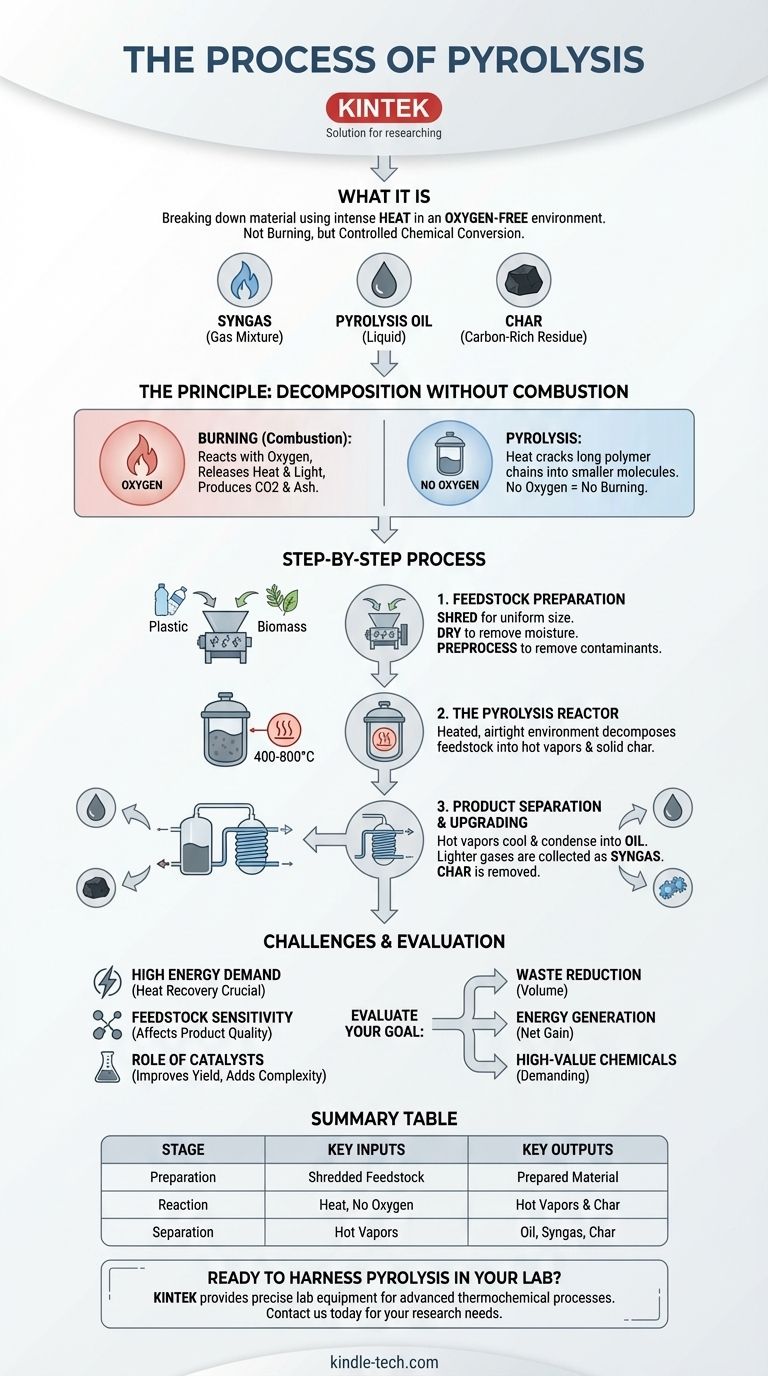
At its core, pyrolysis is the process of breaking down a material using heat in an environment devoid of oxygen. Instead of burning, the intense heat cracks the large, complex molecules of a substance like plastic or biomass into smaller, more valuable components. This thermochemical decomposition results in three primary products: a gas mixture (syngas), a liquid (pyrolysis oil), and a solid, carbon-rich residue (char).
Pyrolysis is not simply incineration without air; it is a controlled chemical conversion process. Its purpose is to reclaim the chemical and energetic value locked inside waste materials, but its success depends entirely on precise control over temperature, feedstock purity, and the complete absence of oxygen.

The Fundamental Principle: Decomposition without Combustion
The distinction between pyrolysis and burning (combustion) is the most critical concept to grasp. It all comes down to the presence or absence of oxygen.
Creating an Oxygen-Free Environment
In a normal fire, oxygen acts as a reactant. Heat breaks down a material, and the resulting molecules rapidly react with oxygen, releasing energy as heat and light, and producing byproducts like carbon dioxide and ash.
Pyrolysis prevents this by taking place in a sealed vessel. By removing oxygen, you remove the key ingredient for combustion. The material cannot "burn."
