyrolysis at lower temperatures (<450°C) to maximize the yield and quality of solid biochar.
- If your primary focus is producing a liquid fuel or chemical feedstock: Use fast pyrolysis at intermediate temperatures (around 500°C) with high heating rates to optimize for bio-oil.
- If your primary focus is generating syngas for power or synthesis: Use fast pyrolysis or gasification at high temperatures (>800°C) to ensure complete thermal cracking into gas.
By mastering temperature, you move from simply heating biomass to precisely engineering its chemical transformation.
Summary Table:
| Temperature Range | Primary Product | Process Type | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Low (<450°C) | Biochar | Slow Pyrolysis | Maximizes solid carbon yield; ideal for soil amendment. |
| Intermediate (~500°C) | Bio-Oil | Fast Pyrolysis | Requires rapid heating; optimizes liquid fuel production. |
| High (>800°C) | Syngas | Gasification / Fast Pyrolysis | Maximizes gas yield for power generation or chemical synthesis. |
Ready to optimize your biomass pyrolysis process?
KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables for all your pyrolysis research and development needs. Whether you are developing processes for biochar, bio-oil, or syngas production, our reliable reactors and precise temperature control systems help you achieve accurate and repeatable results.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can accelerate your bioenergy and biocarbon projects.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the different types of pyrolysis machines? Choose the Right System for Your Output
- What are the products of pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock Bio-Char, Bio-Oil, and Syngas
- What is the process of biomass fast pyrolysis? Turn Biomass into Bio-Oil in Seconds
- How is energy converted into biomass? Harnessing Nature's Solar Power for Renewable Energy
- What are the advantages of pyrolysis technology? Turn Waste into Profit and Reduce Emissions