The Role of High Heat
Without oxygen, heat plays a different role. Instead of fueling combustion, the thermal energy directly attacks the chemical bonds holding the large polymer chains together.
For materials like biomass, the process targets its main components: cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin. In plastics, it breaks down the long hydrocarbon chains. This "thermal cracking" splits them into smaller, lighter, and more volatile molecules.
A Step-by-Step Breakdown of the Process
While specifics vary by feedstock, a typical pyrolysis operation for plastic or biomass waste follows a clear sequence.
Step 1: Feedstock Preparation
The process begins long before the material enters the reactor. The raw material is first shredded into smaller, more uniform pieces to increase surface area and ensure even heating.
It is then dried to remove moisture, as heating water consumes a massive amount of energy that would otherwise be used for pyrolysis. Finally, it undergoes preprocessing to separate non-pyrolyzable contaminants like metals or glass.
Step 2: The Pyrolysis Reactor
This is the heart of the system. The prepared feedstock is fed into an airtight reactor, which is then heated to temperatures typically ranging from 400°C to 800°C.
Inside the reactor, the material is decomposed into a hot mixture of gases and vapors. The solid residue that does not vaporize, known as bio-char or simply char, is removed from the bottom of the reactor.
Step 3: Product Separation and Upgrading
The hot gas and vapor stream exits the reactor and enters a condensation system. As it cools, the heavier molecules condense into a liquid known as pyrolysis oil (or bio-oil). This oil often requires further distillation and purification to become a usable product.
The lighter molecules that do not condense form a mixture of combustible gases called syngas. This gas is collected and can be used as fuel, often to help power the pyrolysis process itself.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
Pyrolysis is a powerful technology, but it is not a silver bullet. A clear-eyed assessment requires understanding its inherent limitations.
High Energy Demand
Heating a reactor to hundreds of degrees Celsius is an energy-intensive process. An efficient plant must be designed to recover and reuse as much heat as possible. Often, the syngas produced is burned to provide the heat, improving the overall energy balance but reducing the amount of sellable output.
Feedstock Sensitivity
The exact composition of the oil, gas, and char is highly dependent on the input material. A feedstock of mixed plastics will produce a very different—and often lower quality—oil than a feedstock of a single, clean plastic type. This variability makes producing a consistent, high-grade product a significant engineering challenge.
The Role of Catalysts
To improve the outcome, a catalyst is often introduced into the reactor. Catalysts promote specific chemical reactions, helping to steer the process toward producing a higher yield of a desired product, such as a more stable and valuable oil from plastic. However, catalysts add cost and complexity to the operation.
How to Evaluate Pyrolysis for Your Application
To determine if pyrolysis is the right solution, you must first define your primary goal.
- If your primary focus is waste volume reduction: Pyrolysis is extremely effective, converting bulky materials like tires or plastics into a dense char and usable fuels, dramatically reducing the volume sent to landfills.
- If your primary focus is energy generation: The process yields combustible oil and gas, but you must carefully calculate the net energy gain after subtracting the significant energy required to run the process itself.
- If your primary focus is creating high-value chemicals: This is the most demanding application, requiring pure feedstocks, precise temperature control, catalysts, and significant downstream purification to create a consistent product suitable for the chemical industry.
Understanding these core principles is the first step toward leveraging pyrolysis as a powerful tool for sustainable material conversion.
Summary Table:
| Pyrolysis Stage | Key Inputs | Key Outputs |
|---|---|---|
| Preparation | Shredded, dried feedstock (e.g., plastic, biomass) | Prepared, contaminant-free material |
| Reaction | Heat (400-800°C), no oxygen | Hot vapor mixture & solid char |
| Separation | Hot vapors | Pyrolysis Oil, Syngas, Char |
| Key Factor | Precise temperature control & oxygen-free environment | Determines product quality and yield |
Ready to harness the power of pyrolysis in your lab?
KINTEK specializes in providing the precise, high-quality lab equipment and consumables needed for advanced thermochemical processes like pyrolysis. Whether you are researching catalyst efficiency, optimizing reaction conditions, or analyzing product yields, our reliable tools are essential for achieving accurate and reproducible results.
Contact us today using the form below to discuss how KINTEK can support your laboratory's innovative work in sustainable material conversion. Let's turn your research into impactful solutions together.
Contact KINTEK for Your Pyrolysis Lab Needs
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
People Also Ask
- What is a disadvantage of biomass energy? The Hidden Environmental and Economic Costs
- What are the conditions for biomass pyrolysis? Optimize Temperature, Heating Rate & Time
- What are the different types of pyrolysis machines? Choose the Right System for Your Output
- What are the products of pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock Bio-Char, Bio-Oil, and Syngas
- What are the components of biomass pyrolysis? A Complete Guide to the System, Products, and Process



















